Abstract
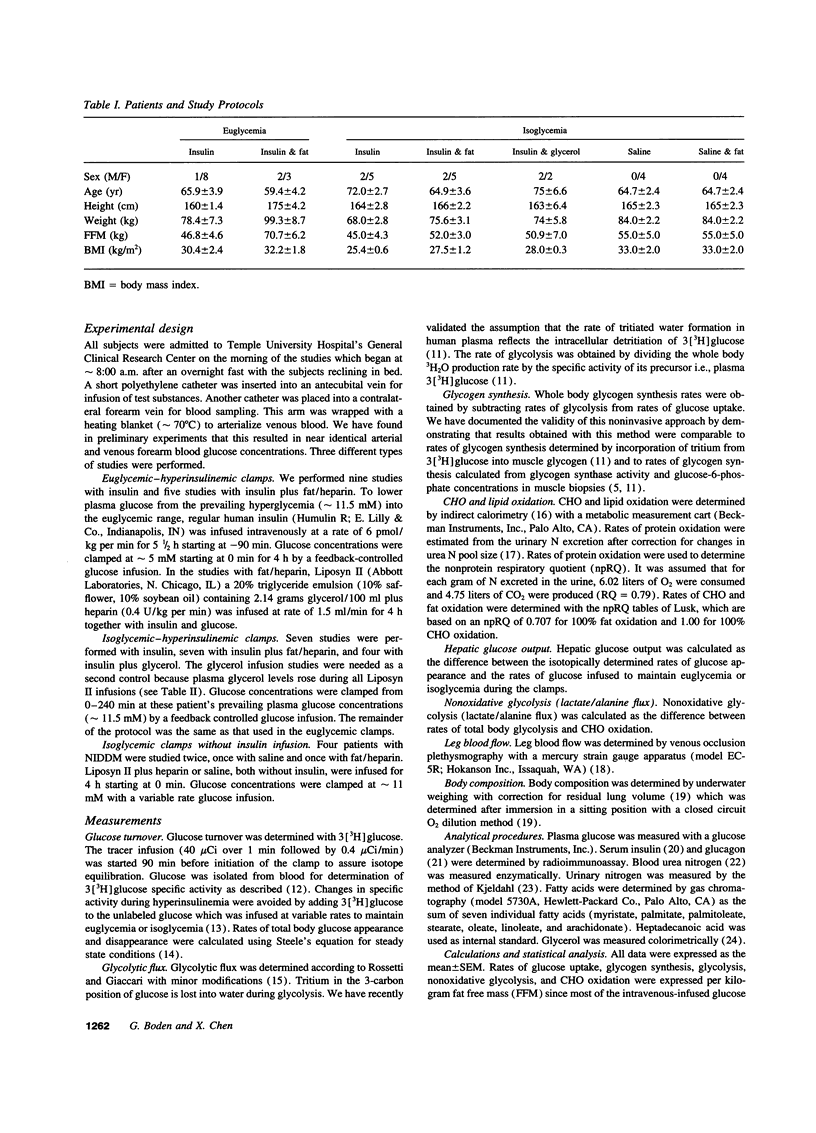
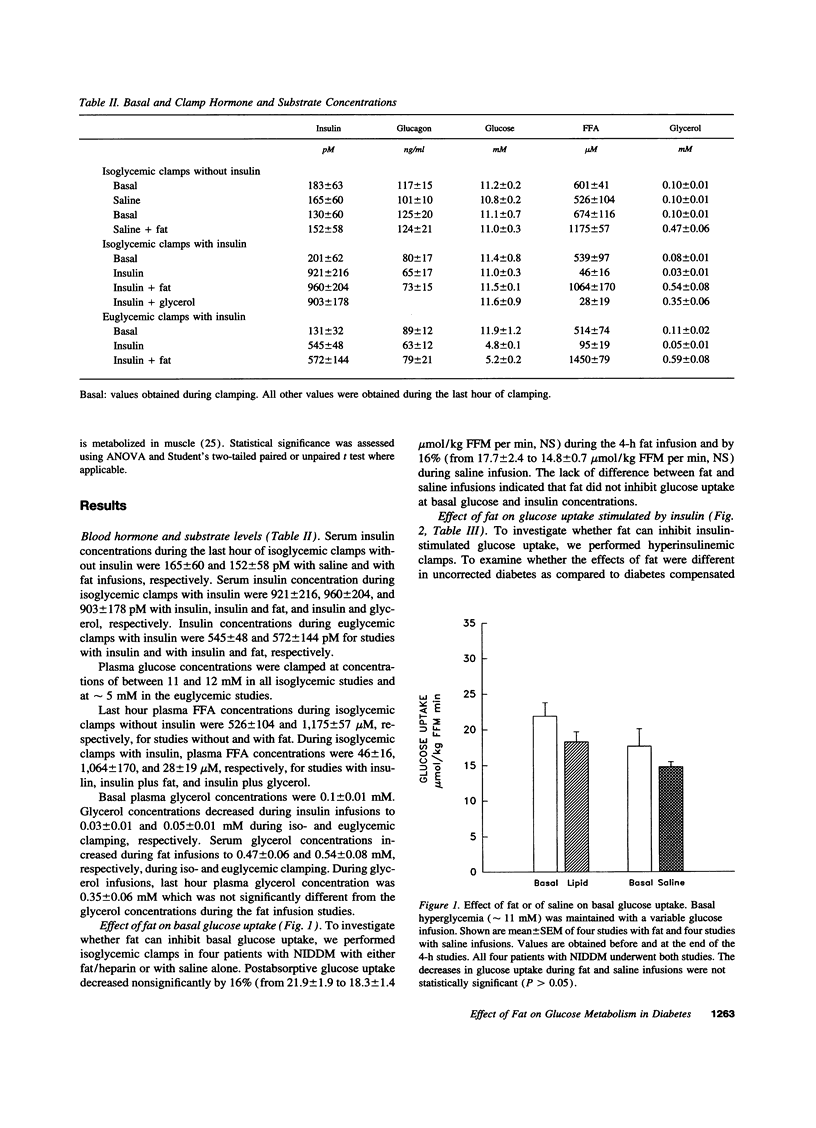
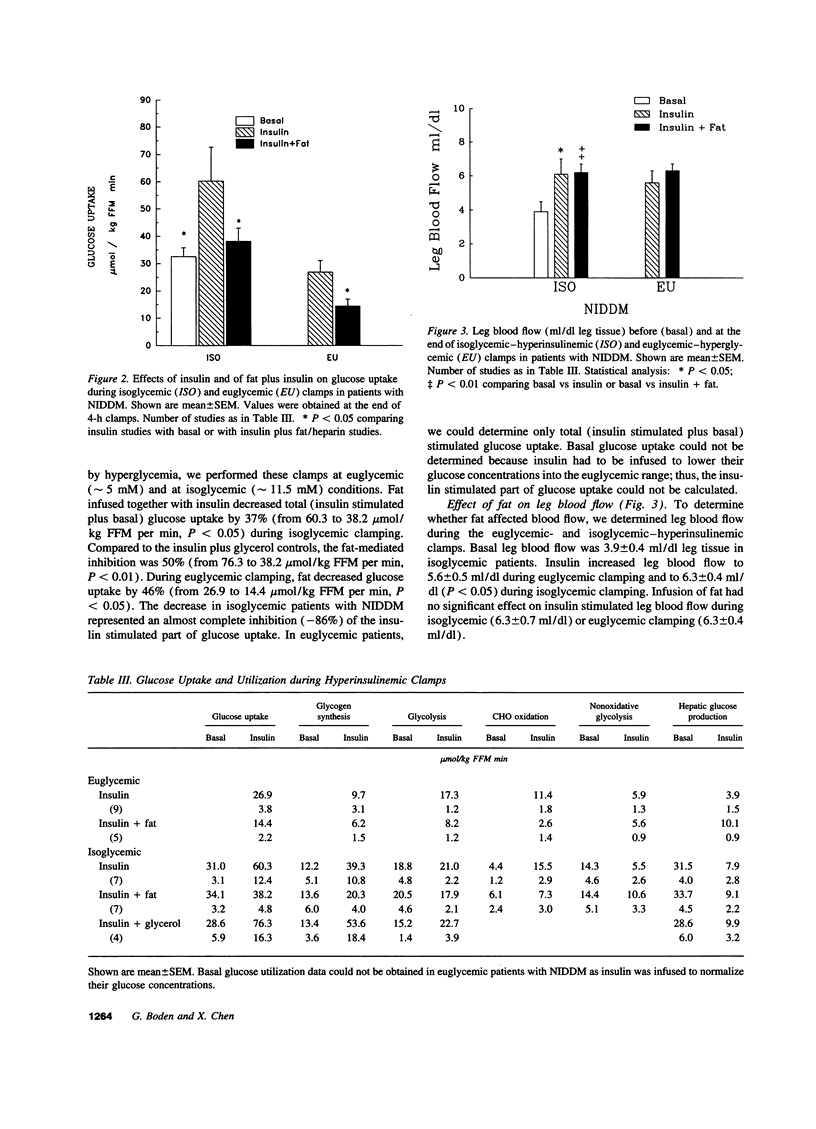
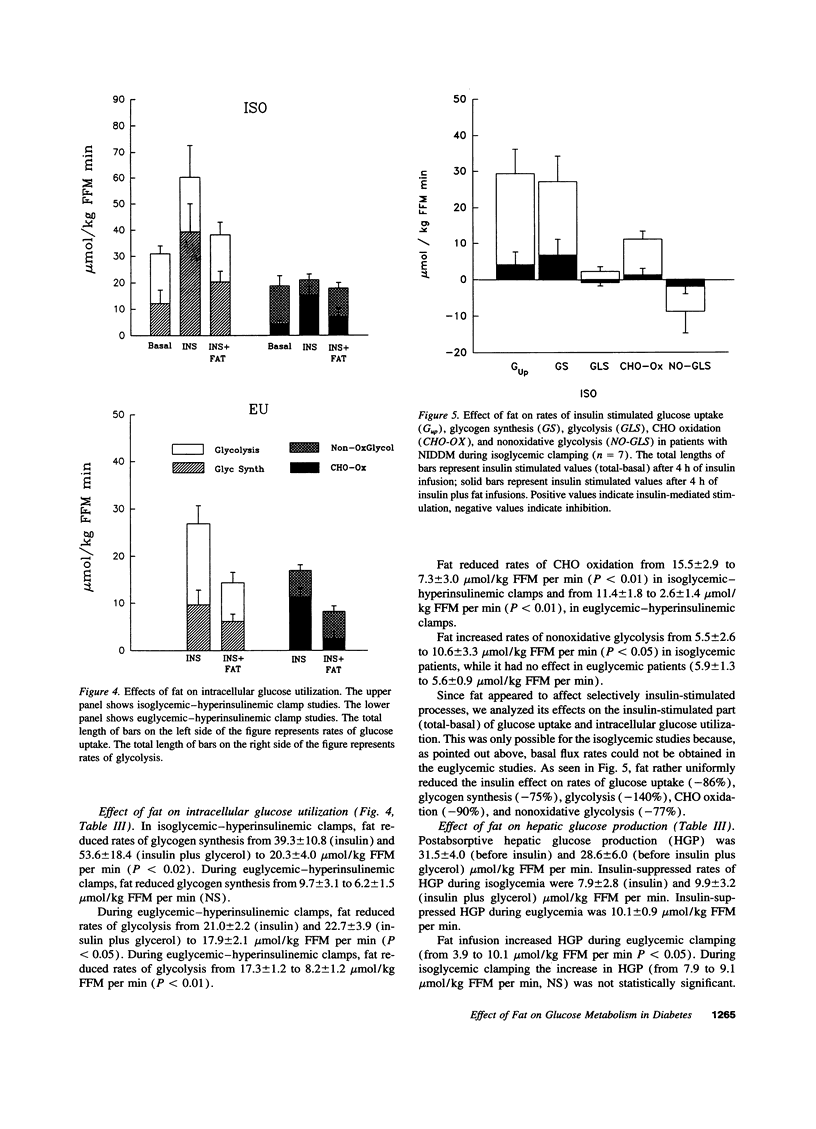
It was the aim of this study to determine whether FFA inhibit insulin-stimulated whole body glucose uptake and utilization in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. We performed five types of isoglycemic (approximately 11mM) clamps: (a) with insulin; (b) with insulin plus fat/heparin; (c) with insulin plus glycerol; (d) with saline; (e) with saline plus fat/heparin and two types of euglycemic (approximately 5mM) clamps: (a) with insulin; (b) with insulin plus fat/heparin. During these studies, we determined rates of glucose uptake, glycolysis (both with 3[3H] glucose), glycogen synthesis (determined as glucose uptake minus glycolysis), carbohydrate oxidation (by indirect calorimetry) and nonoxidative glycolysis (determined as glycolysis minus carbohydrate oxidation). Fat/heparin infusion did not affect basal glucose uptake, but inhibited total stimulated (insulin stimulated plus basal) glucose uptake by 40-50% in isoglycemic and in euglycemic patients at plasma FFA concentration of approximately 950 and approximately 550 microM, respectively. In isoglycemic patients, the 40-50% inhibition of total stimulated glucose uptake was due to near complete inhibition of the insulin-stimulated part of glucose uptake. Proportional inhibition of glucose uptake, glycogen synthesis, and glycolysis suggested a major FFA-mediated defect involving glucose transport and/or phosphorylation. In summary, fat produced proportional inhibitions of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and of intracellular glucose utilization. We conclude, that physiologically elevated levels of FFa could potentially be responsible for a large part of the peripheral insulin resistance in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevilacqua S., Bonadonna R., Buzzigoli G., Boni C., Ciociaro D., Maccari F., Giorico M. A., Ferrannini E. Acute elevation of free fatty acid levels leads to hepatic insulin resistance in obese subjects. Metabolism. 1987 May;36(5):502–506. