Abstract
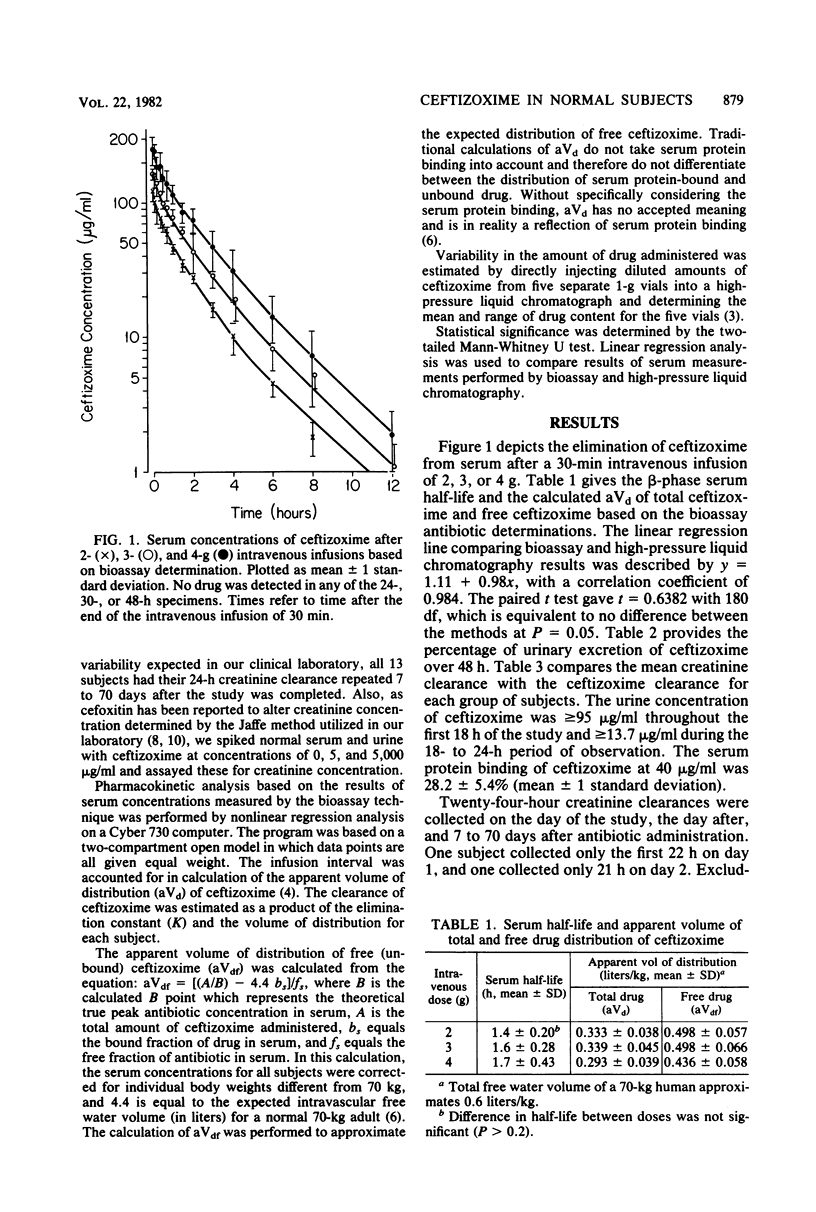
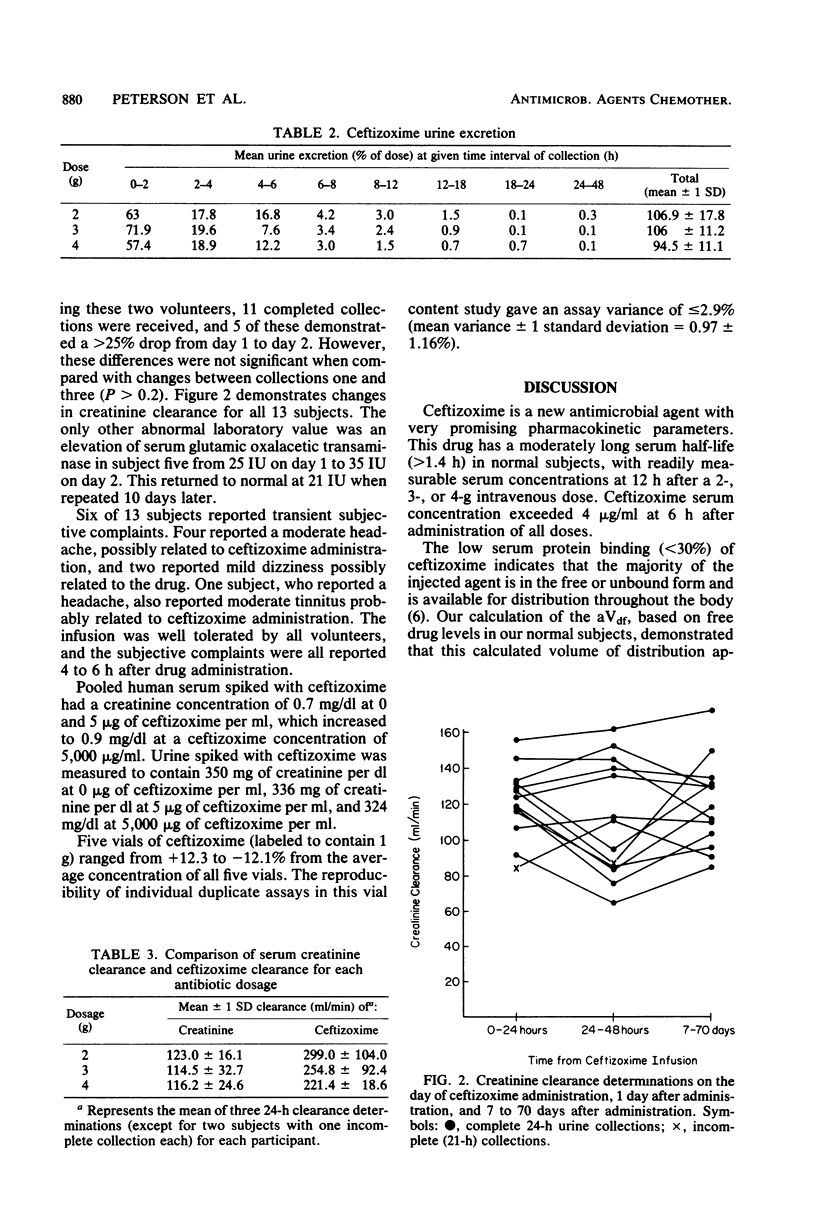
Thirteen normal subjects were given 2, 3, or 4 g of ceftizoxime intravenously in a prospective single-blinded study. Serum and urine concentrations were measured for 48 h. The beta-phase serum half-life ranged from 1.4 to 1.7 h. Approximately 100% of the agent was recovered unchanged in the urine over 48 h. Six of 13 subjects reported subjective complaints consisting of mild dizziness and moderate headache, all of which were transient. One subject also had a minimally elevated serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase level 1 day after drug administration. Based on serum pharmacokinetics and serum protein binding determined in this investigation, unbound ceftizoxime appeared to distribute with the total body water.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dubb J., Actor P., Pitkin D., Alexander F., Familiar R., Ehrlich S., Stote R. Ceftizoxime kinetics and renal handling. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Apr;31(4):516–521. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasching C. E., Peterson L. R. Anion-exchange extraction of cephapirin, cefotaxime, and cefoxitin from serum for liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):628–633. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasching C. E., Peterson L. R., Bettin K. M., Gerding D. N. High-pressure liquid chromatographic assay of ceftizoxime with an anion-exchange extraction technique. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):336–337. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., Pearson N., Eley A., O'Grady F. Comparative in vitro activities of cefotaxime and ceftizoxime (FK749): new cephalosporins with exceptional potency. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):397–401. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Influence of protein binding of antibiotics on serum pharmacokinetics and extravascular penetration: clinically useful concepts. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):340–348. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Hall W. H., Zinneman H. H., Gerding D. N. Standardization of a preparative ultracentrifuge method for quantitative determination or protein binding of seven antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):778–783. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saah A. J., Koch T. R., Drusano G. L. Cefoxitin falsely elevates creatinine levels. JAMA. 1982 Jan 8;247(2):205–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D. The assay of antimicrobial compounds. Hum Pathol. 1976 May;7(3):287–295. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain R. R., Briggs S. L. Positive interference with the Jaffé reaction by cephalosporin antibiotics. Clin Chem. 1977 Jul;23(7):1340–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



