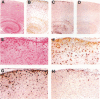
Abstract
Increased expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a hallmark of gliosis, the astrocytic hypertrophy that occurs during a wide variety of diseases of the central nervous system. To determine whether this increase in GFAP expression per se alters astrocyte function, we generated transgenic mice that carry copies of the human GFAP gene driven by its own promoter. Astrocytes of these mice are hypertrophic, up-regulate small heat-shock proteins, and contain inclusion bodies identical histologically and antigenically to the Rosenthal fibers of Alexander's disease. Mice in the highest expressing lines die by the second postnatal week. The results support the notion that Alexander's disease is a disorder of astrocytes, and provide an animal model for studying the causes and consequences of inclusion body disease.
Full text
PDF

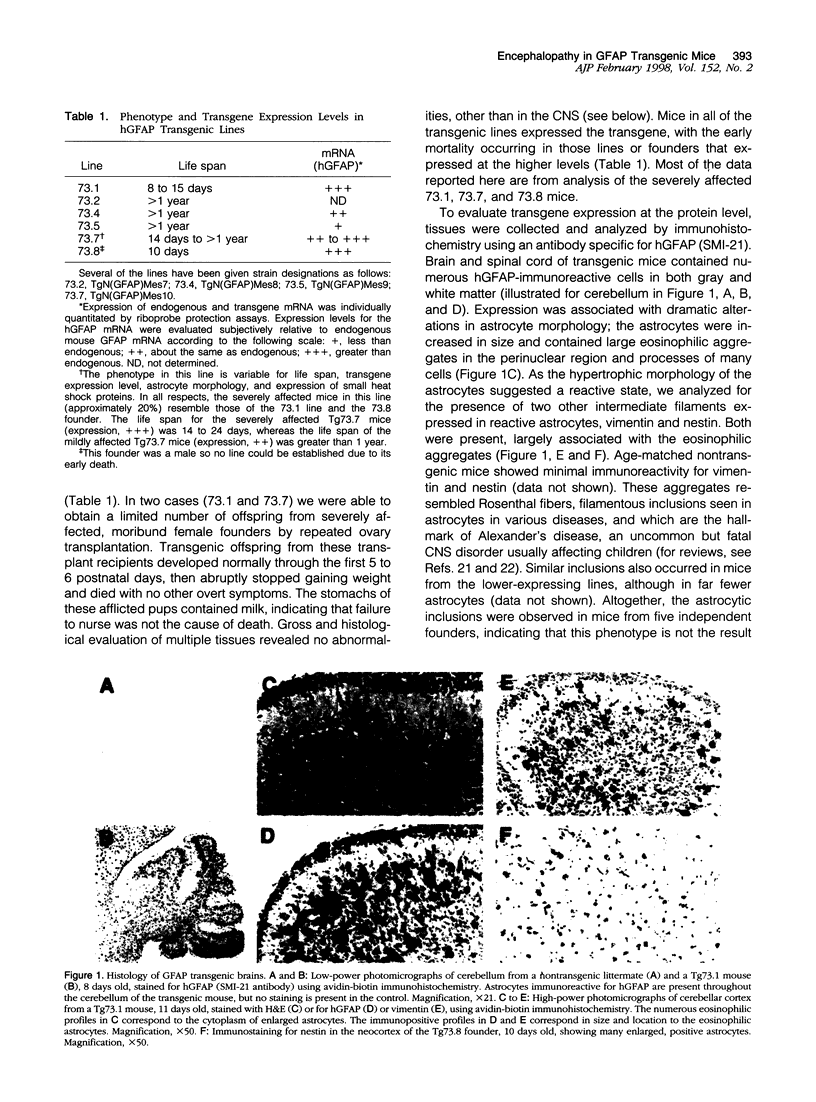
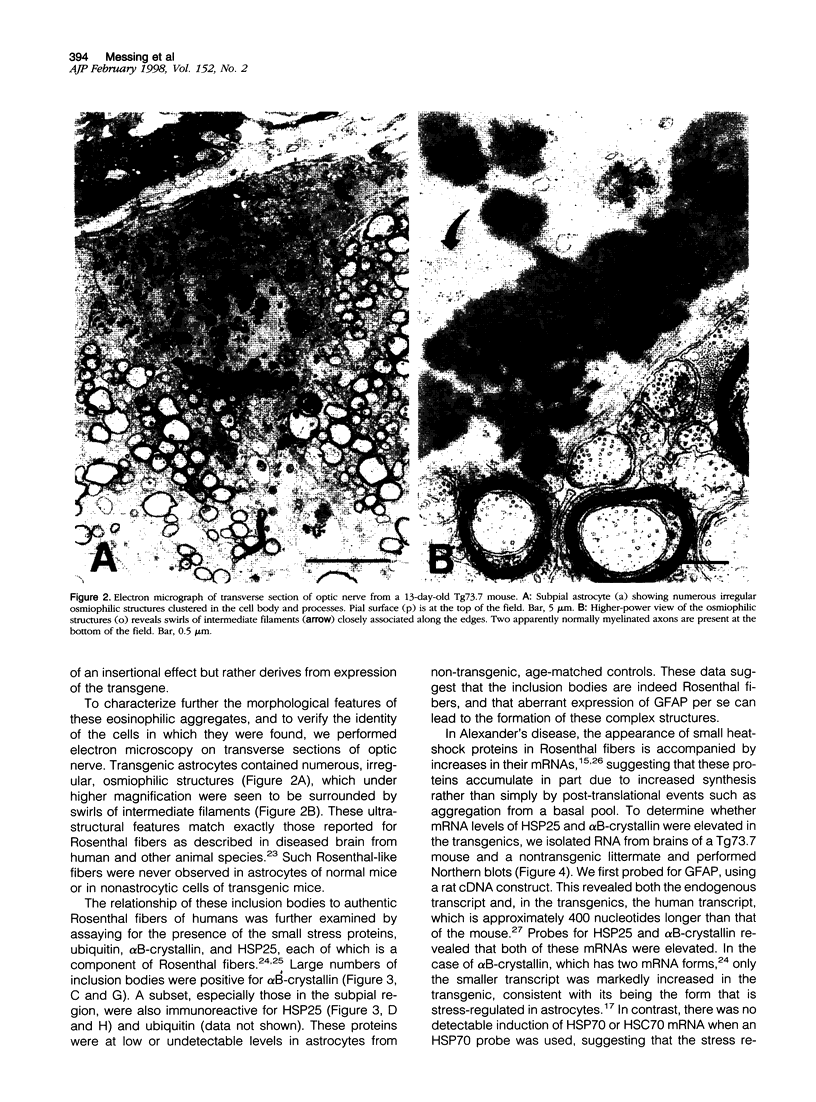
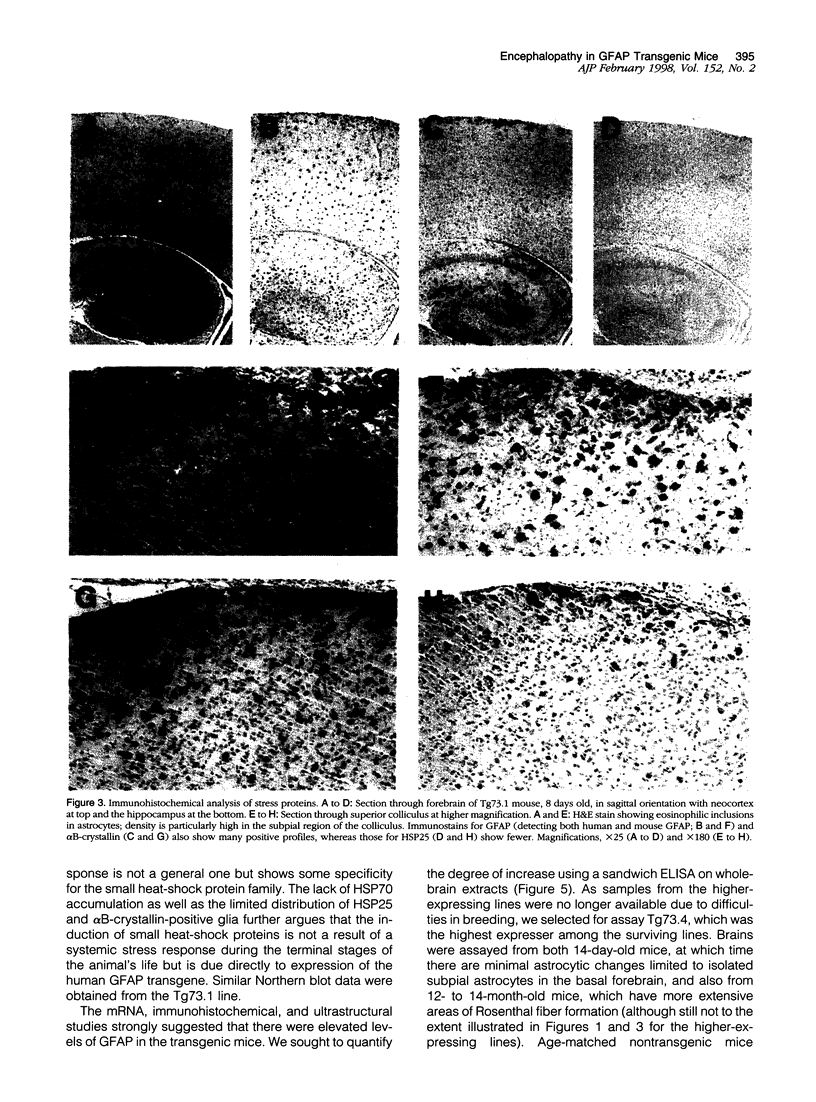


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner M., Kisseberth W. C., Su Y., Besnard F., Messing A. GFAP promoter directs astrocyte-specific expression in transgenic mice. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 1):1030–1037. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01030.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Lampel K., Nakatani Y., Mill J., Banner C., Mearow K., Dohadwala M., Lipsky R., Freese E. Characterization of human cDNA and genomic clones for glial fibrillary acidic protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 May;7(4):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90078-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. Structure and transcriptional regulation of the GFAP gene. Brain Pathol. 1994 Jul;4(3):245–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1994.tb00840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M, Messing A. GFAP Transgenic Mice. Methods. 1996 Dec;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1006/meth.1996.0113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Liem R. K. Reexpression of glial fibrillary acidic protein rescues the ability of astrocytoma cells to form processes in response to neurons. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):813–823. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Goldman J. E. Synthesis and turnover of cytoskeletal proteins in cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):166–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston M., Mucke L. Molecular profile of reactive astrocytes--implications for their role in neurologic disease. Neuroscience. 1993 May;54(1):15–36. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90380-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng L. F., Ghirnikar R. S. GFAP and astrogliosis. Brain Pathol. 