Abstract
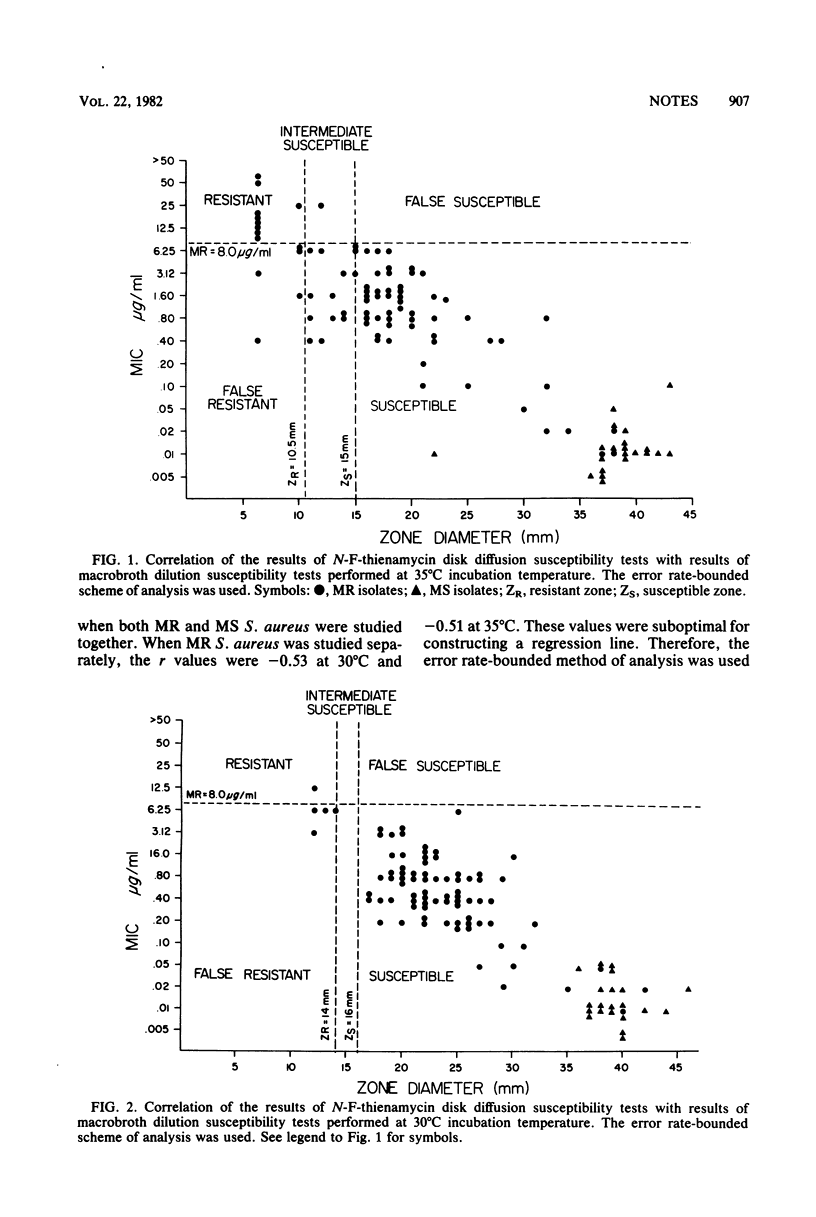
A total of 82 clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and 21 isolates of methicillin-susceptible S. aureus were studied for in vitro susceptibility to N-forminidoyl thienamycin at incubation temperatures of 30 and 35 degrees C. The disk diffusion test results were correlated with the macrobroth dilution test by means of the error rate-bounded method of analysis. Both methicillin-susceptible and (to a lesser degree) methicillin-resistant strains were generally susceptible to the antibiotic as judged from their minimum inhibitory concentrations. The discrepancy between in vitro results obtained at 30 and at 35 degrees C was not very remarkable. However, tolerance of N-formimidoyl thienamycin was observed in 37% of methicillin-resistant strains and 24% of methicillin-susceptible strains at an incubation temperature of 30 degrees C; at 35 degrees C, the values were 54% (methicillin-resistant strains) and 14% (methicillin-susceptible strains).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner E. J., Morthland V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrobial susceptibility. N Engl J Med. 1967 Sep 28;277(13):678–680. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196709282771303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canawati H. N., Sapico F. L., Montgomerie J. Z., Zucchero J. Temperature effect on cephalothin sensitivity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Mar;75(3):391–394. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canawati H. N., Witte J. L., Sapico F. L. Temperature effect on the susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to four different cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):173–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Kahan J. S., Kahan F. M., Birnbaum J. MK0787 (N-formimidoyl thienamycin): evaluation of in vitro and in vivo activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):993–1000. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston W. K., Elliott A. M., Cobbs C. G. In vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) against resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Serratia marcescens, and Enterococcus spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):114–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhall C. G., Medoff G., Marr J. J. Variation in the susceptibility of strains of Staphylococcus aureus to oxacillin, cephalothin, and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):707–712. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler C. M., DeHaan R. M. Susceptibility tests of anaerobic bacteria: statistical and clinical considerations. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):588–594. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wheeler N., Laverdiere M., Blazevic D., Wilkinson B. J. A new type of penicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



