Abstract
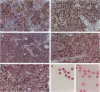
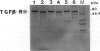
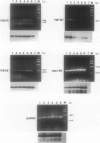
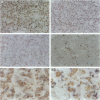
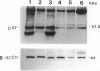
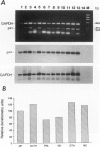
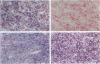
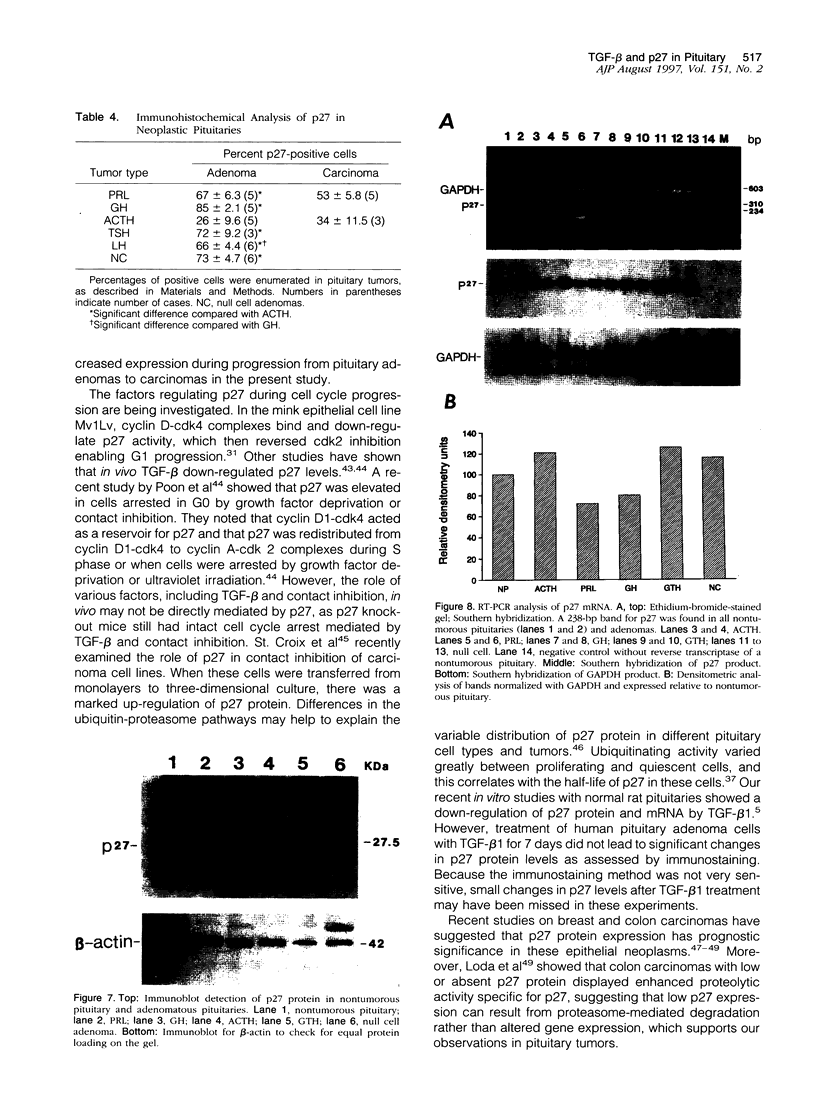
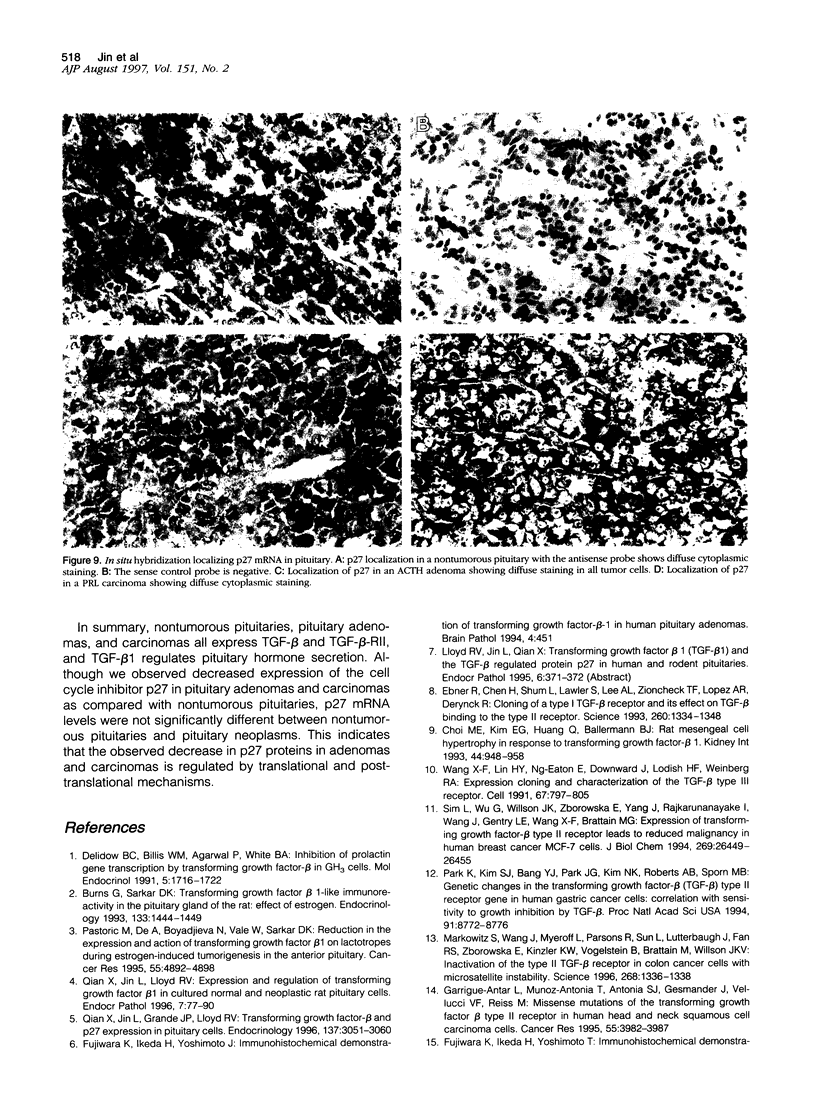
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta has been implicated in the regulation of normal and neoplastic anterior pituitary cell function. TGF-beta regulates the expression of various proteins, including p27Kip1 (p27), a cell cycle inhibitory protein. We examined TGF-beta, TGF-beta type II receptor (TGF-beta-RII), and p27 expression in normal pituitaries, pituitary adenomas, and carcinomas to analyze the possible roles of these proteins in pituitary tumorigenesis. Normal pituitary, pituitary adenomas, and pituitary carcinomas all expressed TGF-beta and TGF-beta-RII immunoreactivity. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis showed TGF-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 isoforms and TGF-beta-RII in normal pituitaries and pituitary adenomas. Pituitary adenomas cells cultured for 7 days in defined media showed a biphasic response to TGF-beta with significant inhibition of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion at higher concentrations (10(-9) mol/L) and stimulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion at lower concentrations (10(-13) mol/L) of TGF-beta 1 in gonadotroph adenomas. Immunohistochemical analysis for p27 protein expression showed the highest levels in nontumorous pituitaries with decreased immunoreactivity in adenomas and carcinomas. When nontumorous pituitaries and various adenomas were analyzed for p27 and specific hormone production, growth hormone, luteinizing hormone, and thyroid-stimulating hormone cells and tumors had the highest percentages of cells expressing p27, whereas adrenocorticotrophic hormone cells and tumors had the lowest percentages. Immunoblotting analysis showed that adrenocorticotrophic