Abstract
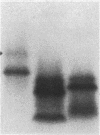
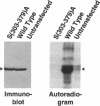
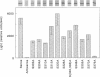
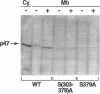
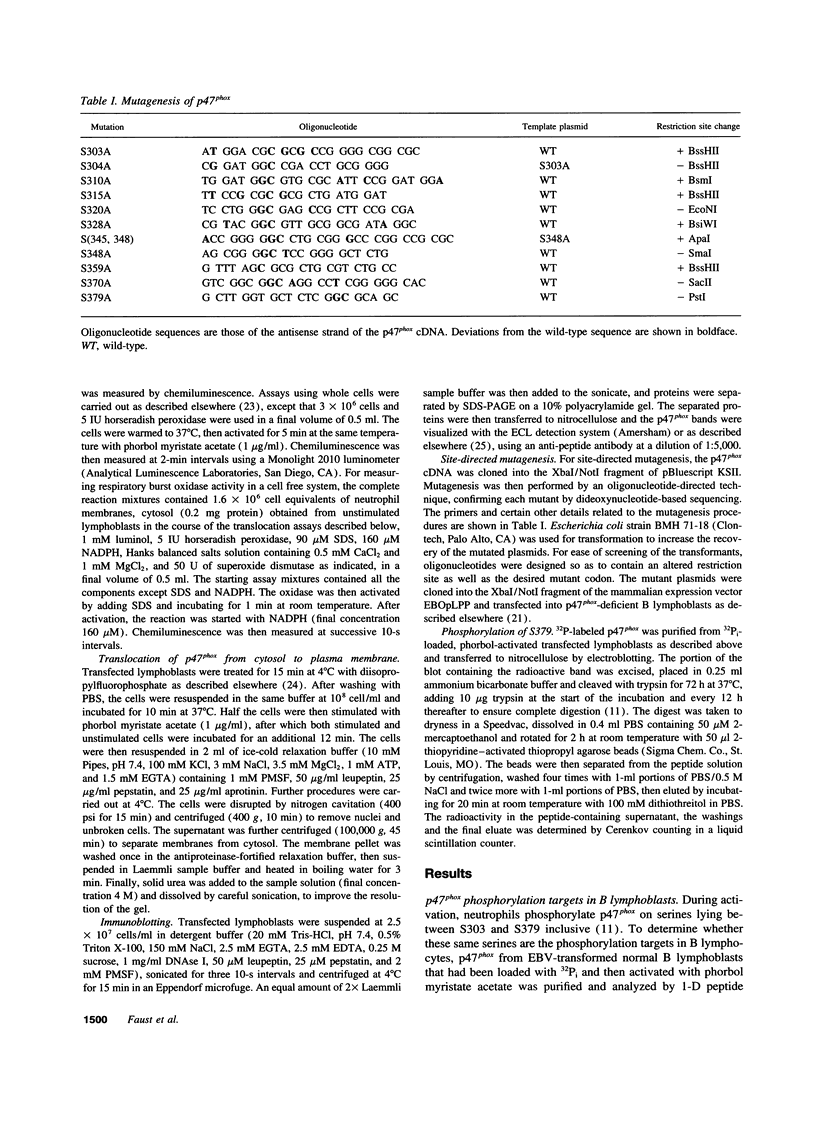
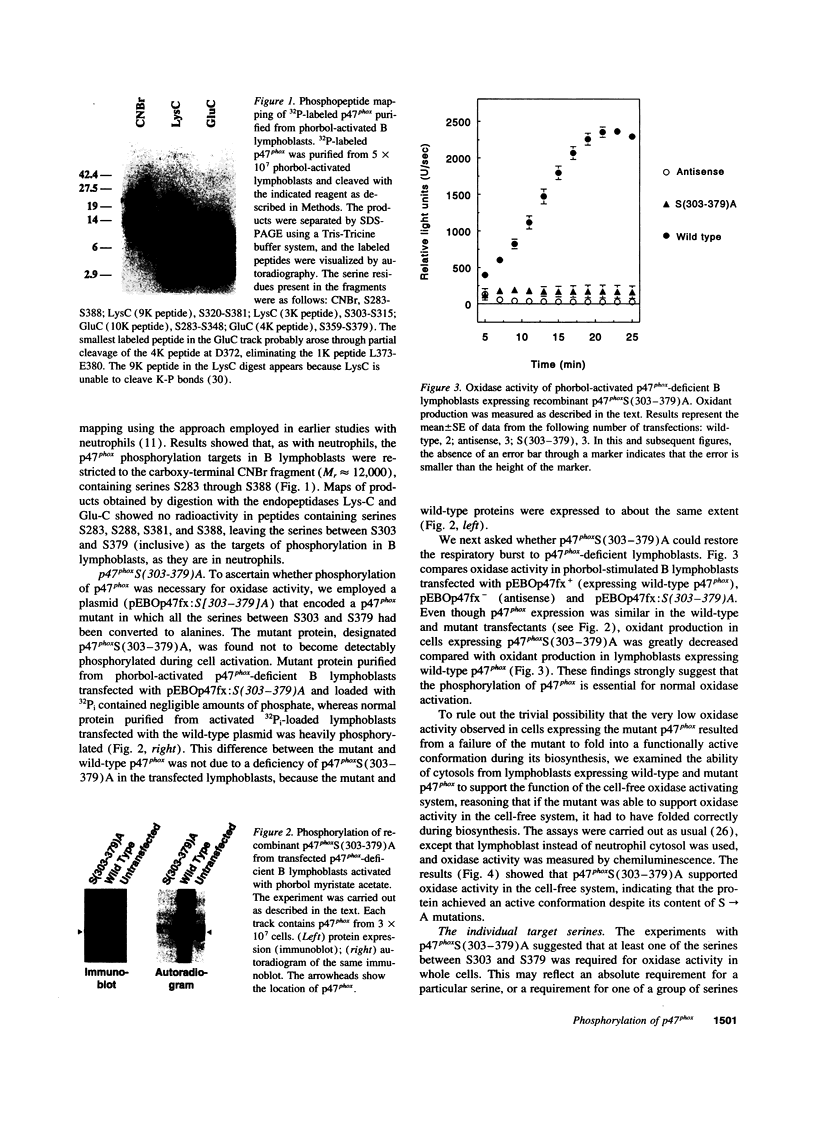
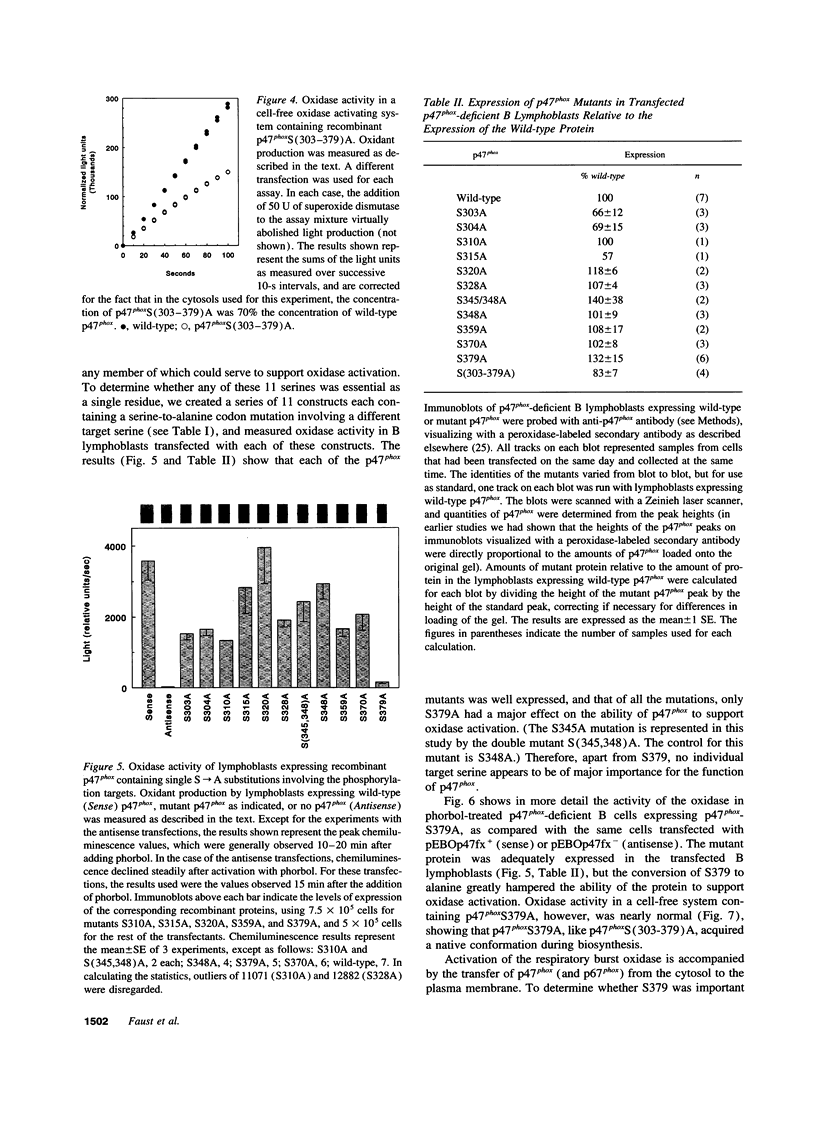
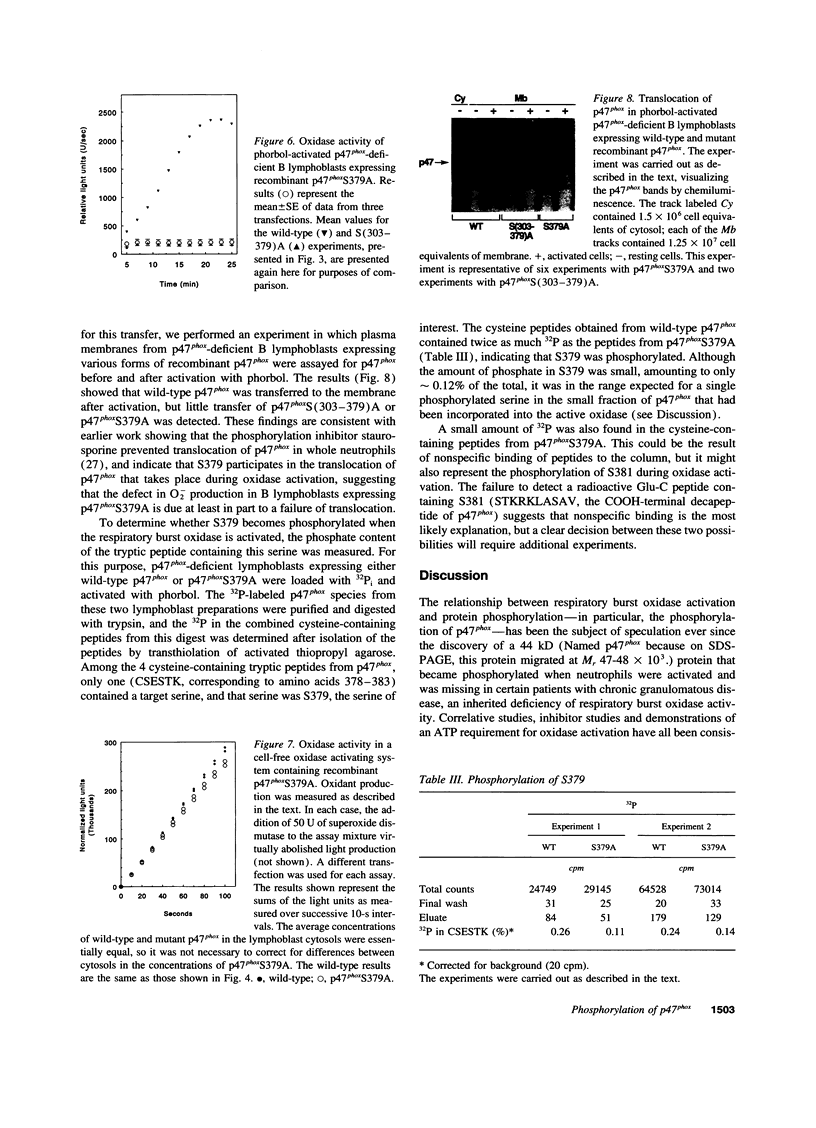
The respiratory burst oxidase of phagocytes and B lymphocytes catalyzes the reduction of oxygen to O2- at the expense of NADPH. Dormant in resting cells, the oxidase is activated by exposing the cells to appropriate stimuli. During activation, p47phox, a cytosolic oxidase subunit, becomes extensively phosphorylated on a number of serines located between S303 and S379. To determine whether this phosphorylation is necessary for oxidase activation, we examined phorbol-elicited oxidase activity in EBV-transformed B lymphoblasts deficient in p47phox after transfection with plasmids expressing various S-->A mutants of p47phox. The mutant containing S-->A mutations involving all serines between S303 and S379 [S(303-379)A] was not phosphorylated, did not translocate to plasma membrane during activation and was almost devoid of function. As to individual serines, S379 was of special interest because (a) p47 phox S379 was phosphorylated in phorbol-activated lymphoblasts expressing wild-type p47phox, and (b) p47phox S379A failed to translocate to the membrane, and was as functionless as p47phox S(303-379)A; other single S-->A mutations had little effect on oxidase activity. These findings suggest that the phosphorylation of S379 may be important for oxidase activation in whole cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock S. J., Faust L. R., Barrett D., Bizal C., Maly F. E., Newburger P. E., Ruedi J. M., Smith R. M., Babior B. M. O2- production by B lymphocytes lacking the respiratory burst oxidase subunit p47phox after transfection with an expression vector containing a p47phox cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10174–10177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock S. J., el Benna J., Smith R. M., Babior B. M. The respiratory burst oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24519–24522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide production by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. The effects of N-ethyl maleimide, divalent cations; and glycolytic and mitochondrial inhibitors on the activation of the superoxide generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1088–1096. doi: 10.1172/JCI109008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combadière C., el Benna J., Pedruzzi E., Hakim J., Périanin A. Stimulation of the human neutrophil respiratory burst by formyl peptides is primed by a protein kinase inhibitor, staurosporine. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2890–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley C. A., Curnutte J. T., Rosin R. E., André-Schwartz J., Gallin J. I., Klempner M., Snyderman R., Southwick F. S., Stossel T. P., Babior B. M. An inherited abnormality of neutrophil adhesion. Its genetic transmission and its association with a missing protein. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 22;302(21):1163–1168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005223022102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J., Badwey J. A. Effects of antagonists of protein phosphatases on superoxide release by neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6442–6448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaut J. R., Carchman R. A. A correlation between phorbol diester-induced protein phosphorylation and superoxide anion generation in HL-60 cells during granulocytic maturation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):826–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Suzuki K., Suzuki S., Andrews P. C., Babior B. M. A possible role for protein phosphorylation in the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Evidence from studies with cells from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9109–9115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth P. G., Curnutte J. T., Nauseef W. M., Volpp B. D., Pearson D. W., Rosen H., Clark R. A. Neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase assembly. Translocation of p47-phox and p67-phox requires interaction between p47-phox and cytochrome b558. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):352–356. doi: 10.1172/JCI114993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessels G. C., Krause K. H., Verhoeven A. J. Protein kinase C activity is not involved in N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced phospholipase D activation in human neutrophils, but is essential for concomitant NADPH oxidase activation: studies with a staurosporine analogue with improved selectivity for protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):781–785. doi: 10.1042/bj2920781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax K. J., Leto T. L., Nunoi H., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Recombinant 