Abstract
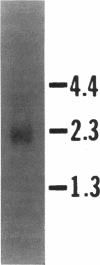
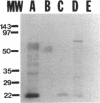
Peanut allergy is a significant health problem because of the frequency, the potential severity, and the chronicity of the allergic sensitivity. Serum IgE from patients with documented peanut hypersensitivity reactions and a peanut cDNA expression library were used to identify clones that encode peanut allergens. One of the major peanut allergens, Ara h I, was selected from these clones using Ara h I specific oligonucleotides and polymerase chain reaction technology. The Ara h I clone identified a 2.3-kb mRNA species on a Northern blot containing peanut poly (A)+ RNA. DNA sequence analysis of the cloned inserts revealed that the Ara h I allergen has significant homology with the vicilin seed storage protein family found in most higher plants. The isolation of the Ara h I clones allowed the synthesis of this protein in E. coli cells and subsequent recognition of this recombinant protein in immunoblot analysis using serum IgE from patients with peanut hypersensitivity. With the production of the recombinant peanut protein it will now be possible to address the pathophysiologic and immunologic mechanisms regarding peanut hypersensitivity reactions specifically and food hypersensitivity in general
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannon G. A., Calzone F. J., Bowen J. K., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Multiple, independently regulated, polyadenylated messages for histone H3 and H4 in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3903–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. A., Atkins F. M. The natural history of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 May;83(5):900–904. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiteneder H., Pettenburger K., Bito A., Valenta R., Kraft D., Rumpold H., Scheiner O., Breitenbach M. The gene coding for the major birch pollen allergen Betv1, is highly homologous to a pea disease resistance response gene. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1935–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks A. W., Williams L. W., Connaughton C., Cockrell G., O'Brien T. J., Helm R. M. Identification and characterization of a second major peanut allergen, Ara h II, with use of the sera of patients with atopic dermatitis and positive peanut challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(6 Pt 1):962–969. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90469-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks A. W., Williams L. W., Helm R. M., Connaughton C., Cockrell G., O'Brien T. Identification of a major peanut allergen, Ara h I, in patients with atopic dermatitis and positive peanut challenges. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Aug;88(2):172–179. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90325-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush R. K., Taylor S. L., Nordlee J. A. Peanut sensitivity. Allergy Proc. 1989 Jul-Aug;10(4):261–264. doi: 10.2500/108854189778959975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. D. Purification of allergens. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989 Apr;1(4):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee P. P., Slightom J. L. Molecular biology of legume vicilin-type seed storage protein genes. Subcell Biochem. 1991;17:31–52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9365-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Stewart G. A., Thomas W. R., Simpson R. J., Dilworth R. J., Plozza T. M., Turner K. J. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen, Der p 1. Homology with cysteine proteases. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):175–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inukai M., Inouye M. Dual functions of the signal peptide in protein transfer across the membrane. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dure L., 3rd An unstable domain in the vicilin genes of higher plants. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):487–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. N., Strøman P., Ipsen H. PCR based cloning and sequencing of isogenes encoding the tree pollen major allergen Car b I from Carpinus betulus, hornbeam. Mol Immunol. 1992 Jun;29(6):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemanske R. F., Jr, Taylor S. L. Standardized extracts, foods. Clin Rev Allergy. 1987 Feb;5(1):23–36. doi: 10.1007/BF02802255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe D. D. Food allergens. Clin Rev Allergy. 1985 Jul;3(3):331–349. doi: 10.1007/BF02992999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. J., Nelson H. S., Bock S. A., Christensen F., Leung D. Y. Treatment of peanut allergy with rush immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Aug;90(2):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90080-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihs H. P., Rozynek P., May-Taube K., Welticke B., Baur X. Polymerase chain reaction based cDNA cloning of wheat profilin: a potential plant allergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1994 Oct;105(2):190–194. doi: 10.1159/000236824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers B. L., Morgenstern J. P., Griffith I. J., Yu X. B., Counsell C. M., Brauer A. W., King T. P., Garman R. D., Kuo M. C. Complete sequence of the allergen Amb alpha II. Recombinant expression and reactivity with T cells from ragweed allergic patients. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2547–2552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., McCaskill C. C. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: evaluation of 113 patients. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):669–675. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., Mendelson L., Rosen J. P. Fatal and near-fatal anaphylactic reactions to food in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 1992 Aug 6;327(6):380–384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199208063270603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A. Role of immediate food hypersensitivity in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 May;71(5):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanti K. N., Martin B. M., Nagpal S., Metcalfe D. D., Rao P. V. Identification of tropomyosin as the major shrimp allergen and characterization of its IgE-binding epitopes. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5354–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression, identification, and characterization of recombinant gene products in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:661–673. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. L., Busse W. W., Sachs M. I., Parker J. L., Yunginger J. W. Peanut oil is not allergenic to peanut-sensitive individuals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Nov;68(5):372–375. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. R., Stewart G. A., Simpson R. J., Chua K. Y., Plozza T. M., Dilworth R. J., Nisbet A., Turner K. J. Cloning and expression of DNA coding for the major house dust mite allergen Der p 1 in Escherichia coli. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;85(1):127–129. doi: 10.1159/000234488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcich M. P., Hamilton D. A., Mascarenhas J. P. Isolation and characterization of pollen-specific maize genes with sequence homology to ragweed allergens and pectate lyases. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Dec;23(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1007/BF00021820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenta R., Duchene M., Ebner C., Valent P., Sillaber C., Deviller P., Ferreira F., Tejkl M., Edelmann H., Kraft D. Profilins constitute a novel family of functional plant pan-allergens. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):377–385. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenta R., Duchêne M., Pettenburger K., Sillaber C., Valent P., Bettelheim P., Breitenbach M., Rumpold H., Kraft D., Scheiner O. Identification of profilin as a novel pollen allergen; IgE autoreactivity in sensitized individuals. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):557–560. doi: 10.1126/science.1857985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine M. D., Schuberth K. C., Kagey-Sobotka A., Graft D. F., Kwiterovich K. A., Szklo M., Lichtenstein L. M. The value of immunotherapy with venom in children with allergy to insect stings. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1601–1603. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. R., Boss M. A., Patel T. P., Emtage J. S. The influence of messenger RNA secondary structure on expression of an immunoglobulin heavy chain in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3937–3950. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunginger J. W., Jones R. T. A review of peanut chemistry. Implications for the standardization of peanut extracts. Arb Paul Ehrlich Inst Georg Speyer Haus Ferdinand Blum Inst Frankf A M. 1987;(80):251–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunginger J. W., Squillace D. L., Jones R. T., Helm R. M. Fatal anaphylactic reactions induced by peanuts. Allergy Proc. 1989 Jul-Aug;10(4):249–253. doi: 10.2500/108854189778959993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]