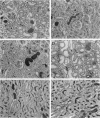
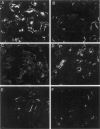
Abstract
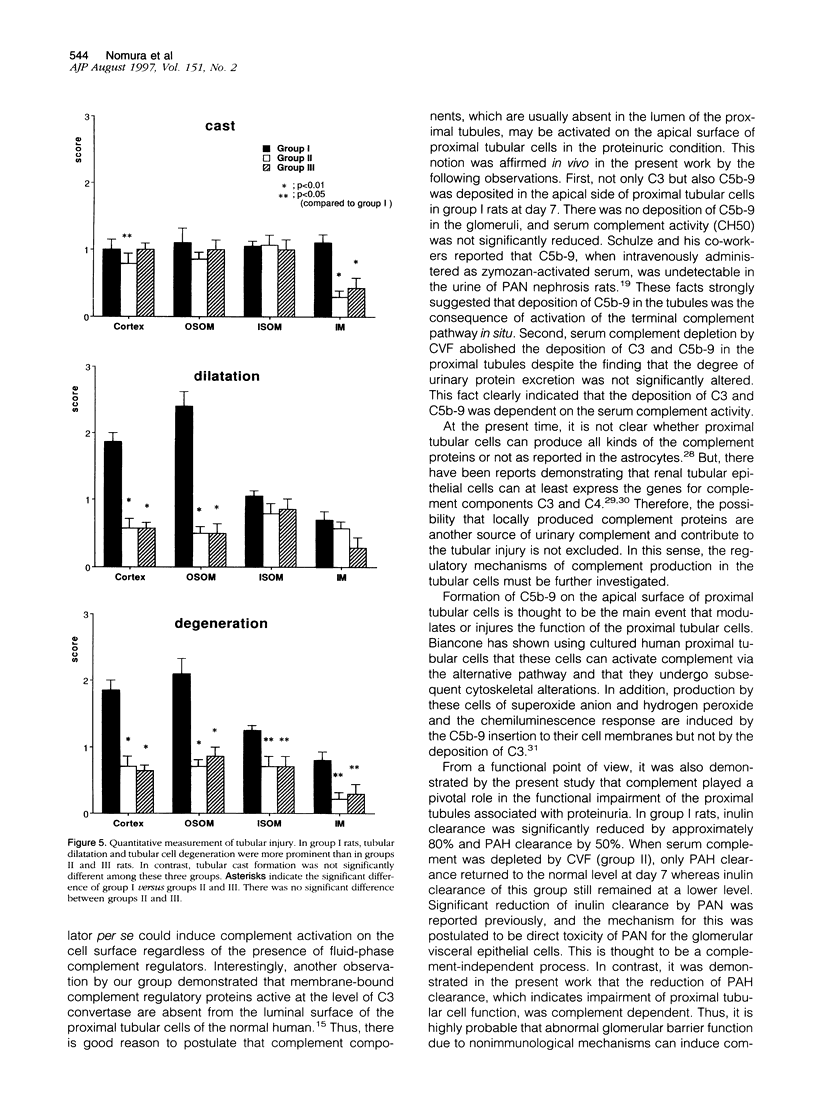
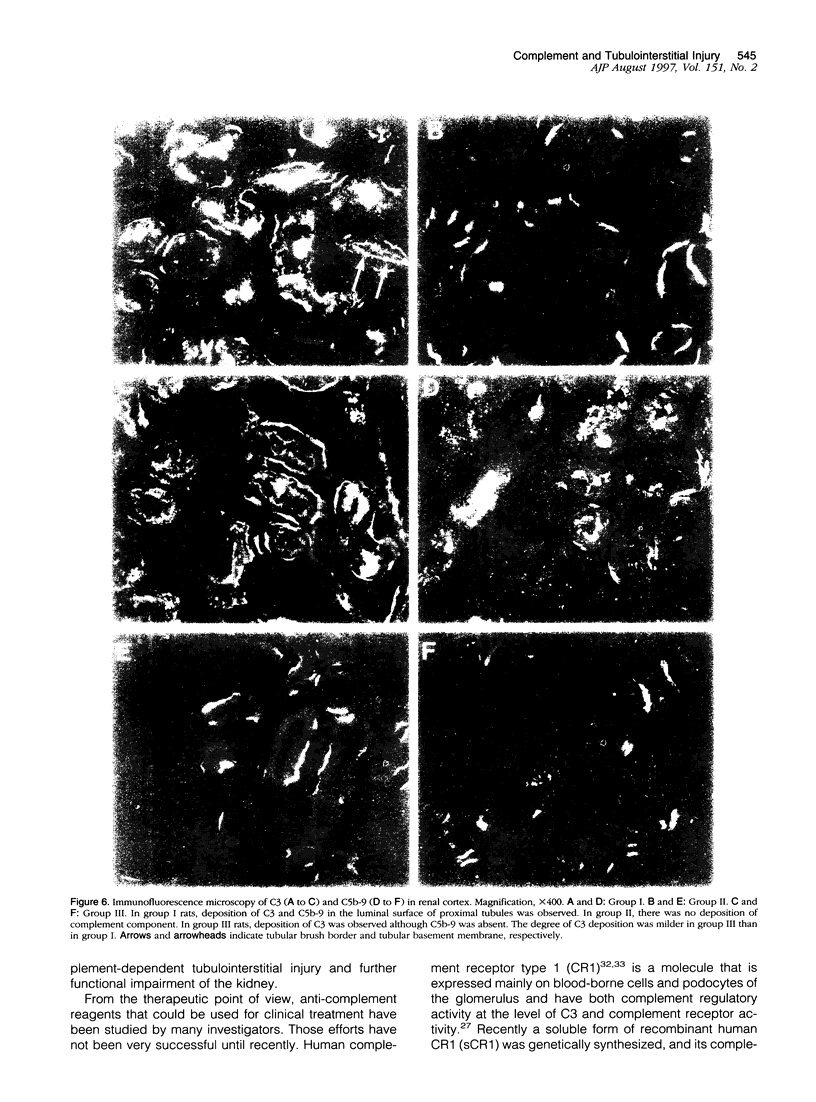
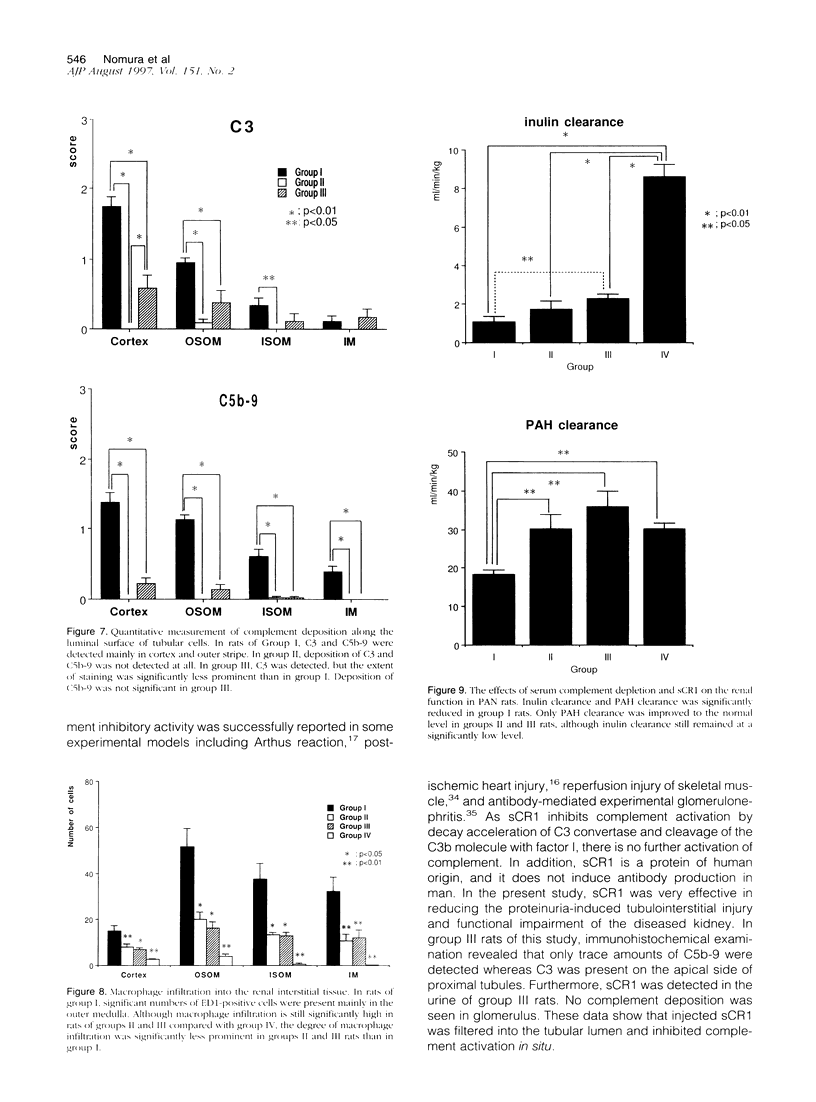
The present work was designed to elucidate the in vivo role of complement in the proteinuria-associated tubulointerstitial injury. Rats were intravenously injected with puromycin aminonucleoside, and massive proteinuria was observed within 5 days. Prominent tubulointerstitial injury characterized by proximal tubular degeneration, tubular dilatation, and leukocyte infiltration were observed 7 days after injection. C3 and C5b-9 were observed in the luminal side of proximal tubular cells. Renal function, assessed by inulin and para-aminohippurate clearance, was significantly decreased. To-assess the role of complement in this model, rats were injected with either cobra venom factor or soluble recombinant human complement receptor type 1 starting at day 3. These manipulations significantly improved tubulointerstitial pathology and para-aminohippurate clearance without affecting the degree of proteinuria. Deposition of C3 and C5b-9 was not detected in the kidney of rats depleted of complement by cobra venom factor. In rats treated with soluble complement receptor, C3 was still detected in the tubules, but deposition of C5b-9 was not observed. Soluble complement receptor was detected at the site of C3 deposition and in the urine. These data strongly suggest that complement plays a pivotal role in proteinuria-associated tubulointerstitial injury and that systemic complement depletion or inhibition of complement in the tubular lumen may diminish the tubulointerstitial damage.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfrey A. C., Froment D. H., Hammond W. S. Role of iron in the tubulo-interstitial injury in nephrotoxic serum nephritis. Kidney Int. 1989 Nov;36(5):753–759. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biancone L., David S., Della Pietra V., Montrucchio G., Cambi V., Camussi G. Alternative pathway activation of complement by cultured human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1994 Feb;45(2):451–460. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Rotunno M., Segoloni G., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. A. In vitro alternative pathway activation of complement by the brush border of proximal tubules of normal rat kidney. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1659–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Johnson R. J., Young B. A., Yeh C. G., Toth C. A., Rudolph A. R. The effects of soluble recombinant complement receptor 1 on complement-mediated experimental glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 May;5(11):1888–1894. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V5111888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A. Interstitial nephritis induced by protein-overload proteinuria. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):719–733. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., Michael A. F. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1988 Jan;33(1):14–23. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., Warren J. S. Expression and function of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Feb;78(2):140–151. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris K. P., Lefkowith J. B., Klahr S., Schreiner G. F. Essential fatty acid deficiency ameliorates acute renal dysfunction in the rat after the administration of the aminonucleoside of puromycin. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1115–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI114816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg R. Bioactivity of glomerular ultrafiltrate during heavy proteinuria may contribute to renal tubulo-interstitial lesions: evidence for a role for insulin-like growth factor I. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jul 1;98(1):116–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI118755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K., Gordon D. L. Biochemistry of C3 and related thiolester proteins in infection and inflammation. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):97–109. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourcade D., Holers V. M., Atkinson J. P. The regulators of complement activation (RCA) gene cluster. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:381–416. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60697-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichida S., Yuzawa Y., Okada H., Yoshioka K., Matsuo S. Localization of the complement regulatory proteins in the normal human kidney. Kidney Int. 1994 Jul;46(1):89–96. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Nussenzweig V. Complement receptor is an inhibitor of the complement cascade. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1138–1150. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kees-Folts D., Sadow J. L., Schreiner G. F. Tubular catabolism of albumin is associated with the release of an inflammatory lipid. Kidney Int. 1994 Jun;45(6):1697–1709. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T. Biology of complement: the overture. Immunol Today. 