Figure 5. MECP2 mutant nuclei male and female human brain samples show increased H3K9ac staining in neuronal nuclei.
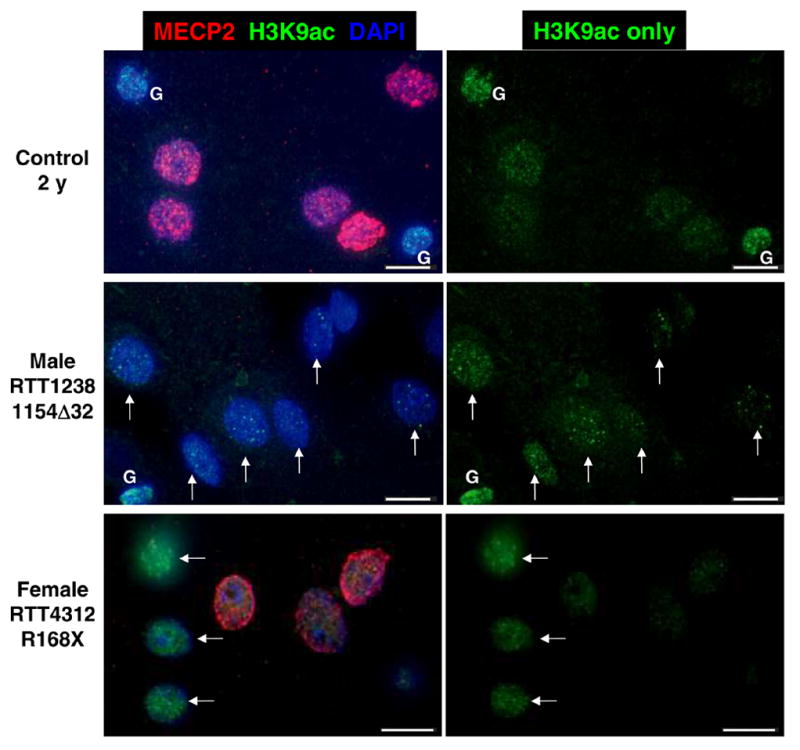
Representative images from control 2 y, MECP2 mutant male, and MECP2 mosaic mutant female RTT cerebral cortex samples. Sections were stained with anti-MeCP2 (red fluorescence), anti-H3K9ac (green fluorescence) and nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue fluorescence). MECP2 mutant nuclei in male and female cortex are characterized by an immature bright punctate pattern of H3K9ac fluorescence. Female RTT brain is mosaic for mutant and wild-type MECP2 expression because of random X chromosome inactivation (7, 33). Mutant MECP2 expressing neurons characterized by absence of MeCP2 red fluorescence have brighter H3K9ac puncta (arrows) than neighboring wild-type expressing nuclei. Glial cells (G) are indicated. Scale bars represent 10 microns.
