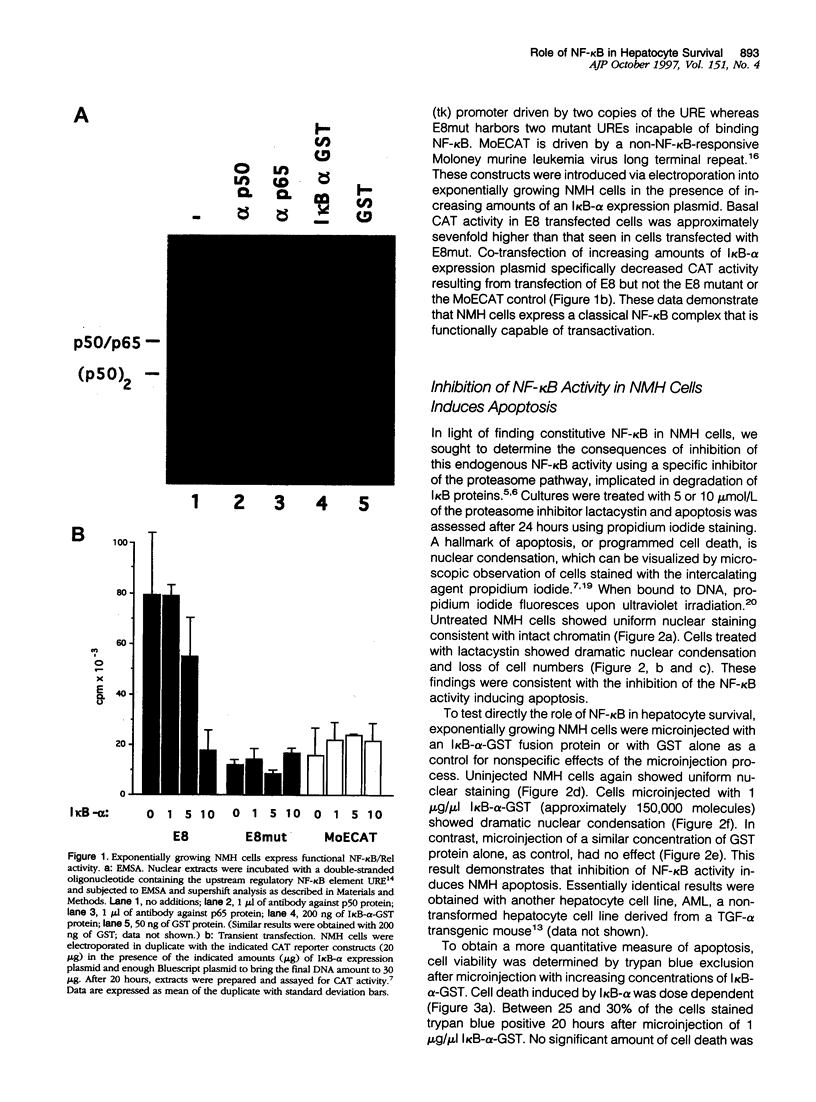
Abstract
Recently we have demonstrated that inhibition of the nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B/Rel family of transcription factors induces apoptosis of B cells. Interestingly, mice lacking the relA gene encoding the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B exhibit embryonic lethality at days 15 to 16 of gestation, accompanied by massive destruction of liver via apoptosis. To determine whether p65 protein plays a direct role in hepatocyte survival, we employed a nontransformed murine hepatocyte (NMH) cell line, which maintains to a high degree the differentiated hepatocyte phenotype. Exponentially growing NMH cells were found to possess a constitutive level of functional classical (p50/p65) NF-kappa B as assayed by electrophoretic mobility shift analysis, antibody supershift, and transient transfection assays. Treatment of NMH cells with the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin, which prevents degradation of the NF-kappa B inhibitor proteins I kappa B, induced apoptosis. Direct inhibition of the endogenous NF-kappa B activity by microinjection of NMH cells with purified specific inhibitor I kappa B-alpha-glutathione-S-transferase fusion protein or an antibody against p65 protein induced apoptosis. These findings suggest that expression of NF-kappa B/Rel activity in murine hepatocytes acts directly to promote survival of these cells and suggest that apoptosis observed in hepatocytes of mice lacking relA is a direct effect of p65 deficiency.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerman P., Cote P., Yang S. Q., McClain C., Nelson S., Bagby G. J., Diehl A. M. Antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibit liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):G579–G585. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.4.G579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsura M., Wu M., Sonenshein G. E. TGF beta 1 inhibits NF-kappa B/Rel activity inducing apoptosis of B cells: transcriptional activation of I kappa B alpha. Immunity. 1996 Jul;5(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr The I kappa B proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2064–2070. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Baltimore D. An essential role for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science. 1996 Nov 1;274(5288):782–784. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5288.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Sha W. C., Bronson R. T., Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1995 Jul 13;376(6536):167–170. doi: 10.1038/376167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellas R. E., Lee J. S., Sonenshein G. E. Expression of a constitutive NF-kappa B-like activity is essential for proliferation of cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2521–2527. doi: 10.1172/JCI118313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirillo P., Falco M., Puri P. L., Artini M., Balsano C., Levrero M., Natoli G. Hepatitis B virus pX activates NF-kappa B-dependent transcription through a Raf-independent pathway. J Virol. 1996 Jan;70(1):641–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.1.641-646.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton M. M. A biochemical hallmark of apoptosis: internucleosomal degradation of the genome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1992 Sep;11(2):105–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00048058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cressman D. E., Greenbaum L. E., DeAngelis R. A., Ciliberto G., Furth E. E., Poli V., Taub R. Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science. 1996 Nov 22;274(5291):1379–1383. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyao M. P., Buckler A. J., Sonenshein G. E. Interaction of an NF-kappa B-like factor with a site upstream of the c-myc promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald M. J., Webber E. M., Donovan J. R., Fausto N. Rapid DNA binding by nuclear factor kappa B in hepatocytes at the start of liver regeneration. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Apr;6(4):417–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B., Upholt W. B., Devinny J., Vinograd J. The use of an ethidium analogue in the dye-buoyant density procedure for the isolation of closed circular DNA: the variation of the superhelix density of mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):813–820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Rosa F. A., Pierce J. W., Sonenshein G. E. Differential regulation of the c-myc oncogene promoter by the NF-kappa B rel family of transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1039–1044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Rustgi A. K., Schievella A. R., Bernards R. Suppression of MHC class I gene expression by N-myc through enhancer inactivation. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3351–3355. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08497.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. G., Hsu H., Goeddel D. V., Karin M. Dissection of TNF receptor 1 effector functions: JNK activation is not linked to apoptosis while NF-kappaB activation prevents cell death. Cell. 1996 Nov 1;87(3):565–576. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolten F. L., Bucher N. L. Regeneration of rat liver: transfer of humoral agent by cross circulation. Science. 1967 Oct 13;158(3798):272–274. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3798.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Thomas S. J., Loring G. Induction of apoptosis during normal and neoplastic B-cell development in the bursa of Fabricius. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5857–5861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Ohba Y., Oka T. Influence of epidermal growth factor on liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. J Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;128(3):425–431. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1280425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. A., Sandgren E. P., Degen J. L., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Replacement of diseased mouse liver by hepatic cell transplantation. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1149–1152. doi: 10.1126/science.8108734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer S. L., Wang Z., Sonenshein G. E., Rothstein T. L. Maintenance of nuclear factor-kappa B/Rel and c-myc expression during CD40 ligand rescue of WEHI 231 early B cells from receptor-mediated apoptosis through modulation of I kappa B proteins. J Immunol. 1996 Jul 1;157(1):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterologist. 1995 Mar;3(1):55–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dobrzanski P., Mohn K. L., Cressman D. E., Hsu J. C., Bravo R., Taub R. Rapid induction in regenerating liver of RL/IF-1 (an I kappa B that inhibits NF-kappa B, RelB-p50, and c-Rel-p50) and PHF, a novel kappa B site-binding complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2898–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Antwerp D. J., Martin S. J., Kafri T., Green D. R., Verma I. M. Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Science. 1996 Nov 1;274(5288):787–789. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5288.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Stevenson J. K., Schwarz E. M., Van Antwerp D., Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2723–2735. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.22.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Mayo M. W., Baldwin A. S., Jr TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science. 1996 Nov 1;274(5288):784–787. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5288.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. W., Roy A., Gilmore T. D. The v-Rel oncoprotein blocks apoptosis and proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha in transformed chicken spleen cells. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 2;10(5):857–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Merlino G., Fausto N. Establishment and characterization of differentiated, nontransformed hepatocyte cell lines derived from mice transgenic for transforming growth factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):674–678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Arsura M., Bellas R. E., FitzGerald M. J., Lee H., Schauer S. L., Sherr D. H., Sonenshein G. E. Inhibition of c-myc expression induces apoptosis of WEHI 231 murine B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Sep;16(9):5015–5025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.9.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Lee H., Bellas R. E., Schauer S. L., Arsura M., Katz D., FitzGerald M. J., Rothstein T. L., Sherr D. H., Sonenshein G. E. Inhibition of NF-kappaB/Rel induces apoptosis of murine B cells. EMBO J. 1996 Sep 2;15(17):4682–4690. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Kirillova I., Peschon J. J., Fausto N. Initiation of liver growth by tumor necrosis factor: deficient liver regeneration in mice lacking type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Feb 18;94(4):1441–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]