Abstract
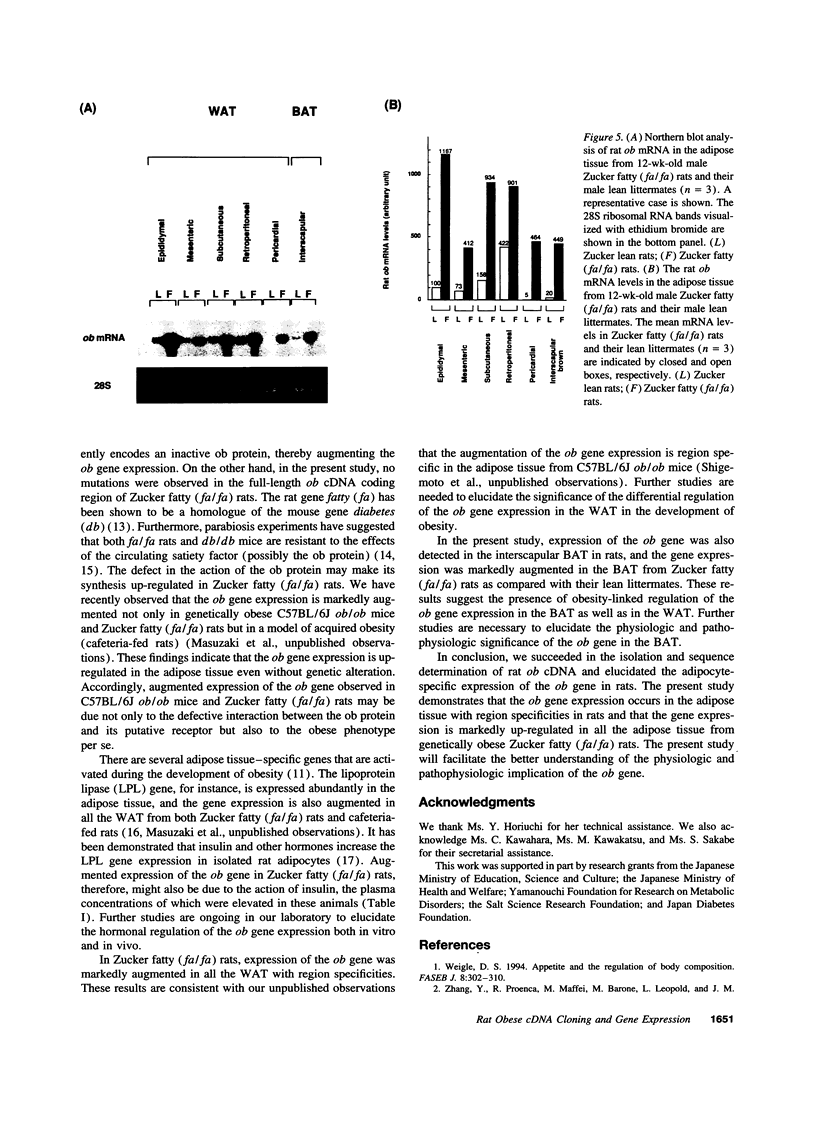
The obese (ob) gene has recently been isolated through a positional cloning approach, the mutation of which causes a marked hereditary obesity and diabetes mellitus in mice. In the present study, we isolated rat ob cDNA and examined the tissue distribution of the ob gene expression in rats. We also studied the gene expression in genetically obese Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rats. The rat ob gene product, a 167 amino acid protein with a putative signal sequence, was 96 and 83% homologous to the mouse and human ob proteins, respectively. Northern blot analysis using the rat ob cDNA probe identified a single mRNA species of 4.5 kb in size in the adipose tissue, while no significant amount of ob mRNA was present in other tissues in rats. The ob gene was expressed in the adipose tissue with region specificities. The rank order of the ob mRNA level in the adipose tissue was epididymal, retroperitoneal, and pericardial white adipose tissue > mesenteric and subcutaneous white adipose tissue > or = interscapular brown adipose tissue. The ob gene expression occurred in mature adipocytes rather than in stromalvascular cells isolated from the rat adipose tissue. Expression of the ob gene was markedly augmented in all the adipose tissue examined in Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rats at the stage of established obesity. The present study leads to the better understanding of the physiologic and pathophysiologic roles of the ob gene.