hormone adenomas also had the lowest levels of p27 protein. Semiquantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Northern hybridization analysis did not show significant differences in p27 mRNA expression in the various types of adenomas or in nontumorous pituitaries. In situ hybridization for p27 mRNA showed similar distributions of the gene product in nontumorous pituitaries, pituitary adenomas, and carcinomas. These results indicate that TGF-beta and TGF-beta-RII are widely expressed in nontumorous pituitaries and in pituitary neoplasms and that TGF-beta 1 regulates pituitary hormone secretion. The levels of the TGF-beta-regulated protein p27 decreases in the progression of normal to neoplastic pituitaries. In contrast, the mRNA levels of p27 remained relatively constant in nontumorous pituitaries, pituitary adenomas, and carcinomas, indicating that p27 protein levels in adenomas and carcinomas are regulated by translational and post-translational mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


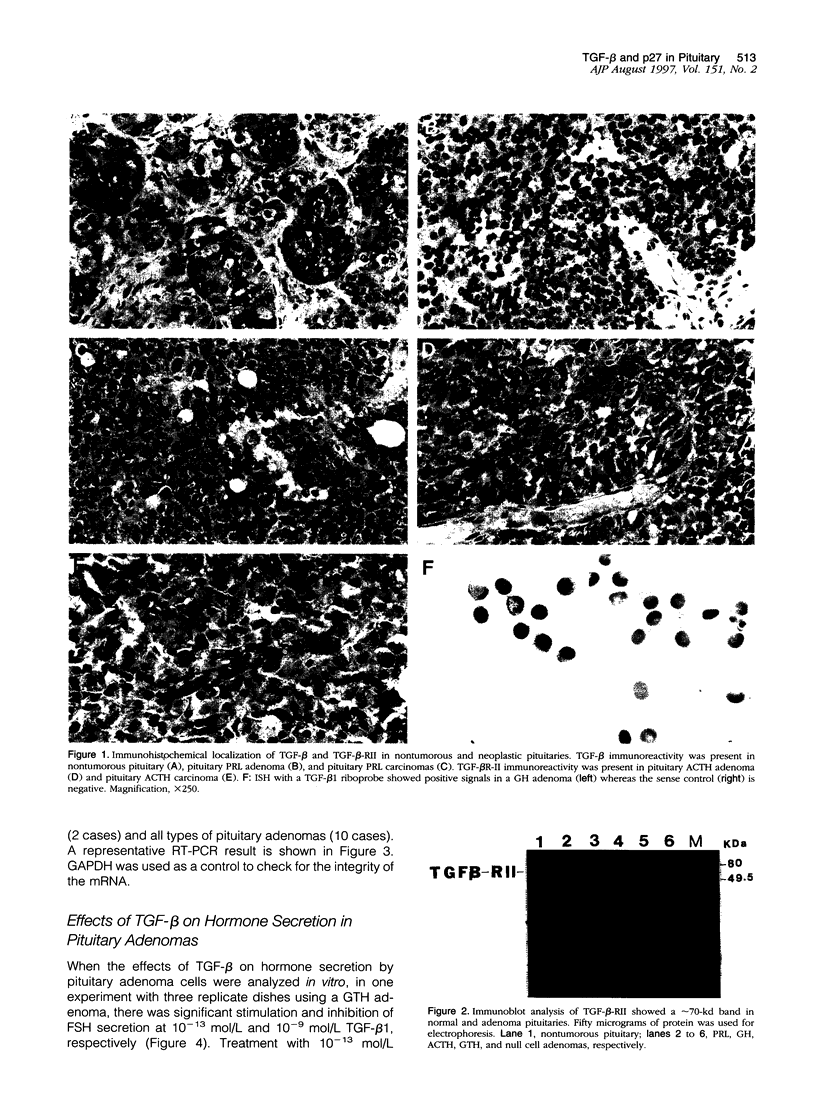
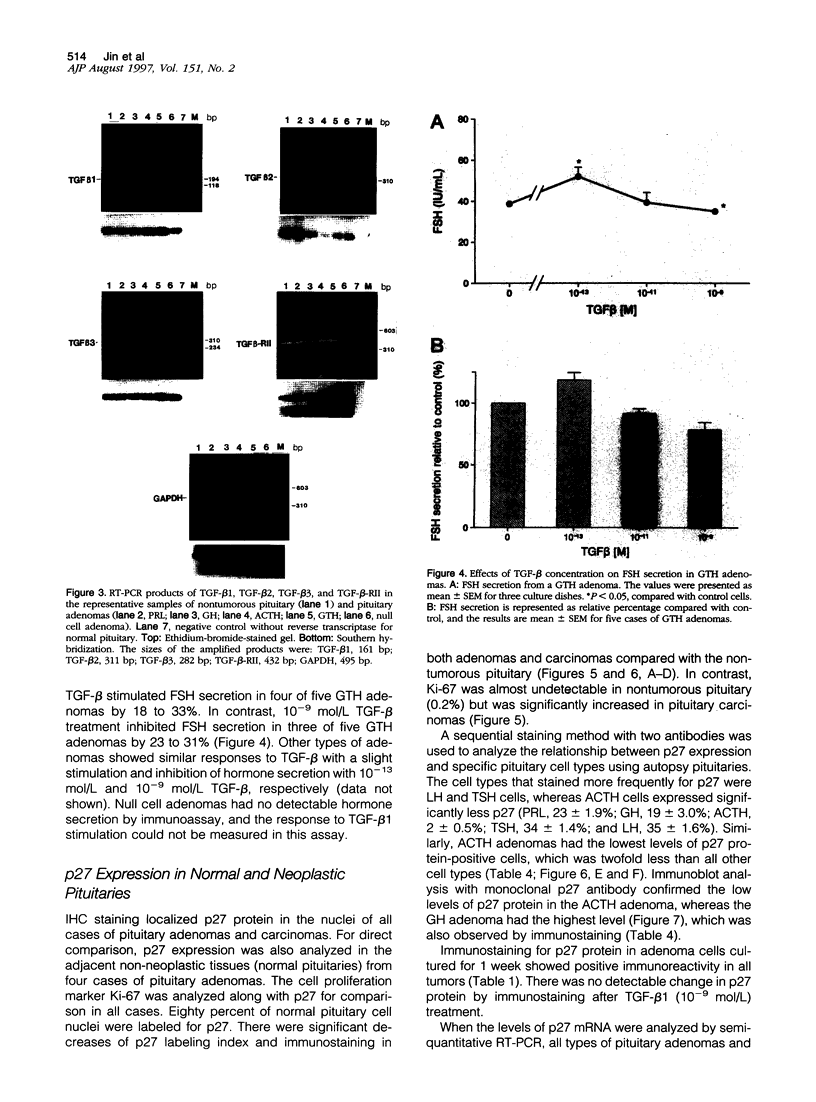
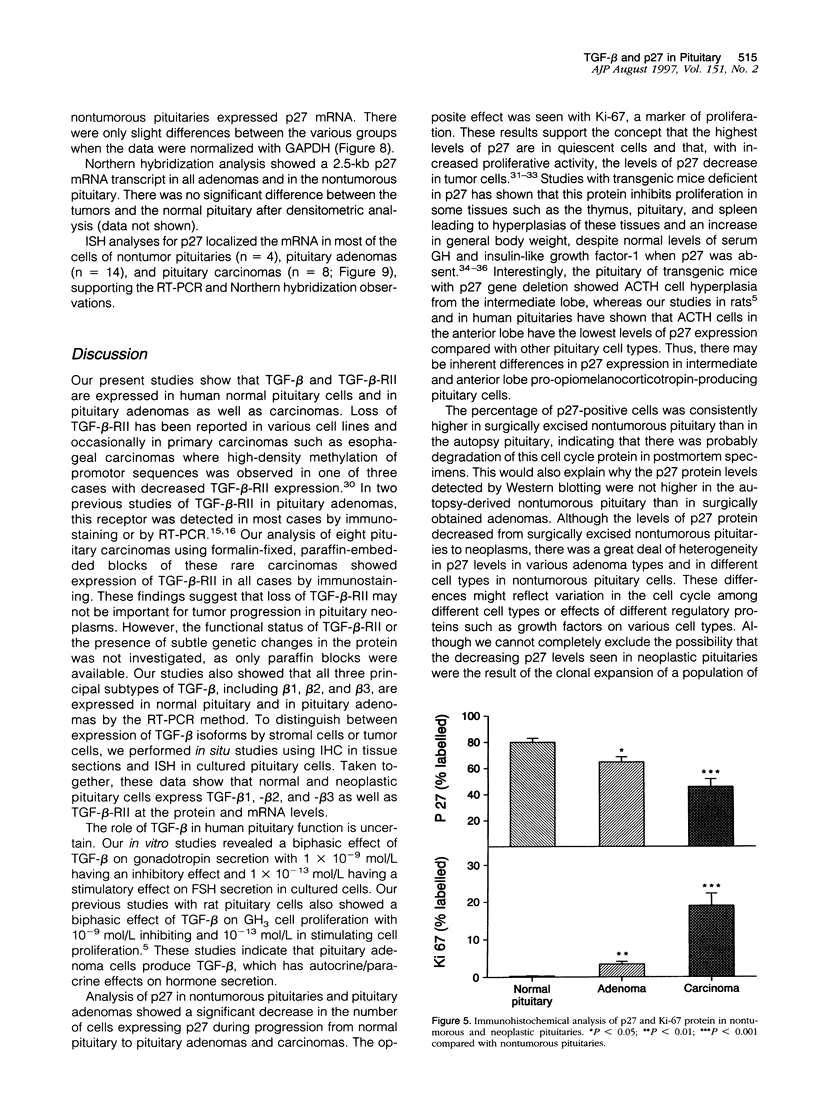
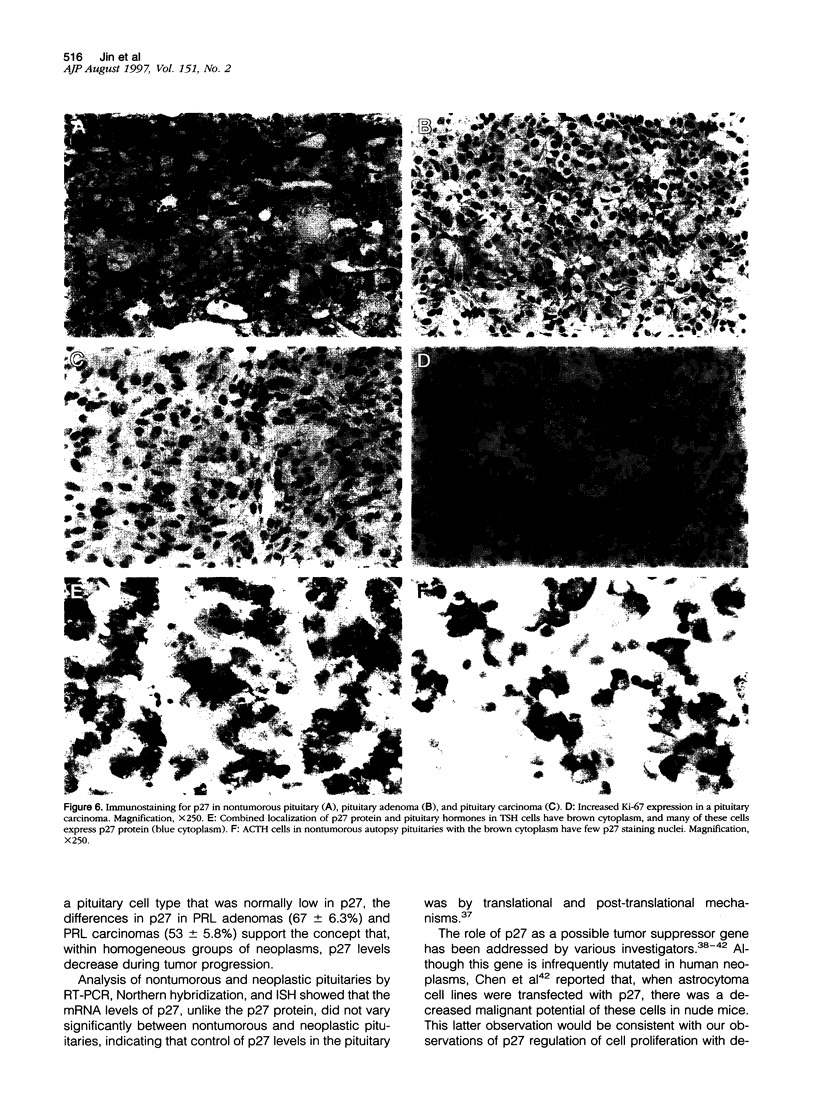

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. M., Bikkal H. A., Zervas N. T., Laws E. R., Jr, Klibanski A. Tumor-specific expression and alternate splicing of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding activin/transforming growth factor-beta receptors in human pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Feb;81(2):783–790. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.2.8636304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Sarkar D. K. Transforming growth factor beta 1-like immunoreactivity in the pituitary gland of the rat: effect of estrogen. Endocrinology. 1993 Sep;133(3):1444–1449. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.3.8365375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catzavelos C., Bhattacharya N., Ung Y. C., Wilson J. A., Roncari L., Sandhu C., Shaw P., Yeger H., Morava-Protzner I., Kapusta L. Decreased levels of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 protein: prognostic implications in primary breast cancer. Nat Med. 1997 Feb;3(2):227–230. doi: 10.1038/nm0297-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Willingham T., Shuford M., Nisen P. D. Tumor suppression and inhibition of aneuploid cell accumulation in human brain tumor cells by ectopic overexpression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27KIP1. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 15;97(8):1983–1988. doi: 10.1172/JCI118631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi M. E., Kim E. G., Huang Q., Ballermann B. J. Rat mesangial cell hypertrophy in response to transforming growth factor-beta 1. Kidney Int. 1993 Nov;44(5):948–958. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delidow B. C., Billis W. M., Agarwal P., White B. A. Inhibition of prolactin gene transcription by transforming growth factor-beta in GH3 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1716–1722. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner R., Chen R. H., Shum L., Lawler S., Zioncheck T. F., Lee A., Lopez A. R., Derynck R. Cloning of a type I TGF-beta receptor and its effect on TGF-beta binding to the type II receptor. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1344–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.8388127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fero M. L., Rivkin M., Tasch M., Porter P., Carow C. E., Firpo E., Polyak K., Tsai L. H., Broudy V., Perlmutter R. M. A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):733–744. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrigue-Antar L., Muñoz-Antonia T., Antonia S. J., Gesmonde J., Vellucci V. F., Reiss M. Missense mutations of the transforming growth factor beta type II receptor in human head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 15;55(18):3982–3987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrigue-Antar L., Souza R. F., Vellucci V. F., Meltzer S. J., Reiss M. Loss of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor gene expression in primary human esophageal cancer. Lab Invest. 