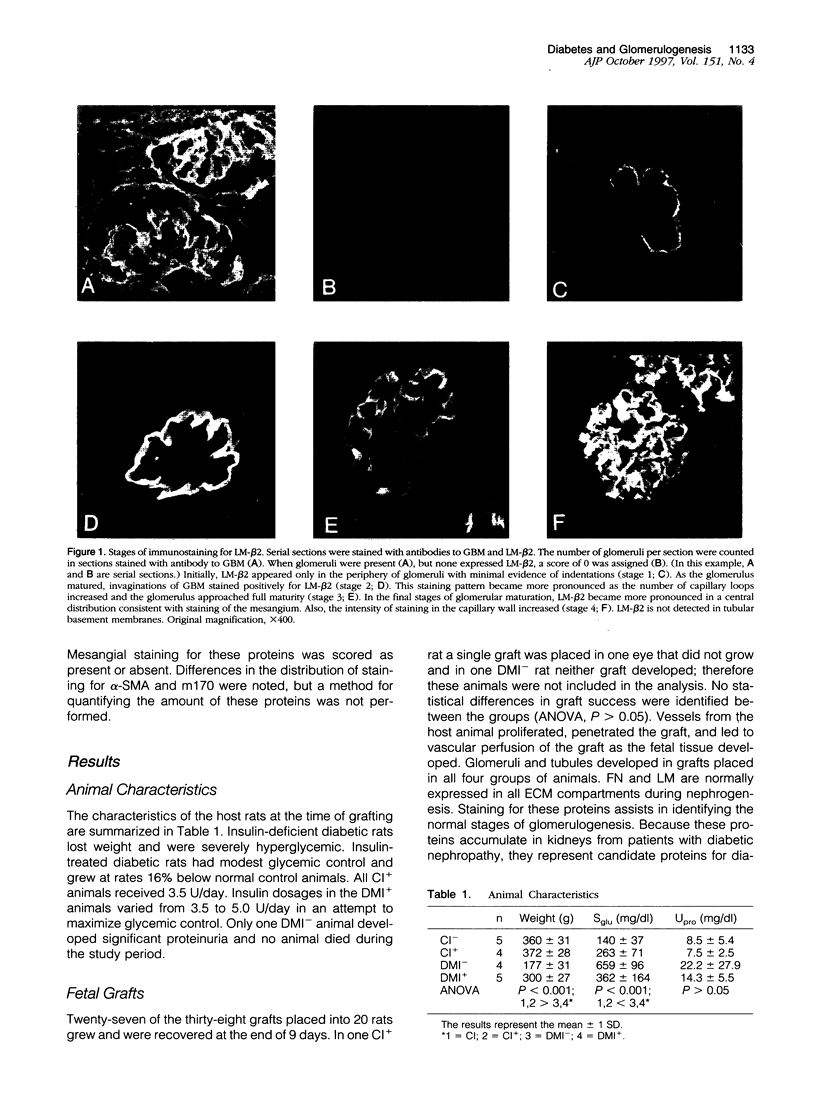
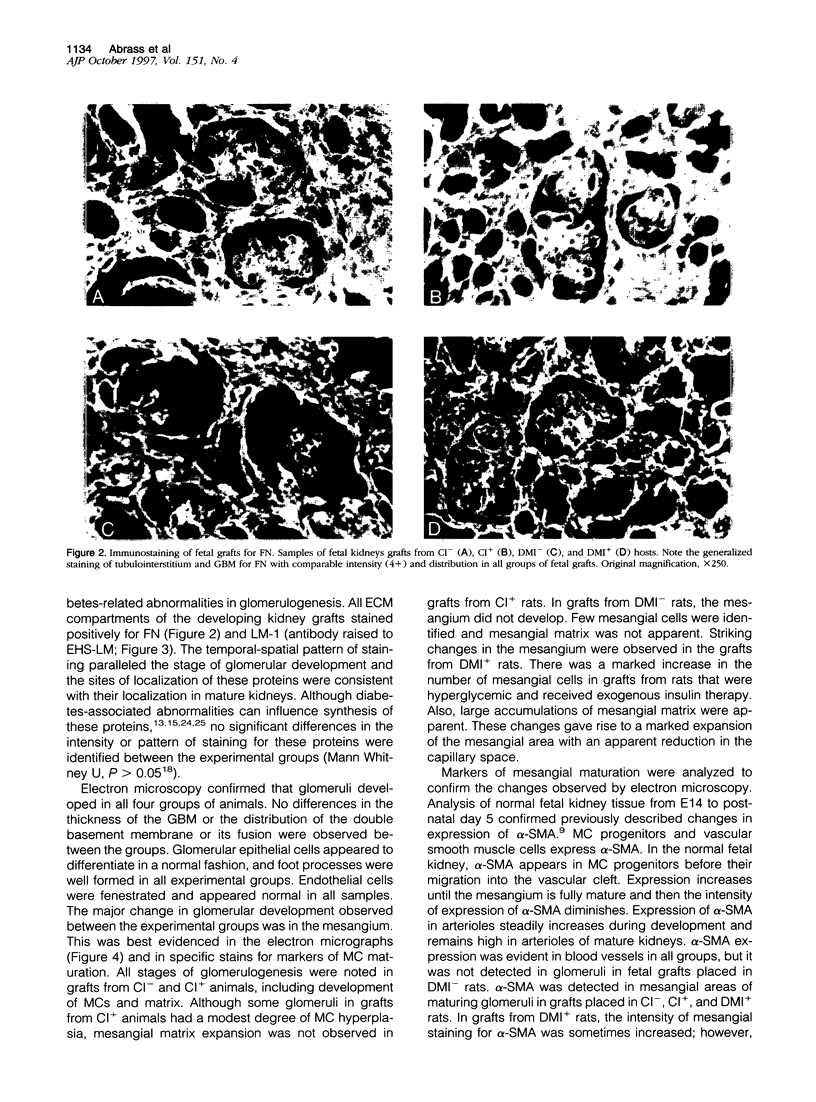
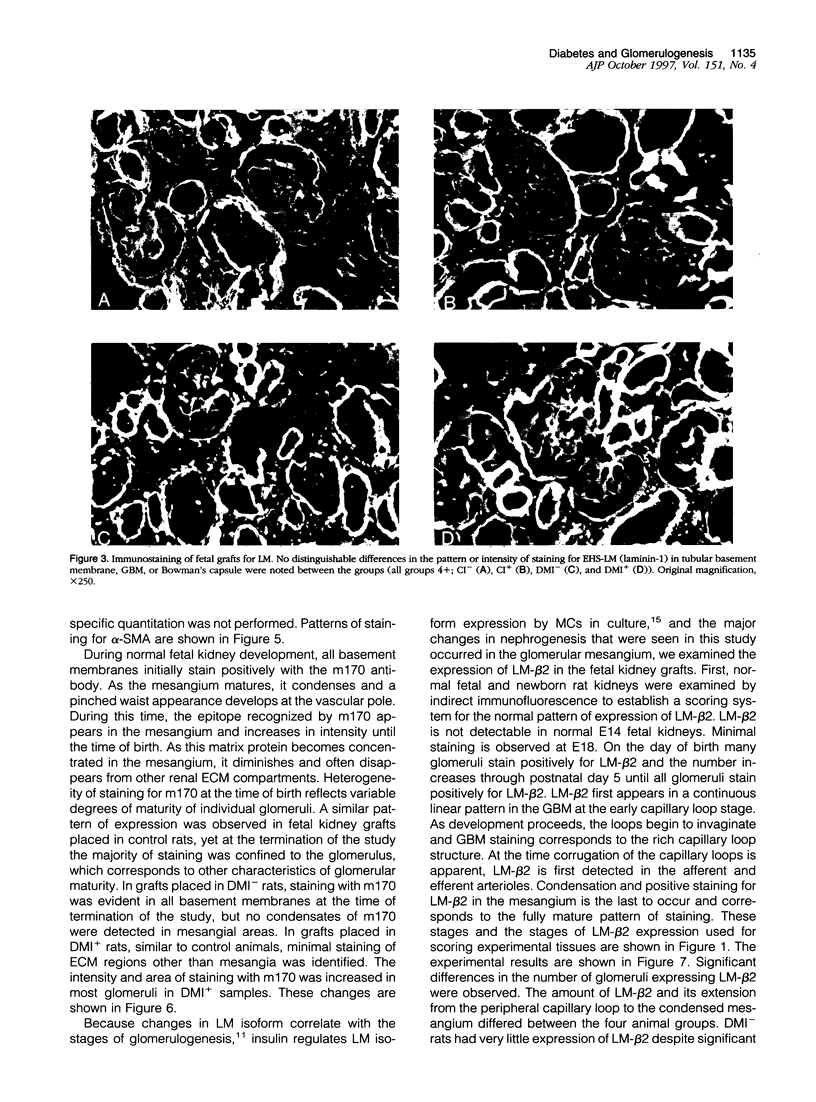
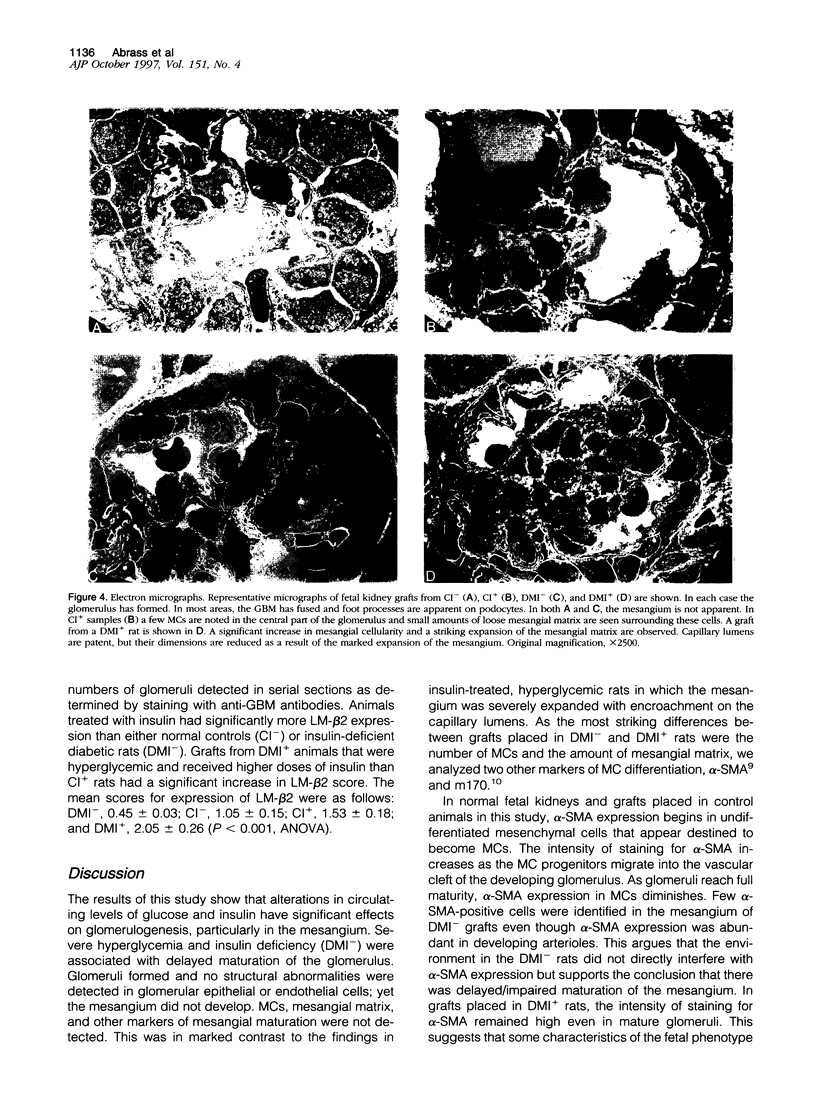
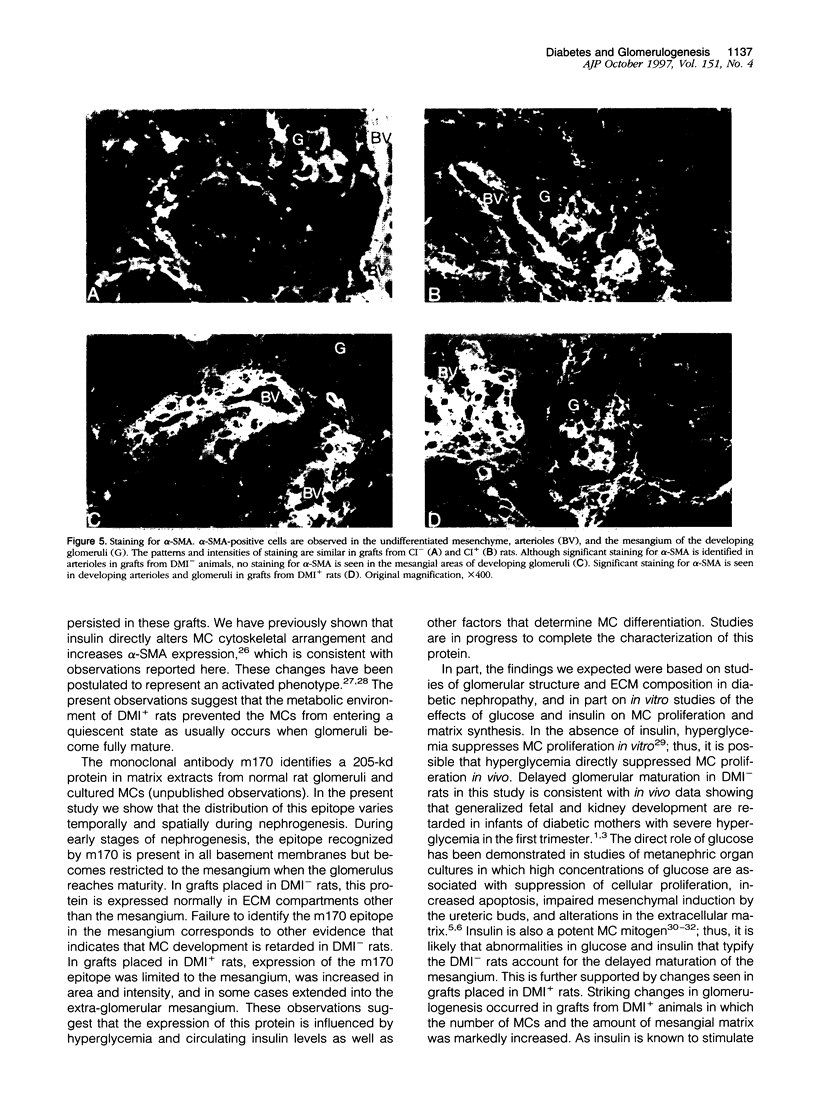
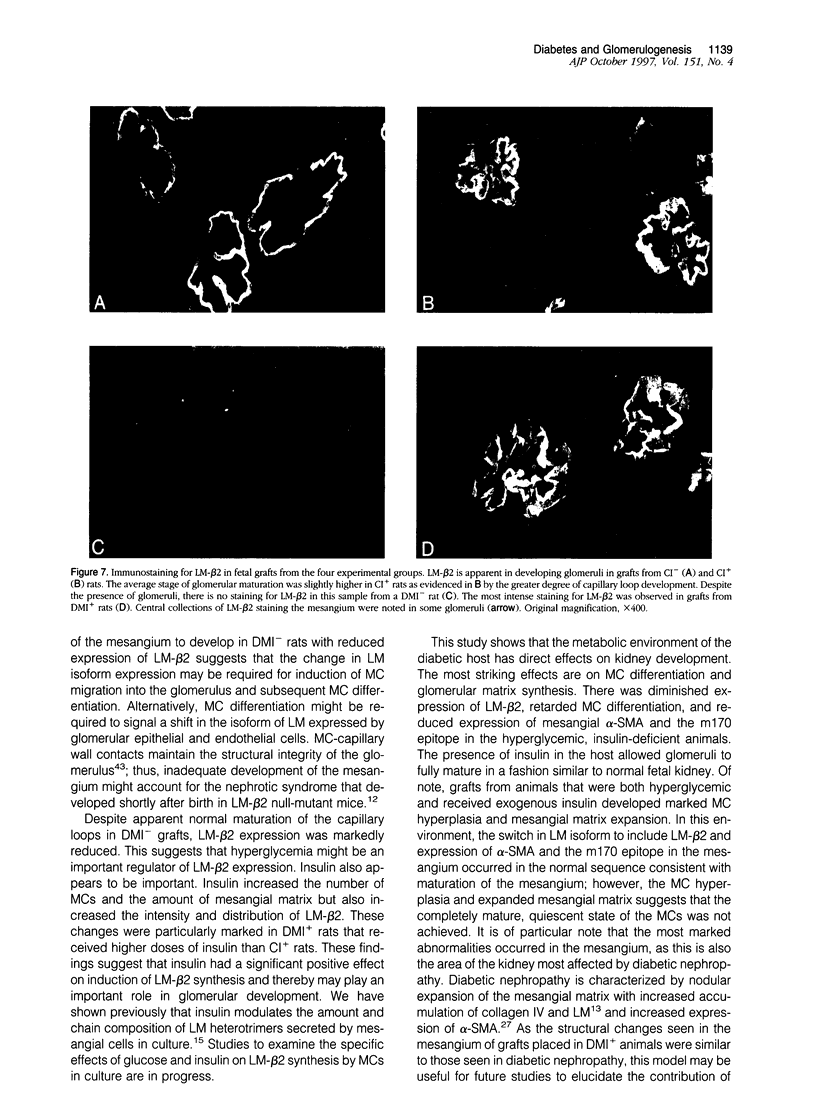
Abstract
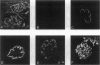
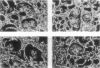
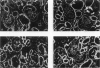
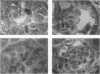
Offspring of diabetic mothers have developmental renal abnormalities; thus, we investigated the effects of the diabetic milieu on kidney development. Four groups of host rats, including insulin-deficient and insulin-treated streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, normal controls, and insulin-treated nondiabetic rats, were prepared. After 38 days, rats received ocular implants of E14 fetal rat kidneys. Nine days later the fetal kidney grafts were harvested for analysis of glomerular development and expression of fibronectin, laminin, laminin-beta 2, and alpha-smooth muscle actin and m170, two additional markers of mesangial maturation. The rate of glomerular maturation was delayed in grafts placed in hyperglycemic, insulin-deficient diabetic rats. These glomeruli contained few mesangial cells or matrix, and laminin-beta 2 expression was reduced as compared with controls. Mesangial expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and m170 was not detected. In contrast, grafts placed in insulin-treated diabetic animals had increased numbers of mesangial cells and expanded mesangial matrix. The content of laminin-beta 2 and expression of m170 and alpha-smooth muscle actin were also increased in these grafts. These data show that hyperglycemia and insulin status influence laminin isoform expression and play important roles in mesangial development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson D. R., St John P. L., Pillion D. J., Tucker D. C. Glomerular development in intraocular and intrarenal grafts of fetal kidneys. Lab Invest. 