Full text
PDF

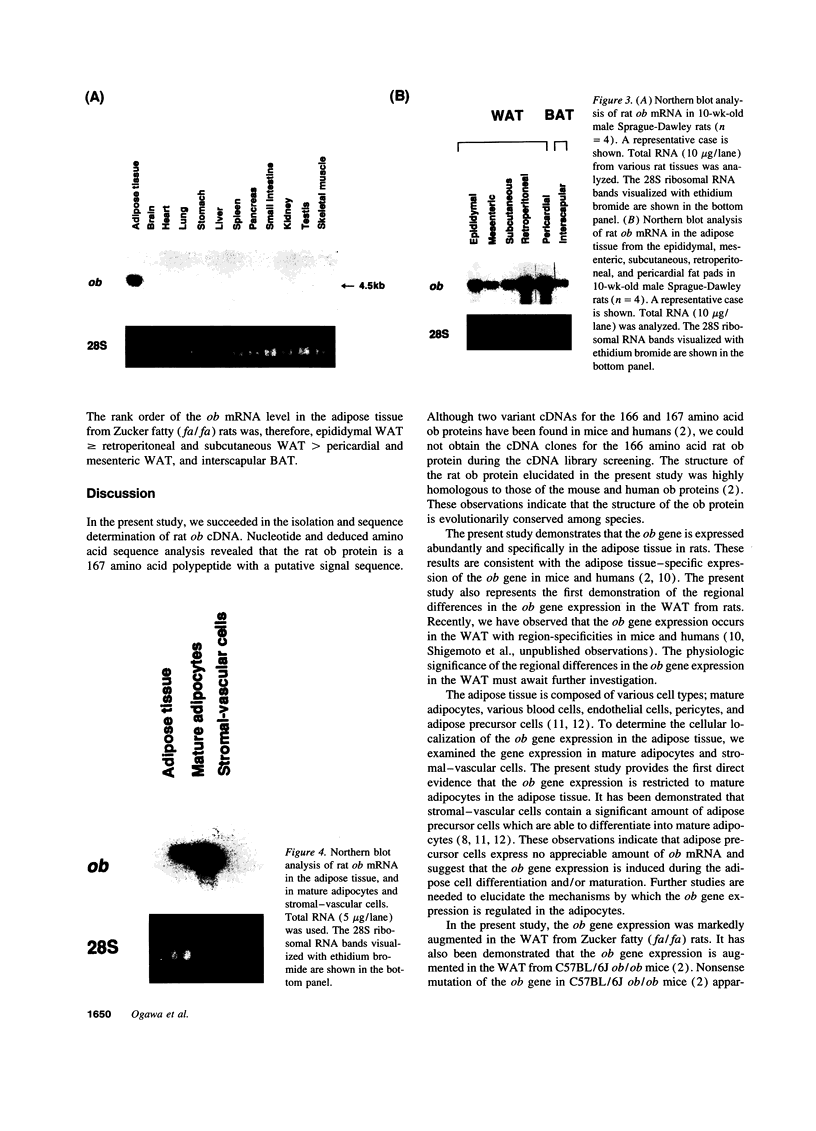

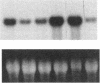
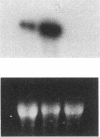
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ailhaud G., Grimaldi P., Négrel R. Cellular and molecular aspects of adipose tissue development. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992;12:207–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.12.070192.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Effects of parabiosis of obese with diabetes and normal mice. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01221857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deslex S., Negrel R., Ailhaud G. Development of a chemically defined serum-free medium for differentiation of rat adipose precursor cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jan;168(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. B., Hervey E., Hervey G. R., Tobin G. Body composition of lean and obese Zucker rats in parabiosis. Int J Obes. 1987;11(3):275–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauner H., Entenmann G., Wabitsch M., Gaillard D., Ailhaud G., Negrel R., Pfeiffer E. F. Promoting effect of glucocorticoids on the differentiation of human adipocyte precursor cells cultured in a chemically defined medium. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1172/JCI114345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Greenwood M. R., Horwitz B. A., Stern J. S. Animal models of obesity: genetic aspects. Annu Rev Nutr. 1991;11:325–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.11.070191.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzaki H., Ogawa Y., Isse N., Satoh N., Okazaki T., Shigemoto M., Mori K., Tamura N., Hosoda K., Yoshimasa Y. Human obese gene expression. Adipocyte-specific expression and regional differences in the adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1995 Jul;44(7):855–858. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.7.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Itoh H., Tamura N., Suga S., Yoshimasa T., Uehira M., Matsuda S., Shiono S., Nishimoto H., Nakao K. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and gene that encode mouse brain natriuretic peptide and generation of transgenic mice that overexpress the brain natriuretic peptide gene. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):1911–1921. doi: 10.1172/JCI117182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong J. M., Kirchgessner T. G., Schotz M. C., Kern P. A. Insulin increases the synthetic rate and messenger RNA level of lipoprotein lipase in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12933–12938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura I., Tokunaga K., Jiao S., Funahashi T., Keno Y., Kobatake T., Kotani K., Suzuki H., Yamamoto T., Tarui S. Marked enhancement of acyl-CoA synthetase activity and mRNA, paralleled to lipoprotein lipase mRNA, in adipose tissues of Zucker obese rats (fa/fa). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 4;1124(2):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90086-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Ogawa Y., Itoh H., Arai H., Suga S., Nakagawa O., Komatsu Y., Kishimoto I., Takaya K., Yoshimasa T. Molecular cloning of hamster brain and atrial natriuretic peptide cDNAs. Cardiomyopathic hamsters are useful models for brain and atrial natriuretic peptides. J Clin Invest. 1994 Sep;94(3):1059–1068. doi: 10.1172/JCI117420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett G. E., Bahary N., Friedman J. M., Leibel R. L. Rat obesity gene fatty (fa) maps to chromosome 5: evidence for homology with the mouse gene diabetes (db). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7806–7809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle D. S. Appetite and the regulation of body composition. FASEB J. 1994 Mar 1;8(3):302–310. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.3.8143936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J. M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):425–432. doi: 10.1038/372425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]