1996 Aug;75(2):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin L., Chandler W. F., Smart J. B., England B. G., Lloyd R. V. Differentiation of human pituitary adenomas determines the pattern of chromogranin/secretogranin messenger ribonucleic acid expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Mar;76(3):728–735. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.3.7680355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin L., Scheithauer B. W., Young W. F., Jr, Davis D. H., Klee G. G., Lloyd R. V. Pancreastatin secretion by pituitary adenomas and regulation of chromogranin B mRNA expression. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):2057–2066. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. C., Jiang N. S., Carpenter P. C. Human corticotropin (ACTH) radioimmunoassay with synthetic 1--24 ACTH. Clin Chem. 1979 Jul;25(7):1267–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamata N., Morosetti R., Miller C. W., Park D., Spirin K. S., Nakamaki T., Takeuchi S., Hatta Y., Simpson J., Wilcyznski S. Molecular analysis of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor gene p27/Kip1 in human malignancies. Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 1;55(11):2266–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa H., Kineman R. D., Manova-Todorova K. O., Soares V. C., Hoffman E. S., Ono M., Khanam D., Hayday A. C., Frohman L. A., Koff A. Enhanced growth of mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor function of p27(Kip1). Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleihues P., Schäuble B., zur Hausen A., Estève J., Ohgaki H. Tumors associated with p53 germline mutations: a synopsis of 91 families. Am J Pathol. 1997 Jan;150(1):1–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Iacangelo A., Eiden L. E., Cano M., Jin L., Grimes M. Chromogranin A and B messenger ribonucleic acids in pituitary and other normal and neoplastic human endocrine tissues. Lab Invest. 