Abstract
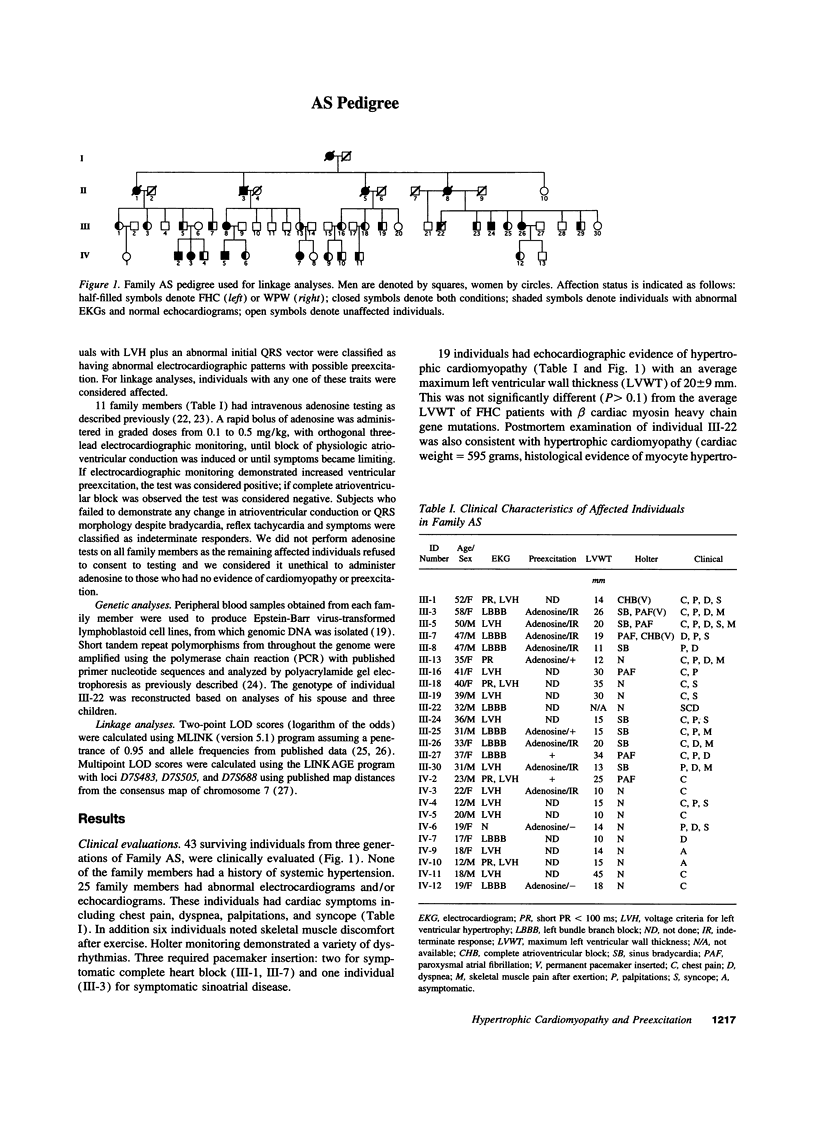
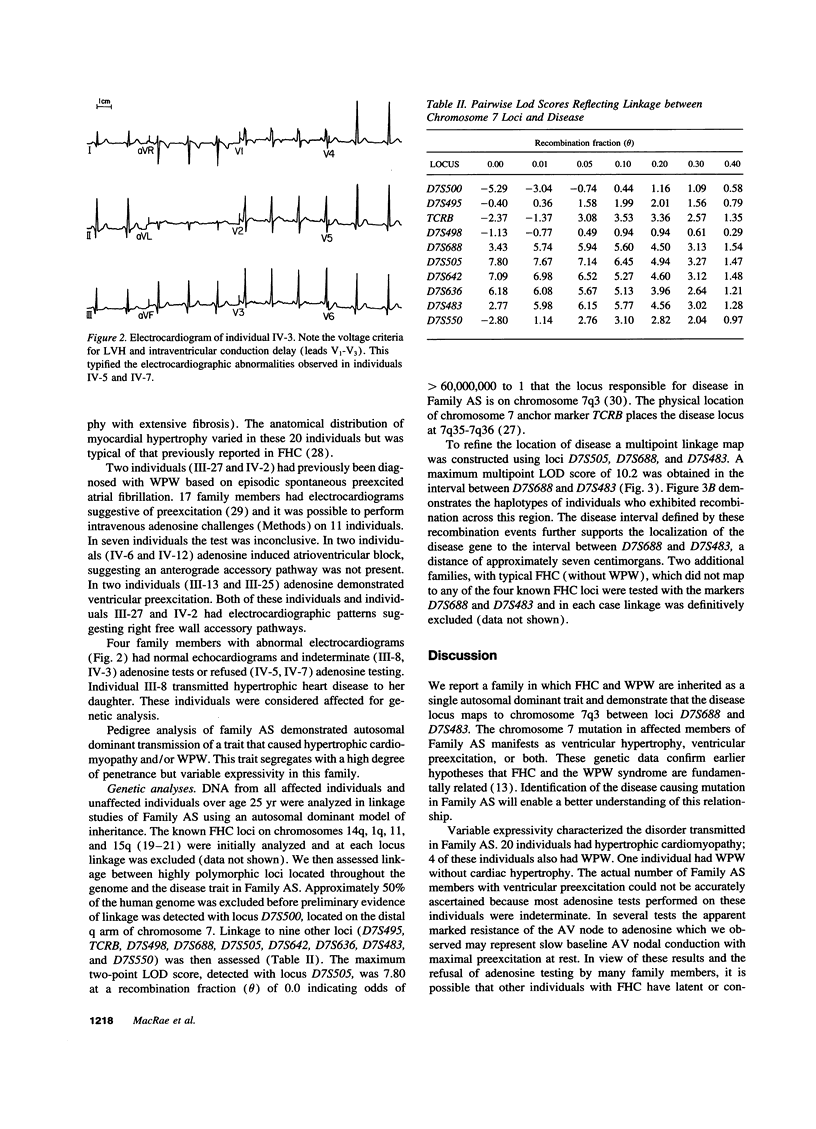
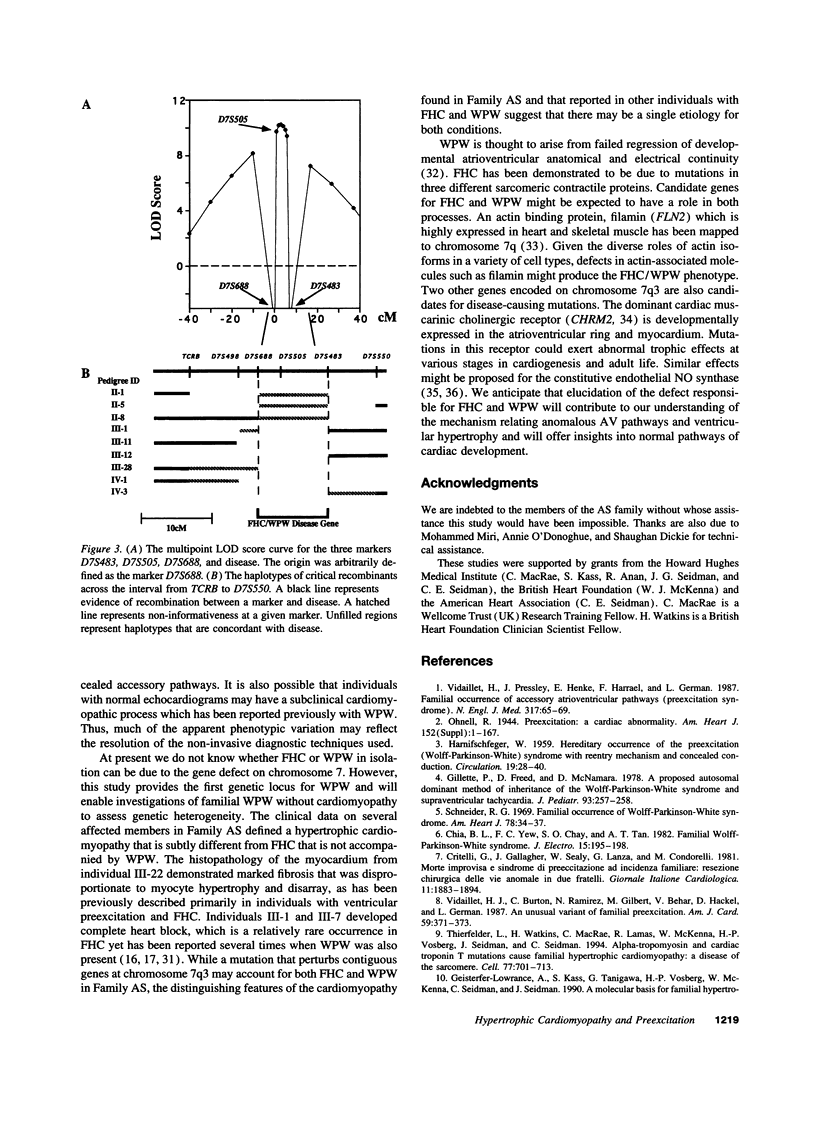
We have mapped a disease locus for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC) segregating in a large kindred to chromosome 7 band q3. Although WPW syndrome and FHC have been observed in members of the same family in prior studies, the relationship between these two diseases has remained enigmatic. A large family with 25 surviving individuals who are affected by one or both of these conditions was studied. The disease locus is closely linked to loci D7S688, D7S505, and D7S483 (maximum two point LOD score at D7S505 was 7.80 at theta = 0). While four different FHC loci have been described this is the first locus that can be mutated to cause both WPW and/or FHC.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bharati S., Strasberg B., Bilitch M., Salibi H., Mandel W., Rosen K. M., Lev M. Anatomic substrate for preexcitation in idiopathic myocardial hypertrophy with fibroelastosis of the left ventricle. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Jul;48(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90571-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier L., Hengstenberg C., Beckmann J. S., Guicheney P., Dufour C., Bercovici J., Dausse E., Berebbi-Bertrand I., Wisnewsky C., Pulvenis D. Mapping of a novel gene for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to chromosome 11. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):311–313. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charmley P., Concannon P. Polymorphism and phylogeny of dinucleotide repeats in human T-cell receptor Vb6 genes. Immunogenetics. 1993;38(2):92–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00190896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia B. L., Yew F. C., Chay S. O., Tan A. T. Familial Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Electrocardiol. 1982 Apr;15(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(82)80016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Brown E. M., Levi T., Crowe G., Atkinson A. B., Arnqvist H. J., Toss G., Fuleihan G. E., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. The gene responsible for familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia maps to chromosome 3q in four unrelated families. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):295–300. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen T. J., Tucker K. J., Abbott J. A., Botvinick E. H., Foster E., Schiller N. B., O'Connell J. W., Scheinman M. M. Usefulness of adenosine in augmenting ventricular preexcitation for noninvasive localization of accessory pathways. Am J Cardiol. 1992 May 1;69(14):1178–1185. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(92)90932-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critelli G., Gallagher J. J., Sealy W. C., Lanza G. G., Condorelli M. Morte improvvisa e sindrome di preeccitazione ad incidenza familiare. Resezione chirurgica delle vie anomale in due fratelli. G Ital Cardiol. 1981;11(12):1883–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fananapazir L., Tracy C. M., Leon M. B., Winkler J. B., Cannon R. O., 3rd, Bonow R. O., Maron B. J., Epstein S. E. Electrophysiologic abnormalities in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A consecutive analysis in 155 patients. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1259–1268. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariboldi M., Maestrini E., Canzian F., Manenti G., De Gregorio L., Rivella S., Chatterjee A., Herman G. E., Archidiacono N., Antonacci R. Comparative mapping of the actin-binding protein 280 genes in human and mouse. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):428–430. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garratt C. J., Antoniou A., Griffith M. J., Ward D. E., Camm A. J. Use of intravenous adenosine in sinus rhythm as a diagnostic test for latent preexcitation. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Apr 1;65(13):868–873. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)91428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillette P. C., Freed D., McNamara D. G. A proposed autosomal dominant method of inheritance of the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and supraventricular tachycardia. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):257–258. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H., Tsui L. C., Green E. D. Report and abstracts of the First International Workshop on Human Chromosome 7 Mapping 1993. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;65(1-2):52–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARNISCHFEGER W. W. Hereditary occurrence of the pre-excitation (Wolff-Parkinson-White) syndrome with re-entry mechanism and concealed conduction. Circulation. 1959 Jan;19(1):28–40. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.19.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarcho J. A., McKenna W., Pare J. A., Solomon S. D., Holcombe R. F., Dickie S., Levi T., Donis-Keller H., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Mapping a gene for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to chromosome 14q1. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1372–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariv I., Kreisler B., Sherf L., Feldman S., Rosenthal T. Familial cardiomyopathy. A review of 11 families. Am J Cardiol. 1971 Dec;28(6):693–706. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(71)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khair G. Z., Soni J. S., Bamrah V. S. Syncope in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. II. Coexistence of atrioventricular block and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am Heart J. 1985 Nov;110(5):1083–1086. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Heng H. H., Scherer S. W., Stewart R. J., Hall A. V., Shi X. M., Tsui L. C., Schappert K. T. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human constitutive endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17478–17488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massumi R. A. Familial Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with cardiomyopathy. Am J Med. 1967 Dec;43(6):951–955. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perosio A. M., Suarez L. D., Bunster A. M., Locreille A., Apkarian O. A., Vallazza M. A., Foye R. Pre-excitation syndrome and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Electrocardiol. 1983 Jan;16(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0736(83)80156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Weremowicz S., Morton C. C., Michel T. Isolation and chromosomal localization of the human endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NOS3) gene. Genomics. 1994 Jan 15;19(2):350–357. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. G. Familial occurrence of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am Heart J. 1969 Jul;78(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(69)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. D., Wolff S., Watkins H., Ridker P. M., Come P., McKenna W. J., Seidman C. E., Lee R. T. Left ventricular hypertrophy and morphology in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated with mutations of the beta-myosin heavy chain gene. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Aug;22(2):498–505. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(93)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierfelder L., MacRae C., Watkins H., Tomfohrde J., Williams M., McKenna W., Bohm K., Noeske G., Schlepper M., Bowcock A. A familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy locus maps to chromosome 15q2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6270–6274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierfelder L., Watkins H., MacRae C., Lamas R., McKenna W., Vosberg H. P., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Alpha-tropomyosin and cardiac troponin T mutations cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a disease of the sarcomere. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):701–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touboul P., Kirkorian G., Atallah G., Cahen P., de Zuloaga C., Moleur P. Atrioventricular block and preexcitation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Mar 15;53(7):961–963. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaillet H. J., Jr, Burton C. S., 3rd, Ramirez N. M., Gilbert M. R., Behar V. S., Hackel D. B., German L. D. An unusual variant of familial preexcitation. Am J Cardiol. 1987 Feb 1;59(4):371–373. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)90822-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaillet H. J., Jr, Pressley J. C., Henke E., Harrell F. E., Jr, German L. D. Familial occurrence of accessory atrioventricular pathways (preexcitation syndrome). N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 9;317(2):65–69. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707093170201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTLAKE R. E., COHEN W., WILLIS W. H. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and familial cardiomegaly. Am Heart J. 1962 Sep;64:314–320. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(62)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins H., MacRae C., Thierfelder L., Chou Y. H., Frenneaux M., McKenna W., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A disease locus for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy maps to chromosome 1q3. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):333–337. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