1991 Sep;12(9):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90001-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo S., Ichida S., Takizawa H., Okada N., Baranyi L., Iguchi A., Morgan B. P., Okada H. In vivo effects of monoclonal antibodies that functionally inhibit complement regulatory proteins in rats. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1619–1627. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Gasque P. Expression of complement in the brain: role in health and disease. Immunol Today. 1996 Oct;17(10):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)20028-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K. A. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992 Jul;20(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Nishikawa K., Yuzawa Y., Okada H., Okada N., Morgan B. P., Piddlesden S. J., Nadai M., Hasegawa T., Matsuo S. Tubulointerstitial injury induced in rats by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits function of a membrane inhibitor of complement. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2348–2356. doi: 10.1172/JCI118291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong A. C., Jowett T. P., Moorhead J. F., Owen J. S. Human high density lipoproteins stimulate endothelin-1 release by cultured human renal proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int. 1994 Nov;46(5):1315–1321. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki I., Ito Y., Fukatsu A., Suzuki N., Yoshida F., Watanabe Y., Sakamoto N., Matsuo S. A plasma membrane antigen of rat glomerular epithelial cells. Antigenic determinants involving N-linked sugar residues in a 140-kilodalton sialoglycoprotein of the podocytes. Lab Invest. 1990 Nov;63(5):707–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton M., Anderson G., Vetvicka V., Justus D. E., Ross G. D. Microvascular effects of complement blockade with soluble recombinant CR1 on ischemia/reperfusion injury of skeletal muscle. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):5104–5113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichler R., Giachelli C. M., Lombardi D., Pippin J., Gordon K., Alpers C. E., Schwartz S. M., Johnson R. J. Tubulointerstitial disease in glomerulonephritis. Potential role of osteopontin (uropontin). Am J Pathol. 1994 May;144(5):915–926. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Michael A. F. Retardation of fading and enhancement of intensity of immunofluorescence by p-phenylenediamine. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jun;31(6):840–842. doi: 10.1177/31.6.6341464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Freestone S., McAuslane J. A. The concentration-dependent disposition of intravenous p-aminohippurate in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;35(1):20–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. W., Herrera G. A., Chen A., Booker B. B., Galla J. H. Differential nephrotoxicity of low molecular weight proteins including Bence Jones proteins in the perfused rat nephron in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2086–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI113830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schainuck L. I., Striker G. E., Cutler R. E., Benditt E. P. Structural-functional correlations in renal disease. II. The correlations. Hum Pathol. 1970 Dec;1(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze M., Baker P. J., Perkinson D. T., Johnson R. J., Ochi R. F., Stahl R. A., Couser W. G. Increased urinary excretion of C5b-9 distinguishes passive Heymann nephritis in the rat. Kidney Int. 1989 Jan;35(1):60–68. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Kamei S., Ohkubo A., Yamanaka M., Ohsawa S., Makino K., Tokuda K. Urinary protein as measured with a pyrogallol red-molybdate complex, manually and in a Hitachi 726 automated analyzer. Clin Chem. 1986 Aug;32(8):1551–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman H. F., Bartow T., Leppo M. K., Marsh H. C., Jr, Carson G. R., Concino M. F., Boyle M. P., Roux K. H., Weisfeldt M. L., Fearon D. T. Soluble human complement receptor type 1: in vivo inhibitor of complement suppressing post-ischemic myocardial inflammation and necrosis. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):146–151. doi: 10.1126/science.2371562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. R., Beischel L. S., Witte D. P. Differential expression of complement C3 and C4 in the human kidney. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1451–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI116722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. S., Fass G., Bone J. M. Renal pathology and proteinuria determine progression in untreated mild/moderate chronic renal failure. Q J Med. 1988 Apr;67(252):343–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte D. P., Welch T. R., Beischel L. S. Detection and cellular localization of human C4 gene expression in the renal tubular epithelial cells and other extrahepatic epithelial sources. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):717–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh C. G., Marsh H. C., Jr, Carson G. R., Berman L., Concino M. F., Scesney S. M., Kuestner R. E., Skibbens R., Donahue K. A., Ip S. H. Recombinant soluble human complement receptor type 1 inhibits inflammation in the reversed passive arthus reaction in rats. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]