Abstract
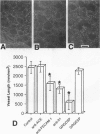
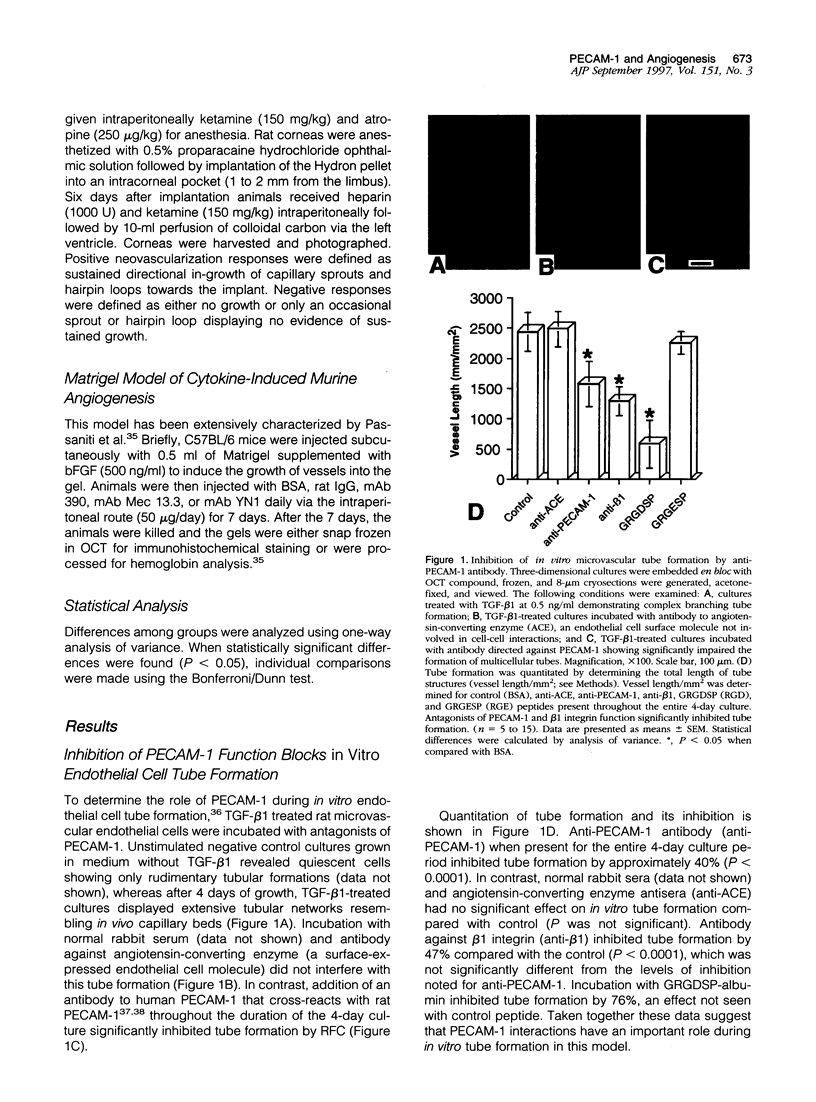
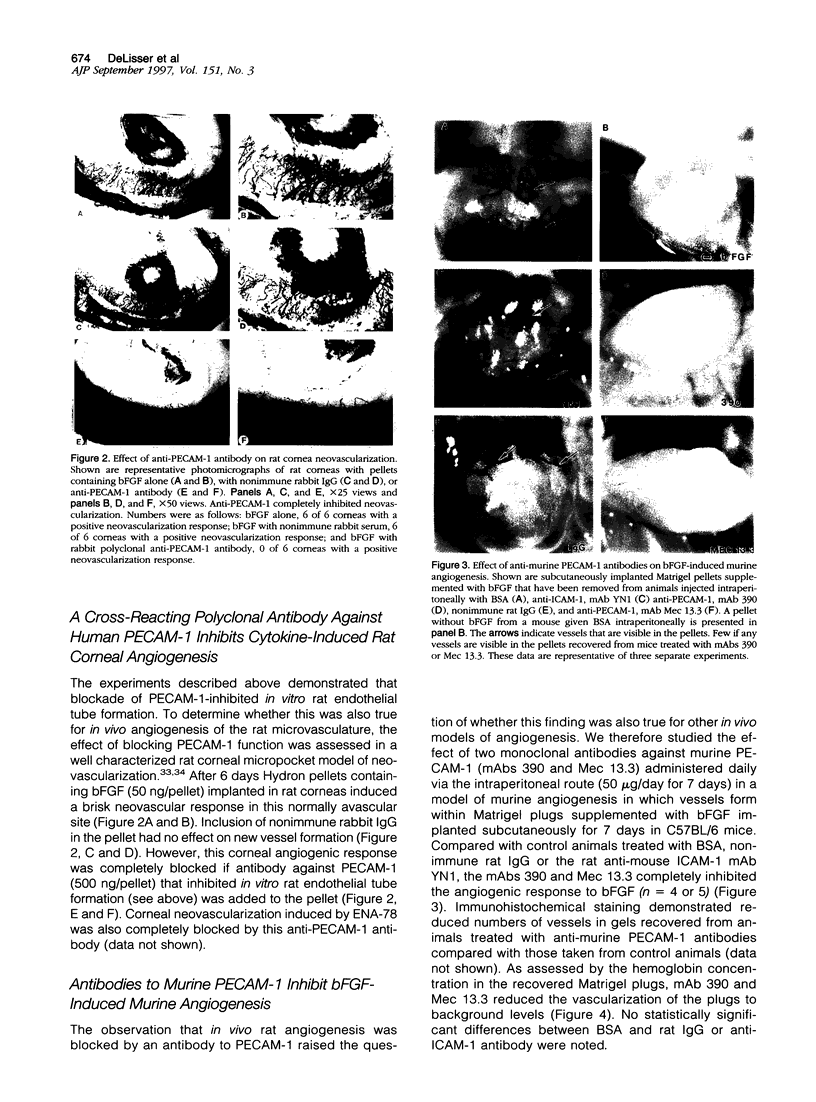
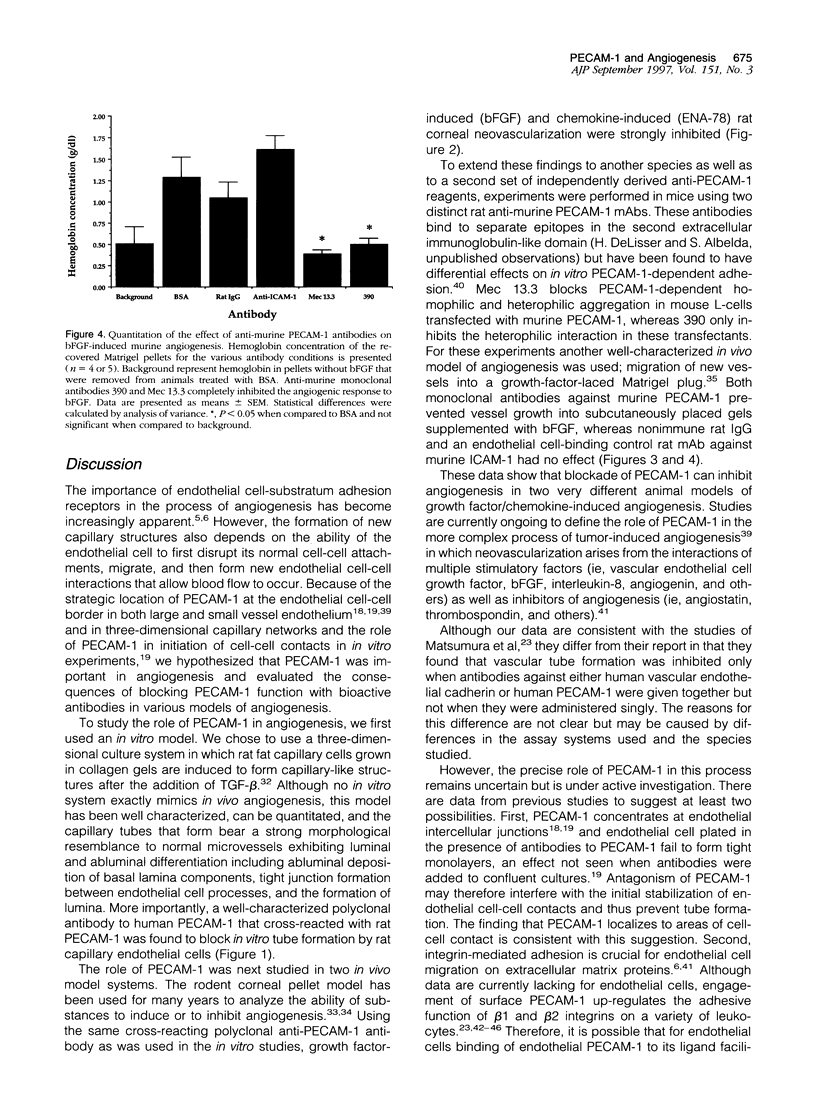
The adhesive interactions of endothelial cells with each other and the adhesion receptors that mediate these interactions are probably of fundamental importance to the process of angiogenesis. We therefore studied the effect of inhibiting the function of the endothelial cell-cell adhesion molecule, PECAM-1/ CD31, in rat and murine models of angiogenesis. A polyclonal antibody to human PECAM-1, which cross-reacts with rat PECAM-1, was found to block in vitro tube formation by rat capillary endothelial cells and cytokine-induced rat corneal neovascularization. In mice, two monoclonal antibodies against murine PECAM-1 prevented vessel growth into subcutaneously implanted gels supplemented with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). Taken together these findings provide evidence that PECAM-1 is involved in angiogenesis and suggest that the interactions of endothelial cell-cell adhesion molecules are important in the formation of new vessels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M., Buck C. A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2868–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M. Differential expression of integrin cell-substratum adhesion receptors on endothelium. EXS. 1992;61:188–192. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7001-6_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Muller W. A., Buck C. A., Newman P. J. Molecular and cellular properties of PECAM-1 (endoCAM/CD31): a novel vascular cell-cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):1059–1068. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Oliver P. D., Romer L. H., Buck C. A. EndoCAM: a novel endothelial cell-cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1227–1237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenberg D. A., Kunkel S. L., Polverini P. J., Glass M., Burdick M. D., Strieter R. M. Inhibition of interleukin-8 reduces tumorigenesis of human non-small cell lung cancer in SCID mice. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jun 15;97(12):2792–2802. doi: 10.1172/JCI118734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenberg D. A., Kunkel S. L., Polverini P. J., Morris S. B., Burdick M. D., Glass M. C., Taub D. T., Iannettoni M. D., Whyte R. I., Strieter R. M. Interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) is an angiostatic factor that inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumorigenesis and spontaneous metastases. J Exp Med. 1996 Sep 1;184(3):981–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold F., West D. C. Angiogenesis in wound healing. Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Dec;52(3):407–422. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90034-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayalon O., Sabanai H., Lampugnani M. G., Dejana E., Geiger B. Spatial and temporal relationships between cadherins and PECAM-1 in cell-cell junctions of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):247–258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin H. S., Shen H. M., Yan H. C., DeLisser H. M., Chung A., Mickanin C., Trask T., Kirschbaum N. E., Newman P. J., Albelda S. M. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31): alternatively spliced, functionally distinct isoforms expressed during mammalian cardiovascular development. Development. 