1991 May;64(5):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrass C. K., Adcox M. J., Raugi G. J. Aging-associated changes in renal extracellular matrix. Am J Pathol. 1995 Mar;146(3):742–752. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrass C. K. Evaluation of sequential glomerular eluates from rats with Heymann nephritis. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):530–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrass C. K., Peterson C. V., Raugi G. J. Phenotypic expression of collagen types in mesangial matrix of diabetic and nondiabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1695–1702. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrass C. K., Raugi G. J., Gabourel L. S., Lovett D. H. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I binding to cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Nov;123(5):2432–2439. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-5-2432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrass C. K., Spicer D., Raugi G. J. Induction of nodular sclerosis by insulin in rat mesangial cells in vitro: studies of collagen. Kidney Int. 1995 Jan;47(1):25–37. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrass C. K., Spicer D., Raugi G. J. Insulin induces a change in extracellular matrix glycoproteins synthesized by rat mesangial cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1994 Sep;46(3):613–620. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpers C. E., Hudkins K. L., Gown A. M., Johnson R. J. Enhanced expression of "muscle-specific" actin in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1992 May;41(5):1134–1142. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J., Liu J. P., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barss V. A. Diabetes and pregnancy. Med Clin North Am. 1989 May;73(3):685–700. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30666-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berfield A. K., Raugi G. J., Abrass C. K. Insulin induces rapid and specific rearrangement of the cytoskeleton of rat mesangial cells in vitro. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996 Feb;44(2):91–101. doi: 10.1177/44.2.8609378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J., Cheng F., Roszka J. Increased glucose increases glomerular basement membrane in metanephric culture. Pediatr Nephrol. 1987 Jan;1(1):3–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00866877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Chiquet M., Deutzmann R., Ekblom P., Engel J., Kleinman H., Martin G. R., Meneguzzi G., Paulsson M., Sanes J. A new nomenclature for the laminins. Matrix Biol. 1994 Apr;14(3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0945-053x(94)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio F. G. Effects of high glucose concentrations on human mesangial cell proliferation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 Feb;5(8):1600–1609. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V581600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom M., Klein G., Mugrauer G., Fecker L., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Ekblom P. Transient and locally restricted expression of laminin A chain mRNA by developing epithelial cells during kidney organogenesis. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Klein G., Ekblom M., Sorokin L. Laminin isoforms and their receptors in the developing kidney. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991 Jun;17(6):603–605. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Lehtonen E., Saxén L., Timpl R. Shift in collagen type as an early response to induction of the metanephric mesenchyme. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):276–283. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Earwicker D., Haaparanta T., Ruoslahti E., Sanes J. R. Distribution and isolation of four laminin variants; tissue restricted distribution of heterotrimers assembled from five different subunits. Cell Regul. 1990 Sep;1(10):731–740. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.10.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foo I. T., Naylor I. L., Timmons M. J., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Intracellular actin as a marker for myofibroblasts in vitro. Lab Invest. 1992 Dec;67(6):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N. Banting Lecture 1980. Of pregnancy and progeny. Diabetes. 1980 Dec;29(12):1023–1035. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.12.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui M., Nakamura T., Ebihara I., Shirato I., Tomino Y., Koide H. ECM gene expression and its modulation by insulin in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1992 Dec;41(12):1520–1527. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.12.1520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Pomerantz K. B. Signal transduction in atherosclerosis: integration of cytokines and the eicosanoid network. FASEB J. 1992 Aug;6(11):2933–2941. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.11.1644257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Sanes J. R. Synaptic structure and development: the neuromuscular junction. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):99–121. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman M. R. Growth factors in renal development. Semin Nephrol. 1995 Jul;15(4):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod M., Diamant Y. Z. The offspring of a diabetic mother--short- and long-range implications. Isr J Med Sci. 1992 Feb;28(2):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. D., Shah V., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. A laminin-like adhesive protein concentrated in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):229–234. doi: 10.1038/338229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyink D. P., Tucker D. C., St John P. L., Leardkamolkarn V., Accavitti M. A., Abrass C. K., Abrahamson D. R. Endogenous origin of glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells in grafts of embryonic kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1996 May;270(5 Pt 2):F886–F899. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.270.5.F886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Liu Z. Z., Kumar A., Usman M. I., Wada J., Wallner E. I. D-glucose-induced dysmorphogenesis of embryonic kidney. J Clin Invest. 1996 Dec 1;98(11):2478–2488. doi: 10.1172/JCI119066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Liu Z. Z., Wallner E. I. Influence of glucose on murine metanephric development and proteoglycans: morphologic and biochemical studies. Lab Invest. 1997 May;76(5):671–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Weeks B. S., Schnaper H. W., Kibbey M. C., Yamamura K., Grant D. S. The laminins: a family of basement membrane glycoproteins important in cell differentiation and tumor metastases. Vitam Horm. 1993;47:161–186. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1983 Mar;23(3):439–447. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz W., Elger M., Lemley K. V., Sakai T. Mesangial cell-glomerular basement membrane connections counteract glomerular capillary and mesangium expansion. Am J Nephrol. 