47-kilodalton cytosol factor restores NADPH oxidase in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):409–412. doi: 10.1126/science.2547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D. J., Grinstein S. ATP and guanine nucleotide dependence of neutrophil activation. Evidence for the involvement of two distinct GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13721–13729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Gilbert C., Caon A. C., Gaudry M., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Umezawa K., McColl S. R. Selective inhibition of human neutrophil functional responsiveness by erbstatin, an inhibitor of tyrosine protein kinase. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2098–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauseef W. M., Volpp B. D., McCormick S., Leidal K. G., Clark R. A. Assembly of the neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. Protein kinase C promotes cytoskeletal and membrane association of cytosolic oxidase components. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5911–5917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoi H., Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Two forms of autosomal chronic granulomatous disease lack distinct neutrophil cytosol factors. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1298–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.2848319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka T., Okamura N., Ishibashi S. Involvement of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of 46 kDa proteins which are phosphorylated in parallel with activation of NADPH oxidase in intact guinea-pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 10;888(3):332–337. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Curnutte J. T., Roberts R. L., Babior B. M. Relationship of protein phosphorylation to the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Defects in the phosphorylation of a group of closely related 48-kDa proteins in two forms of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. W., Ma M., Ruedi J. M., Smith R. M., Babior B. M. The cytosolic components of the respiratory burst oxidase exist as a M(r) approximately 240,000 complex that acquires a membrane-binding site during activation of the oxidase in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17327–17332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Heyworth P. G., Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M. Stimulated neutrophils from patients with autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease fail to phosphorylate a Mr-44,000 protein. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):547–549. doi: 10.1038/316547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Affinity labeling of the cytosolic and membrane components of the respiratory burst oxidase by the 2',3'-dialdehyde derivative of NADPH. Evidence for a cytosolic location of the nucleotide-binding site in the resting cell. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1958–1962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumimoto H., Kage Y., Nunoi H., Sasaki H., Nose T., Fukumaki Y., Ohno M., Minakami S., Takeshige K. Role of Src homology 3 domains in assembly and activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrasher A., Chetty M., Casimir C., Segal A. W. Restoration of superoxide generation to a chronic granulomatous disease-derived B-cell line by retrovirus mediated gene transfer. Blood. 1992 Sep 1;80(5):1125–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Two cytosolic neutrophil oxidase components absent in autosomal chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1295–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.2848318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Donelson J. E., Moser D. R., Clark R. A. Cloning of the cDNA and functional expression of the 47-kilodalton cytosolic component of human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou M. J., Brown E. J. CR3 (Mac-1, alpha M beta 2, CD11b/CD18) and Fc gamma RIII cooperate in generation of a neutrophil respiratory burst: requirement for Fc gamma RIII and tyrosine phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1407–1416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Benna J., Faust L. P., Babior B. M. The phosphorylation of the respiratory burst oxidase component p47phox during neutrophil activation. Phosphorylation of sites recognized by protein kinase C and by proline-directed kinases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23431–23436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Benna J., Ruedi J. M., Babior B. M. Cytosolic guanine nucleotide-binding protein Rac2 operates in vivo as a component of the neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. Transfer of Rac2 and the cytosolic oxidase components p47phox and p67phox to the submembranous actin cytoskeleton during oxidase activation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6729–6734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]