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua S., Buzzigoli G., Bonadonna R., Brandi L. S., Oleggini M., Boni C., Geloni M., Ferrannini E. Operation of Randle's cycle in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Mar;39(3):383–389. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Chen X., Ruiz J., White J. V., Rossetti L. Mechanisms of fatty acid-induced inhibition of glucose uptake. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2438–2446. doi: 10.1172/JCI117252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Jadali F. Effects of lipid on basal carbohydrate metabolism in normal men. Diabetes. 1991 Jun;40(6):686–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Jadali F., White J., Liang Y., Mozzoli M., Chen X., Coleman E., Smith C. Effects of fat on insulin-stimulated carbohydrate metabolism in normal men. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):960–966. doi: 10.1172/JCI115399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Stone K., Mott D. Correlation between muscle glycogen synthase activity and in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. C., Kryshak E. J., Marsh M., Rizza R. A. Effect of insulin on oxidation of intracellularly and extracellularly derived glucose in patients with NIDDM. Evidence for primary defect in glucose transport and/or phosphorylation but not oxidation. Diabetes. 1990 Nov;39(11):1373–1380. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consoli A., Nurjhan N., Capani F., Gerich J. Predominant role of gluconeogenesis in increased hepatic glucose production in NIDDM. Diabetes. 1989 May;38(5):550–557. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.5.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Bonadonna R. C., Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):318–368. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Jun;37(6):667–687. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prato S., Bonadonna R. C., Bonora E., Gulli G., Solini A., Shank M., DeFronzo R. A. Characterization of cellular defects of insulin action in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):484–494. doi: 10.1172/JCI116226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Barrett E. J., Bevilacqua S., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1737–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groop L. C., Bonadonna R. C., DelPrato S., Ratheiser K., Zyck K., Ferrannini E., DeFronzo R. A. Glucose and free fatty acid metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Evidence for multiple sites of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):205–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI114142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Mandarino L. J. Hyperglycemia normalizes insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose oxidation and storage in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1999–2007. doi: 10.1172/JCI114935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Mokan M., Simoneau J. A., Mandarino L. J. Interaction between glucose and free fatty acid metabolism in human skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):91–98. doi: 10.1172/JCI116603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Reilly J. P., Veneman T., Mandarino L. J. Effects of insulin on skeletal muscle glucose storage, oxidation, and glycolysis in humans. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):E923–E929. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.6.E923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laakso M., Edelman S. V., Brechtel G., Baron A. D. Decreased effect of insulin to stimulate skeletal muscle blood flow in obese man. A novel mechanism for insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1844–1852. doi: 10.1172/JCI114644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH W. H., FINGERHUT B., MILLER H. AUTOMATED AND MANUAL DIRECT METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF BLOOD UREA. Clin Chem. 1965 Jun;11:624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina J. M., Baron A. D., Edelman S. V., Brechtel G., Wallace P., Olefsky J. M. Use of a variable tracer infusion method to determine glucose turnover in humans. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):E16–E23. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.1.E16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Trapp V. E., Reichard G. A., Jr, Mozzoli M. A., Smith R., Boden G. Effects of therapy on the nature and quantity of fuels oxidized during diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):365–372. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascoe W. S., Storlien L. H. Inducement by fat feeding of basal hyperglycemia in rats with abnormal beta-cell function. Model for study of etiology and pathogenesis of NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):226–233. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Garland P. B., Newsholme E. A., Hales C. N. The glucose fatty acid cycle in obesity and maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):324–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Hollenbeck C., Jeng C. Y., Wu M. S., Chen Y. D. Measurement of plasma glucose, free fatty acid, lactate, and insulin for 24 h in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Aug;37(8):1020–1024. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.8.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Giaccari A. Relative contribution of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis to insulin-mediated glucose uptake. A dose-response euglycemic clamp study in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Lee Y. T., Ruiz J., Aldridge S. C., Shamoon H., Boden G. Quantitation of glycolysis and skeletal muscle glycogen synthesis in humans. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):E761–E769. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.265.5.E761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saloranta C., Franssila-Kallunki A., Ekstrand A., Taskinen M. R., Groop L. Modulation of hepatic glucose production by non-esterified fatty acids in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991 Jun;34(6):409–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00403179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyama R., Ray T. K., Savage C. R., Jr, Owen O. E., Boden G. In vivo and in vitro effects of antiinsulin receptor antibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):916–923. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Rothman D. L., Jue T., Stein P., DeFronzo R. A., Shulman R. G. Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):223–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims E. A., Danforth E., Jr, Horton E. S., Bray G. A., Glennon J. A., Salans L. B. Endocrine and metabolic effects of experimental obesity in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1973;29:457–496. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571129-6.50016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappy L., Owen O. E., Boden G. Effect of hyperinsulinemia on urea pool size and substrate oxidation rates. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1212–1216. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébaud D., DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Golay A., Acheson K., Maeder E., Jéquier E., Felber J. P. Effect of long chain triglyceride infusion on glucose metabolism in man. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1128–1136. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn A. W., Gumbiner B., Bulacan F., Wallace P., Henry R. R. Intracellular glucose oxidation and glycogen synthase activity are reduced in non-insulin-dependent (type II) diabetes independent of impaired glucose uptake. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):522–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI114468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhäusl W., Bratusch-Marrain P., Gasić S., Korn A., Nowotny P. Insulin production rate, hepatic insulin retention and splanchnic carbohydrate metabolism after oral glucose ingestion in hyperinsulinaemic Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1982 Jul;23(1):6–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00257722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. M., Klein S., Peters E. J., Schmidt B. F., Wolfe R. R. Effect of elevated free fatty acids on glucose oxidation in normal humans. Metabolism. 1988 Apr;37(4):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Puhakainen I., Saloranta C., Groop L., Taskinen M. R. Demonstration of a novel feedback mechanism between FFA oxidation from intracellular and intravascular sources. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):E680–E689. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.5.E680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