1994 Sep;120(9):2539–2553. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.9.2539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson C. T., Knowles W. J., Bell L., Albelda S. M., Castronovo V., Liotta L. A., Madri J. A. Spatiotemporal segregation of endothelial cell integrin and nonintegrin extracellular matrix-binding proteins during adhesion events. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):789–801. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger R., Albelda S. M., Berd D., Ioffreda M., Whitaker D., Murphy G. F. Expression of platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) during melanoma-induced angiogenesis in vivo. J Cutan Pathol. 1993 Oct;20(5):399–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1993.tb00661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. E., Muller W. A. Ligation of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1/CD31) on monocytes and neutrophils increases binding capacity of leukocyte CR3 (CD11b/CD18). J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. E., Xie Y., Muller W. A. Roles of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1, CD31) in natural killer cell transendothelial migration and beta 2 integrin activation. J Immunol. 1996 Feb 15;156(4):1515–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. Cell adhesion and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1997 Feb 1;99(3):373–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI119168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogen S., Pak J., Garifallou M., Deng X., Muller W. A. Monoclonal antibody to murine PECAM-1 (CD31) blocks acute inflammation in vivo. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):1059–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breviario F., Caveda L., Corada M., Martin-Padura I., Navarro P., Golay J., Introna M., Gulino D., Lampugnani M. G., Dejana E. Functional properties of human vascular endothelial cadherin (7B4/cadherin-5), an endothelium-specific cadherin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):1229–1239. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.8.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Clark R. A., Cheresh D. A. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.7512751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Montgomery A. M., Rosenfeld M., Reisfeld R. A., Hu T., Klier G., Cheresh D. A. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1157–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley C. D., Doyonnas R., Newton J. P., Blystone S. D., Brown E. J., Watt S. M., Simmons D. L. Identification of alpha v beta 3 as a heterotypic ligand for CD31/PECAM-1. J Cell Sci. 1996 Feb;109(Pt 2):437–445. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.2.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns A. R., Takei F., Doerschuk C. M. Quantitation of ICAM-1 expression in mouse lung during pneumonia. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 1;153(7):3189–3198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisser H. M., Newman P. J., Albelda S. M. Molecular and functional aspects of PECAM-1/CD31. Immunol Today. 1994 Oct;15(10):490–495. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisser H. M., Yan H. C., Newman P. J., Muller W. A., Buck C. A., Albelda S. M. Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31)-mediated cellular aggregation involves cell surface glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):16037–16046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 28;333(26):1757–1763. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512283332608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M., Brooks P. C., Shaffer R. W., Kincaid C. M., Varner J. A., Cheresh D. A. Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1500–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes H. P., Brownlee M., Jonczyk A., Sutter A., Preissner K. T. Subcutaneous injection of a cyclic peptide antagonist of vitronectin receptor-type integrins inhibits retinal neovascularization. Nat Med. 1996 May;2(5):529–533. doi: 10.1038/nm0596-529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996 Aug 9;86(3):353–364. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram R. T., Bonde S. K., Riggs B. L., Fitzpatrick L. A. Effects of transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) and 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 on the function, cytochemistry and morphology of normal human osteoblast-like cells. Differentiation. 1994 Jan;55(2):153–163. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1994.5520153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampugnani M. G., Resnati M., Raiteri M., Pigott R., Pisacane A., Houen G., Ruco L. P., Dejana E. A novel endothelial-specific membrane protein is a marker of cell-cell contacts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1511–1522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastres P., Almendro N., Bellón T., López-Guerrero J. A., Eritja R., Bernabéu C. Functional regulation of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 by TGF-beta 1 in promonocytic U-937 cells. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 1;153(9):4206–4218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavesley D. I., Oliver J. M., Swart B. W., Berndt M. C., Haylock D. N., Simmons P. J. Signals from platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule enhance the adhesive activity of the very late antigen-4 integrin of human CD34+ hemopoietic progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4673–4683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Huynh H. K., Eiroa A., Greene T., Polizzi E., Muller W. A. Migration of monocytes across endothelium and passage through extracellular matrix involve separate molecular domains of PECAM-1. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1337–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscinskas F. W., Lawler J. Integrins as dynamic regulators of vascular function. FASEB J. 1994 Sep;8(12):929–938. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.12.7522194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Pratt B. M., Tucker A. M. Phenotypic modulation of endothelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta depends upon the composition and organization of the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1375–1384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Williams S. K. Capillary endothelial cell cultures: phenotypic modulation by matrix components. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):153–165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura T., Wolff K., Petzelbauer P. Endothelial cell tube formation depends on cadherin 5 and CD31 interactions with filamentous actin. J Immunol. 1997 Apr 1;158(7):3408–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick B. A., Zetter B. R. Adhesive interactions in angiogenesis and metastasis. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;53(2):239–260. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merwin J. R., Anderson J. M., Kocher O., Van Itallie C. M., Madri J. A. Transforming growth factor beta 1 modulates extracellular matrix organization and cell-cell junctional complex formation during in vitro angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jan;142(1):117–128. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merwin J. R., Madri J. A., Lynch M. Cancer cell binding to E-selectin transfected human endothelia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91560-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. A., Ratti C. M., McDonnell S. L., Cohn Z. A. A human endothelial cell-restricted, externally disposed plasmalemmal protein enriched in intercellular junctions. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murohara T., Delyani J. A., Albelda S. M., Lefer A. M. Blockade of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in cats. J Immunol. 1996 May 1;156(9):3550–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. J., Berndt M. C., Gorski J., White G. C., 2nd, Lyman S., Paddock C., Muller W. A. PECAM-1 (CD31) cloning and relation to adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1219–1222. doi: 10.1126/science.1690453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passaniti A., Taylor R. M., Pili R., Guo Y., Long P. V., Haney J. A., Pauly R. R., Grant D. S., Martin G. R. A simple, quantitative method for assessing angiogenesis and antiangiogenic agents using reconstituted basement membrane, heparin, and fibroblast growth factor. Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):519–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piali L., Albelda S. M., Baldwin H. S., Hammel P., Gisler R. H., Imhof B. A. Murine platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1)/CD31 modulates beta 2 integrins on lymphokine-activated killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Oct;23(10):2464–2471. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piali L., Hammel P., Uherek C., Bachmann F., Gisler R. H., Dunon D., Imhof B. A. CD31/PECAM-1 is a ligand for alpha v beta 3 integrin involved in adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;130(2):451–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J. Cellular adhesion molecules. Newly identified mediators of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1996 Apr;148(4):1023–1029. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E., Sunder-Plassmann R., Hansmann C., Koch C., Holter W., Knapp W., Stockinger H. Interaction of CD31 with a heterophilic counterreceptor involved in downregulation of human T cell responses. J Exp Med. 1996 Jul 1;184(1):41–50. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanic A. M., Madri J. A. The induction of 72-kD gelatinase in T cells upon adhesion to endothelial cells is VCAM-1 dependent. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1165–1178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romer L. H., McLean N. V., Yan H. C., Daise M., Sun J., DeLisser H. M. IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha induce redistribution of PECAM-1 (CD31) on human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 15;154(12):6582–6592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Williams J., Yan H. C., Amin K. M., Albelda S. M., DeLisser H. M. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) homophilic adhesion is mediated by immunoglobulin-like domains 1 and 2 and depends on the cytoplasmic domain and the level of surface expression. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 2;271(31):18561–18570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.31.18561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q. H., DeLisser H. M., Zukowski M. M., Paddock C., Albelda S. M., Newman P. J. Individually distinct Ig homology domains in PECAM-1 regulate homophilic binding and modulate receptor affinity. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 10;271(19):11090–11098. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.19.11090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Albelda S. M., Horgan K. J., van Seventer G. A., Shimizu Y., Newman W., Hallam J., Newman P. J., Buck C. A., Shaw S. CD31 expressed on distinctive T cell subsets is a preferential amplifier of beta 1 integrin-mediated adhesion. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):245–253. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torimoto Y., Rothstein D. M., Dang N. H., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD31, a novel cell surface marker for CD4 cells of suppressor lineage, unaltered by state of activation. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):388–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaporciyan A. A., DeLisser H. M., Yan H. C., Mendiguren I. I., Thom S. R., Jones M. L., Ward P. A., Albelda S. M. Involvement of platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in neutrophil recruitment in vivo. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1580–1582. doi: 10.1126/science.8248808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchi A., Garlanda C., Lampugnani M. G., Resnati M., Matteucci C., Stoppacciaro A., Schnurch H., Risau W., Ruco L., Mantovani A. Monoclonal antibodies specific for endothelial cells of mouse blood vessels. Their application in the identification of adult and embryonic endothelium. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;63(2):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin M. W., Sanz M. J., Dewar A., Albelda S. M., Larkin S. W., Boughton-Smith N., Williams T. J., Nourshargh S. An anti-platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 antibody inhibits leukocyte extravasation from mesenteric microvessels in vivo by blocking the passage through the basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1996 Jul 1;184(1):229–239. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt S. M., Williamson J., Genevier H., Fawcett J., Simmons D. L., Hatzfeld A., Nesbitt S. A., Coombe D. R. The heparin binding PECAM-1 adhesion molecule is expressed by CD34+ hematopoietic precursor cells with early myeloid and B-lymphoid cell phenotypes. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2649–2663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H. C., Baldwin H. S., Sun J., Buck C. A., Albelda S. M., DeLisser H. M. Alternative splicing of a specific cytoplasmic exon alters the binding characteristics of murine platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1). J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23672–23680. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder J. L., Shatsky M., Leung L. L., Butcher E. C., McGregor J. L., Levitt L. J. Involvement of CD31 in lymphocyte-mediated immune responses: importance of the membrane-proximal immunoglobulin domain and identification of an inhibiting CD31 peptide. Blood. 1995 Mar 1;85(5):1282–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]