1994 Jul;4(3):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1994.tb00838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidzianska A., Goebel H. H., Osborn M., Lenard H. G., Osse G., Langenbeck U. Mallory body-like inclusions in a hereditary congenital neuromuscular disease. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Mar-Apr;6(3):195–200. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Corbin E. Rosenthal fibers contain ubiquitinated alpha B-crystallin. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):933–938. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi H., Yokoyama T., Fujimoto K., Ikeda T., Katoh A., Itoh T., Itohara S. Mice devoid of the glial fibrillary acidic protein develop normally and are susceptible to scrapie prions. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan R., Denk H., Franke W. W., Lackinger E., Schiller D. L. Change of cytokeratin organization during development of Mallory bodies as revealed by a monoclonal antibody. Lab Invest. 1986 May;54(5):543–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head M. W., Corbin E., Goldman J. E. Overexpression and abnormal modification of the stress proteins alpha B-crystallin and HSP27 in Alexander disease. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1743–1753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head M. W., Hurwitz L., Goldman J. E. Transcription regulation of alpha B-crystallin in astrocytes: analysis of HSF and AP1 activation by different types of physiological stress. J Cell Sci. 1996 May;109(Pt 5):1029–1039. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.5.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki T., Iwaki A., Tateishi J., Sakaki Y., Goldman J. E. Alpha B-crystallin and 27-kd heat shock protein are regulated by stress conditions in the central nervous system and accumulate in Rosenthal fibers. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):487–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki T., Kume-Iwaki A., Liem R. K., Goldman J. E. Alpha B-crystallin is expressed in non-lenticular tissues and accumulates in Alexander's disease brain. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liedtke W., Edelmann W., Bieri P. L., Chiu F. C., Cowan N. J., Kucherlapati R., Raine C. S. GFAP is necessary for the integrity of CNS white matter architecture and long-term maintenance of myelination. Neuron. 1996 Oct;17(4):607–615. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Blanchard A., Morrell K., Lennox G., Reynolds L., Billett M., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament inclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as Rosenthal fibres in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol. 1988 May;155(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M. A., Gregg R. G., Behringer R. R., Brenner M., Delaney C. L., Galbreath E. J., Zhang C. L., Pearce R. A., Chiu S. Y., Messing A. Targeted deletion in astrocyte intermediate filament (Gfap) alters neuronal physiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6361–6366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan J. P. Quantification of glial fibrillary acidic protein: comparison of slot-immunobinding assays with a novel sandwich ELISA. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1991 May-Jun;13(3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(91)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi N., Kobayashi K., Maehara M., Nakayama A., Negoro T., Shinohara H., Watanabe K., Nagatsu T., Kato K. Increment of alpha B-crystallin mRNA in the brain of patient with infantile type Alexander's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):1030–1035. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91922-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekny M., Levéen P., Pekna M., Eliasson C., Berthold C. H., Westermark B., Betsholtz C. Mice lacking glial fibrillary acidic protein display astrocytes devoid of intermediate filaments but develop and reproduce normally. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1590–1598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07147.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure S. J., Lee V. M., Nelson D. L. Site-specific phosphorylation of the middle molecular weight human neurofilament protein in transfected non-neuronal cells. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2428–2437. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02428.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollanen M. S., Dickson D. W., Bergeron C. Pathology and biology of the Lewy body. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 May;52(3):183–191. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199305000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutka J. T., Smith S. L. Transfection of human astrocytoma cells with glial fibrillary acidic protein complementary DNA: analysis of expression, proliferation, and tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 1;53(15):3624–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuki K., Gomi H., Chen L., Bao S., Kim J. J., Wakatsuki H., Fujisaki T., Fujimoto K., Katoh A., Ikeda T. Deficient cerebellar long-term depression, impaired eyeblink conditioning, and normal motor coordination in GFAP mutant mice. Neuron. 1996 Mar;16(3):587–599. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. E., Shelanski M. L., Liem R. K. Suppression by antisense mRNA demonstrates a requirement for the glial fibrillary acidic protein in the formation of stable astrocytic processes in response to neurons. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1205–1213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]