Abstract
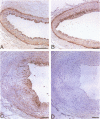
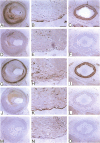
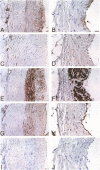
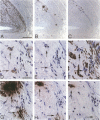
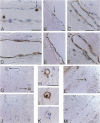
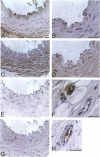
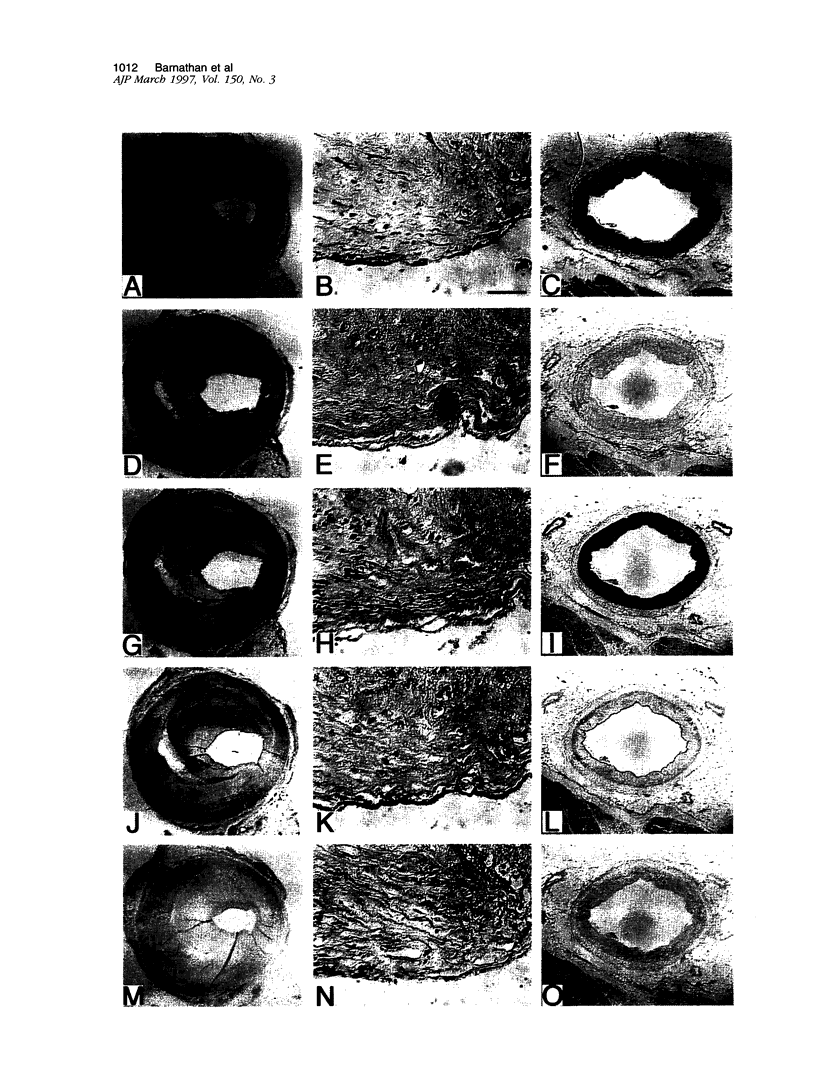
Neutrophil defensins comprise a family of cationic peptides that possess potent antimicrobial activity. Defensins are normally sequestered in cytoplasmic granules with their primary site of action in phagolysosomes, although some peptide is released into the circulation during the course of infection or inflammation. In view of the fact that neutrophils adhere to the endothelium and that defensins have been reported to bind to human endothelial cells in vitro, we used immunohistochemistry to study the distribution of these peptides in normal and in atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Defensin was found primarily in the intima of normal and atherosclerotic vessels, most prominently in association with intimal smooth muscle cells. Both large- and small-vessel endothelium stained focally for defensin. Defensin was also found in the media near the external elastic lamina and in some periadventitial vessels. The same distribution was seen in vessels that had been perfusion fixed immediately upon procurement, excluding diffusion of defensin from PMNs ex vivo. These data indicate that neutrophil defensin is present in the walls of human coronary arteries. The deposition of defensin in vessels may contribute to the pathophysiological consequences of inflammation in addition to their role in host defense.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensch K. W., Raida M., Mägert H. J., Schulz-Knappe P., Forssmann W. G. hBD-1: a novel beta-defensin from human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 17;368(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00687-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertov O., Michiel D. F., Xu L., Wang J. M., Tani K., Murphy W. J., Longo D. L., Taub D. D., Oppenheim J. J. Identification of defensin-1, defensin-2, and CAP37/azurocidin as T-cell chemoattractant proteins released from interleukin-8-stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 9;271(6):2935–2940. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.6.2935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond G., Zasloff M., Eck H., Brasseur M., Maloy W. L., Bevins C. L. Tracheal antimicrobial peptide, a cysteine-rich peptide from mammalian tracheal mucosa: peptide isolation and cloning of a cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin M. Y., Jacobi A. B., Büttner D. W., Schönberger O., Marti T., Erttmann K. D. Human autoantibody to defensin: disease association with hyperreactive onchocerciasis (sowda). J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):41–47. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T. Extracellular release of antimicrobial defensins by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):568–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.568-571.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Liu L., Valore E. V., Oren A. Posttranslational processing and targeting of transgenic human defensin in murine granulocyte, macrophage, fibroblast, and pituitary adenoma cell lines. Blood. 1993 Jul 15;82(2):641–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger D. J., Kemp P. R., Liu A. C., Lawn R. M., Metcalfe J. C. Activation of transforming growth factor-beta is inhibited in transgenic apolipoprotein(a) mice. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):460–462. doi: 10.1038/370460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger D. J., Kemp P. R., Metcalfe J. C., Liu A. C., Lawn R. M., Williams N. R., Grace A. A., Schofield P. M., Chauhan A. The serum concentration of active transforming growth factor-beta is severely depressed in advanced atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):74–79. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Neutrophil defensins: purification, characterization, and antimicrobial testing. Methods Enzymol. 1994;236:160–172. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)36015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higazi A. A., Barghouti I. I., Abu-Much R. Identification of an inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator-mediated fibrinolysis in human neutrophils. A role for defensin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9472–9477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higazi A. A., Ganz T., Kariko K., Cines D. B. Defensin modulates tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen binding to fibrin and endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 26;271(30):17650–17655. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.30.17650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J., Jothy S., Solomon S. Localization and measurement of corticostatin-I in nonpregnant and pregnant rabbit tissues during late gestation. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2351–2359. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Bevins C. L. Defensin-6 mRNA in human Paneth cells: implications for antimicrobial peptides in host defense of the human bowel. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 4;315(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Defensins: a family of antimicrobial and cytotoxic peptides. Toxicology. 1994 Feb 28;87(1-3):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(94)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Shor A., Campbell L. A., Fukushi H., Patton D. L., Grayston J. T. Demonstration of Chlamydia pneumoniae in atherosclerotic lesions of coronary arteries. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):841–849. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenfant C. NHLBI funding policies. Enhancing stability, predictability, and cost control. Circulation. 1994 Jul;90(1):1–1. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy O. Antibiotic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Eur J Haematol. 1996 May;56(5):263–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1996.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallow E. B., Harris A., Salzman N., Russell J. P., DeBerardinis R. J., Ruchelli E., Bevins C. L. Human enteric defensins. Gene structure and developmental expression. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 23;271(8):4038–4045. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.8.4038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. J., Foster B. A., Mannis M. J., Selsted M. E., Reid T. W. Defensins are mitogenic for epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1993 May;155(2):408–413. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041550223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard S. D., Ganz T., Peterson M. W. Defensins reduce the barrier integrity of a cultured epithelial monolayer without cytotoxicity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Feb;8(2):193–200. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S. S., Grobmyer S. R., Barnathan E. S. Contrasting effects of plasminogen activators, urokinase receptor, and LDL receptor-related protein on smooth muscle cell migration and invasion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):1269–1276. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.16.10.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Miller S. I., Henschen A. H., Selsted M. E. Purification and primary structure of murine cryptdin-1, a Paneth cell defensin. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80606-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutich A. V., Panyutich E. A., Krapivin V. A., Baturevich E. A., Ganz T. Plasma defensin concentrations are elevated in patients with septicemia or bacterial meningitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1993 Aug;122(2):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutich A. V., Voitenok N. N., Lehrer R. I., Ganz T. An enzyme immunoassay for human defensins. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Aug 9;141(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath P. N., Tomaszewski J. E., Brady S. T., Caron R. J., Okada S. S., Barnathan E. S. Plasminogen activator system in human coronary atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):1432–1443. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.9.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonwetter B. S., Stolzenberg E. D., Zasloff M. A. Epithelial antibiotics induced at sites of inflammation. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1645–1648. doi: 10.1126/science.7886453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson S., Lawrence D. A. The serpin PAI-1 inhibits cell migration by blocking integrin alpha V beta 3 binding to vitronectin. Nature. 1996 Oct 3;383(6599):441–443. doi: 10.1038/383441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Territo M. C., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. Monocyte-chemotactic activity of defensins from human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2017–2020. doi: 10.1172/JCI114394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y., Lukashev M., Simon D. I., Bodary S. C., Rosenberg S., Doyle M. V., Chapman H. A. Regulation of integrin function by the urokinase receptor. Science. 1996 Sep 13;273(5281):1551–1555. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5281.1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., Wimley W. C., Selsted M. E. Structure, function, and membrane integration of defensins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995 Aug;5(4):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(95)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Saito K. Purification, primary structure, and biological activity of guinea pig neutrophil cationic peptides. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2405–2409. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2405-2409.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yomogida S., Nagaoka I., Saito K., Yamashita T. Evaluation of the effects of defensins on neutrophil functions. Inflamm Res. 1996 Feb;45(2):62–67. doi: 10.1007/BF02265117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount N. Y., Wang M. S., Yuan J., Banaiee N., Ouellette A. J., Selsted M. E. Rat neutrophil defensins. Precursor structures and expression during neutrophilic myelopoiesis. J Immunol. 1995 Nov 1;155(9):4476–4484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]