1990;10 (Suppl 1):4–13. doi: 10.1159/000168186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Horikoshi S., Killen P. D., Segui-Real B., Yamada Y. In situ hybridization reveals temporal and spatial changes in cellular expression of mRNA for a laminin receptor, laminin, and basement membrane (type IV) collagen in the developing kidney. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1351–1362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Q., Bissell M. J. Multi-faceted regulation of cell differentiation by extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):737–743. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Sanes J. R. Collagen IV alpha 3, alpha 4, and alpha 5 chains in rodent basal laminae: sequence, distribution, association with laminins, and developmental switches. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):879–891. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan P. S., Carter W. G., Spiro R. G. Occurrence of type VI collagen in extracellular matrix of renal glomeruli and its increase in diabetes. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):31–37. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noakes P. G., Miner J. H., Gautam M., Cunningham J. M., Sanes J. R., Merlie J. P. The renal glomerulus of mice lacking s-laminin/laminin beta 2: nephrosis despite molecular compensation by laminin beta 1. Nat Genet. 1995 Aug;10(4):400–406. doi: 10.1038/ng0895-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Sala R., Cagliero E., Lorenzi M. Overexpression of fibronectin induced by diabetes or high glucose: phenomenon with a memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):404–408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Hunter D. D., Green T. L., Merlie J. P. S-laminin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:419–430. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]