Abstract
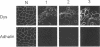
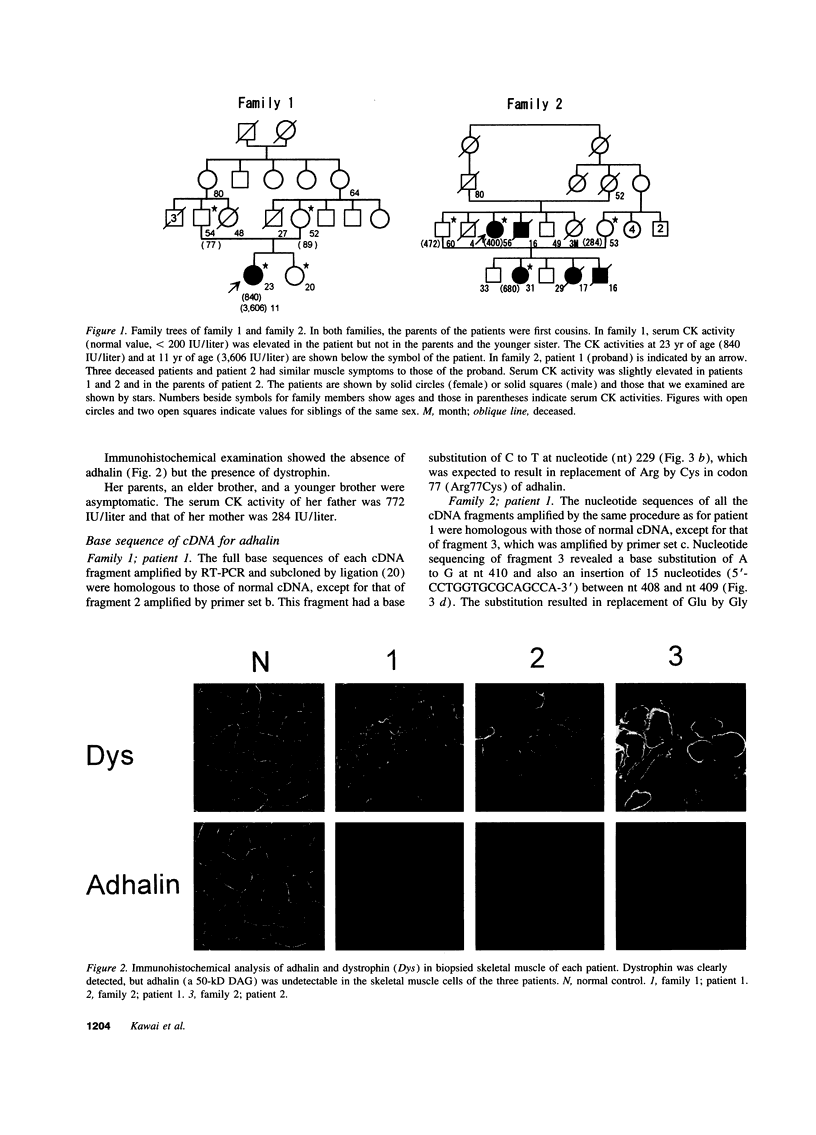
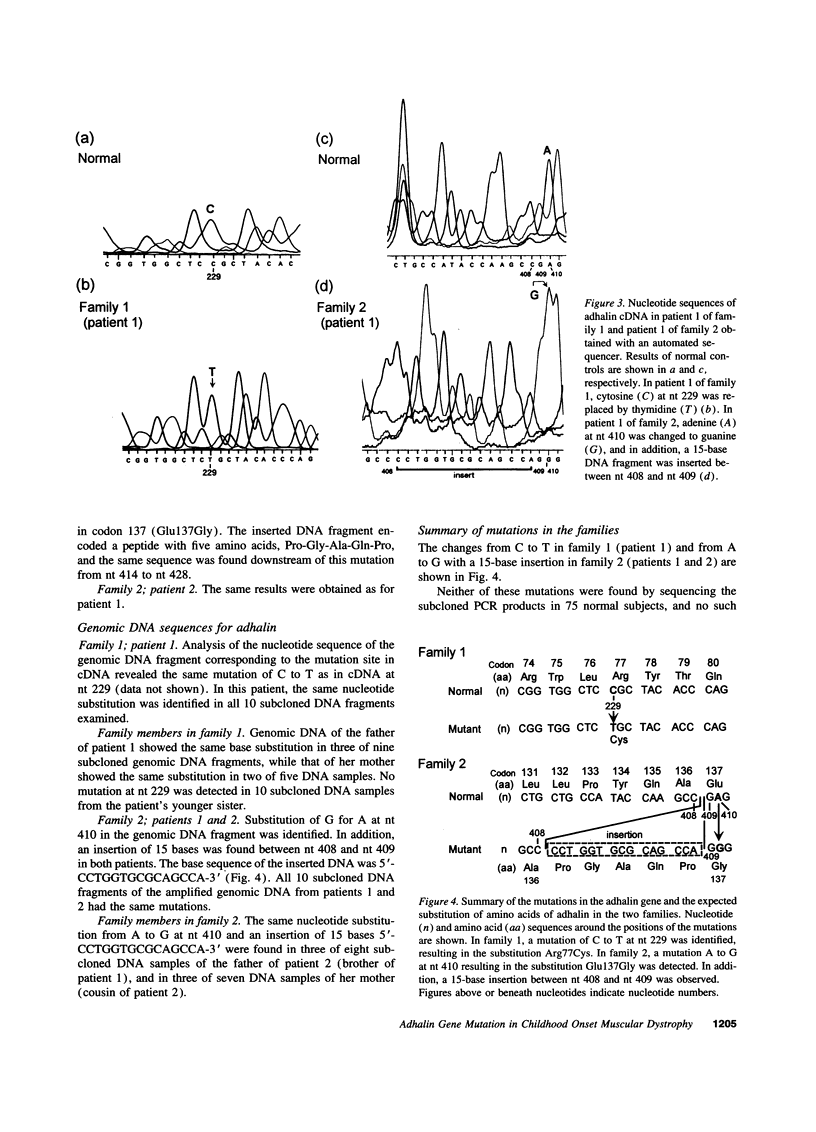
Homozygous adhalin gene mutations were found in three patients from two consanguineous families with autosomal recessive childhood onset muscular dystrophy. Muscle biopsies from patients in each family showed complete absence of adhalin. Sequencing of adhalin cDNA prepared from skeletal muscle by reverse transcription PCR demonstrated a cytosine to thymidine substitution at nt 229 in the patient in family 1 and an adenine to guanine substitution at nt 410 and a 15-base insertion between nt 408 and 409 in the two patients in family 2. Sequencing of genomic DNA prepared from peripheral blood leukocytes by PCR confirmed these mutations. The parents in each family were found to be heterozygous for the respective mutations. These adhalin gene mutations are presumed to be responsible for the absence of adhalin in the skeletal muscle. Adhalin deficiency likely causes disruption of the muscle cell membrane, resulting in dystrophic changes in the skeletal muscle similar to dystrophin deficiency in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azibi K., Bachner L., Beckmann J. S., Matsumura K., Hamouda E., Chaouch M., Chaouch A., Ait-Ouarab R., Vignal A., Weissenbach J. Severe childhood autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy with the deficiency of the 50 kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein maps to chromosome 13q12. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Sep;2(9):1423–1428. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.9.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hamida M., Fardeau M., Attia N. Severe childhood muscular dystrophy affecting both sexes and frequent in Tunisia. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Sep;6(7):469–480. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Othmane K., Ben Hamida M., Pericak-Vance M. A., Ben Hamida C., Blel S., Carter S. C., Bowcock A. M., Petruhkin K., Gilliam T. C., Roses A. D. Linkage of Tunisian autosomal recessive Duchenne-like muscular dystrophy to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 13q. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):315–317. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervasti J. M., Campbell K. P. Dystrophin-associated glycoproteins: their possible roles in the pathogenesis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Mol Cell Biol Hum Dis Ser. 1993;3:139–166. doi: 10.1007/978-94-011-1528-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervasti J. M., Campbell K. P. Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1121–1131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90035-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi I., Yamada H., Fukunaga H., Iwaki H., Okubo R., Nakagawa M., Osame M., Roberds S. L., Shimizu T., Campbell K. P. Abnormal expression of laminin suggests disturbance of sarcolemma-extracellular matrix interaction in Japanese patients with autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy deficient in adhalin. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):601–606. doi: 10.1172/JCI117375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON H. A. SEVERE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY IN GIRLS. J Med Genet. 1964 Dec;1(2):79–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLOEPFER H. W., TALLEY C. Autosomal recessive inheritance of Duchennetype muscular dystrophy. Ann Hum Genet. 1958 Feb;22(2):138–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1957.tb01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Evans G. A. Restriction endonuclease cleavage at the termini of PCR products. Biotechniques. 1990 Sep;9(3):304–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura K., Tomé F. M., Collin H., Azibi K., Chaouch M., Kaplan J. C., Fardeau M., Campbell K. P. Deficiency of the 50K dystrophin-associated glycoprotein in severe childhood autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):320–322. doi: 10.1038/359320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally E. M., Yoshida M., Mizuno Y., Ozawa E., Kunkel L. M. Human adhalin is alternatively spliced and the gene is located on chromosome 17q21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9690–9694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passos-Bueno M. R., Oliveira J. R., Bakker E., Anderson R. D., Marie S. K., Vainzof M., Roberds S., Campbell K. P., Zatz M. Genetic heterogeneity for Duchenne-like muscular dystrophy (DLMD) based on linkage and 50 DAG analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1945–1947. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A. S., Lisak R. P., Rowland L. P. Muscular dystrophy in young girls. Neurology. 1970 Feb;20(2):147–159. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perloff J. K., Roberts W. C., de Leon A. C., Jr, O'Doherty D. The distinctive electrocardiogram of Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy. An electrocardiographic-pathologic correlative study. Am J Med. 1967 Feb;42(2):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberds S. L., Anderson R. D., Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O., Campbell K. P. Primary structure and muscle-specific expression of the 50-kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (adhalin). J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23739–23742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberds S. L., Leturcq F., Allamand V., Piccolo F., Jeanpierre M., Anderson R. D., Lim L. E., Lee J. C., Tomé F. M., Romero N. B. Missense mutations in the adhalin gene linked to autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero N. B., Tomé F. M., Leturcq F., el Kerch F. E., Azibi K., Bachner L., Anderson R. D., Roberds S. L., Campbell K. P., Fardeau M. Genetic heterogeneity of severe childhood autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy with adhalin (50 kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein) deficiency. C R Acad Sci III. 1994 Jan;317(1):70–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Engvall E., Butkowski R., Hunter D. D. Molecular heterogeneity of basal laminae: isoforms of laminin and collagen IV at the neuromuscular junction and elsewhere. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1685–1699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. K., Leung R. K., Tierney R. C., Gilmartin R., Pitner S. Mitral valve prolapse syndrome in children with Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy. Pediatrics. 1979 Jan;63(1):116–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealock R., Froehner S. C. Dystrophin-associated proteins and synapse formation: is alpha-dystroglycan the agrin receptor? Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):617–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Matsumura K., Vainzof M., Passos-Bueno M. R., Pavanello R. C., Marie S. K., Campbell K. P. Assessment of the 50-kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein in Brazilian patients with severe childhood autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1994 May;123(1-2):122–128. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Kerch F., Sefiani A., Azibi K., Boutaleb N., Yahyaoui M., Bentahila A., Vinet M. C., Leturcq F., Bachner L., Beckmann J. Linkage analysis of families with severe childhood autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy in Morocco indicates genetic homogeneity of the disease in north Africa. J Med Genet. 1994 Apr;31(4):342–343. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.4.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]