1989 Apr;60(4):548–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loda M., Cukor B., Tam S. W., Lavin P., Fiorentino M., Draetta G. F., Jessup J. M., Pagano M. Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas. Nat Med. 1997 Feb;3(2):231–234. doi: 10.1038/nm0297-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Wang J., Myeroff L., Parsons R., Sun L., Lutterbaugh J., Fan R. S., Zborowska E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Inactivation of the type II TGF-beta receptor in colon cancer cells with microsatellite instability. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1336–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.7761852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Polyak K. Mammalian antiproliferative signals and their targets. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Ishida N., Shirane M., Inomata A., Inoue T., Shishido N., Horii I., Loh D. Y., Nakayama K. Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):707–720. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Tam S. W., Theodoras A. M., Beer-Romero P., Del Sal G., Chau V., Yew P. R., Draetta G. F., Rolfe M. Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science. 1995 Aug 4;269(5224):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7624798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panoskaltsis-Mortari A., Bucy R. P. In situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled RNA probes: facts and artifacts. Biotechniques. 1995 Feb;18(2):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Kim S. J., Bang Y. J., Park J. G., Kim N. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Genetic changes in the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) type II receptor gene in human gastric cancer cells: correlation with sensitivity to growth inhibition by TGF-beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8772–8776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastorcic M., De A., Boyadjieva N., Vale W., Sarkar D. K. Reduction in the expression and action of transforming growth factor beta 1 on lactotropes during estrogen-induced tumorigenesis in the anterior pituitary. Cancer Res. 1995 Nov 1;55(21):4892–4898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Bohlander S. K., Sato Y., Papadopoulos N., Liu B., Friedman C., Trask B. J., Roberts J. M., Kinzler K. W., Rowley J. D. Assignment of the human p27Kip1 gene to 12p13 and its analysis in leukemias. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1206–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Kato J. Y., Solomon M. J., Sherr C. J., Massague J., Roberts J. M., Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Castañeda M. V., Lee M. H., Latres E., Polyak K., Lacombe L., Montgomery K., Mathew S., Krauter K., Sheinfeld J., Massague J. p27Kip1: chromosomal mapping to 12p12-12p13.1 and absence of mutations in human tumors. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1211–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Toyoshima H., Hunter T. Redistribution of the CDK inhibitor p27 between different cyclin.CDK complexes in the mouse fibroblast cell cycle and in cells arrested with lovastatin or ultraviolet irradiation. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Sep;6(9):1197–1213. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.9.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P. L., Malone K. E., Heagerty P. J., Alexander G. M., Gatti L. A., Firpo E. J., Daling J. R., Roberts J. M. Expression of cell-cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients. Nat Med. 1997 Feb;3(2):222–225. doi: 10.1038/nm0297-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., Jin L., Grande J. P., Lloyd R. V. Transforming growth factor-beta and p27 expression in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1996 Jul;137(7):3051–3060. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.7.8770931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Xiang, Jin Long, Lloyd Ricardo V. Expression and Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor B1 in Cultured Normal and Neoplastic Rat Pituitary Cells. Endocr Pathol. 1996 Spring;7(1):77–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02739918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravitz M. J., Yan S., Herr K. D., Wenner C. E. Transforming growth factor beta-induced activation of cyclin E-cdk2 kinase and down-regulation of p27Kip1 in C3H 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1995 Apr 1;55(7):1413–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravitz M. J., Yan S., Herr K. D., Wenner C. E. Transforming growth factor beta-induced activation of cyclin E-cdk2 kinase and down-regulation of p27Kip1 in C3H 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1995 Apr 1;55(7):1413–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996 Dec 6;274(5293):1672–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin K. S., Simpson J. F., Takeuchi S., Kawamata N., Miller C. W., Koeffler H. P. p27/Kip1 mutation found in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996 May 15;56(10):2400–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Croix B., Flørenes V. A., Rak J. W., Flanagan M., Bhattacharya N., Slingerland J. M., Kerbel R. S. Impact of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 on resistance of tumor cells to anticancer agents. Nat Med. 1996 Nov;2(11):1204–1210. doi: 10.1038/nm1196-1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Wu G., Willson J. K., Zborowska E., Yang J., Rajkarunanayake I., Wang J., Gentry L. E., Wang X. F., Brattain M. G. Expression of transforming growth factor beta type II receptor leads to reduced malignancy in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26449–26455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thapar K., Stefaneanu L., Kovacs K., Scheithauer B. W., Lloyd R. V., Muller P. J., Laws E. R., Jr Estrogen receptor gene expression in craniopharyngiomas: an in situ hybridization study. Neurosurgery. 1994 Dec;35(6):1012–1017. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199412000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. F., Lin H. Y., Ng-Eaton E., Downward J., Lodish H. F., Weinberg R. A. Expression cloning and characterization of the TGF-beta type III receptor. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]