Abstract
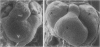
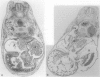
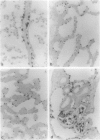
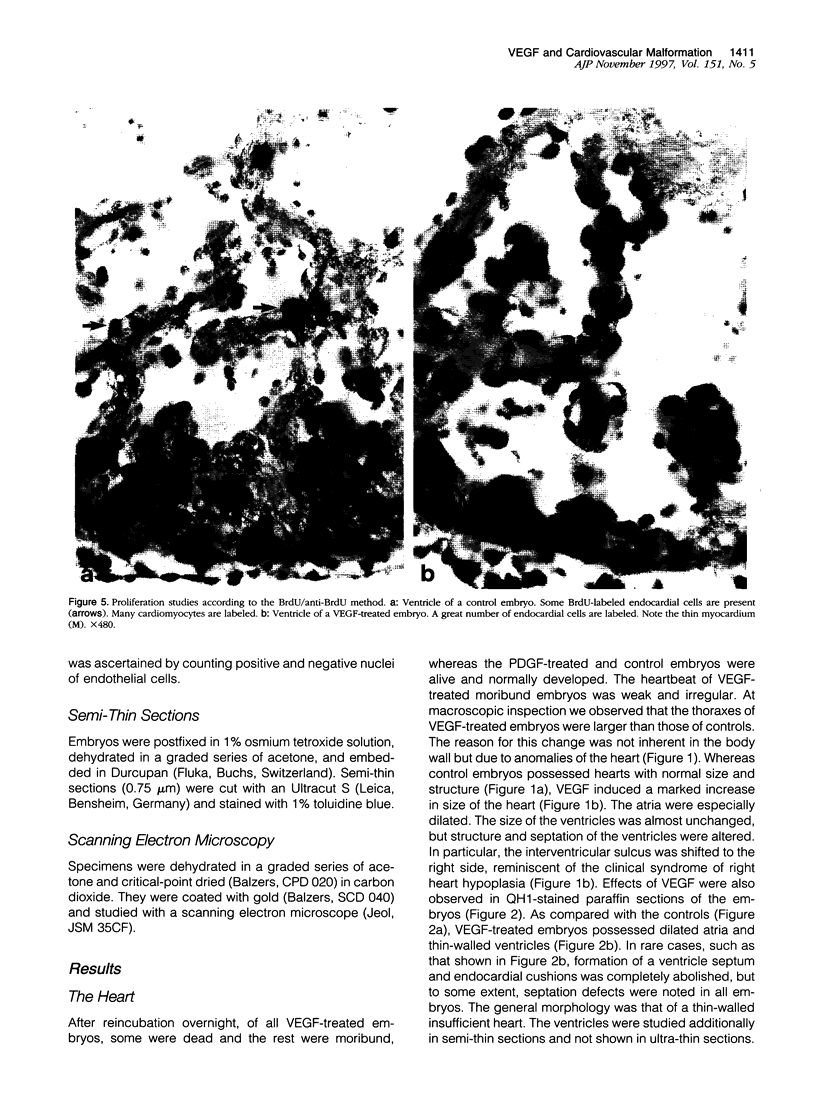
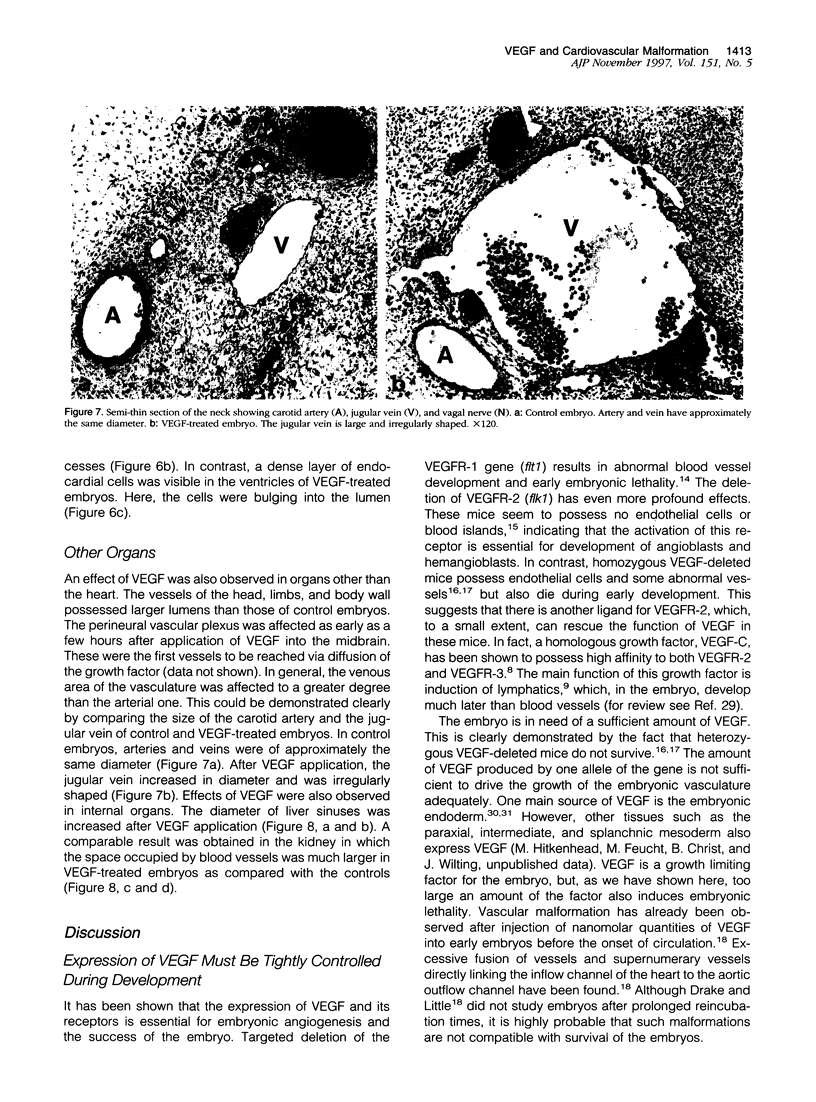
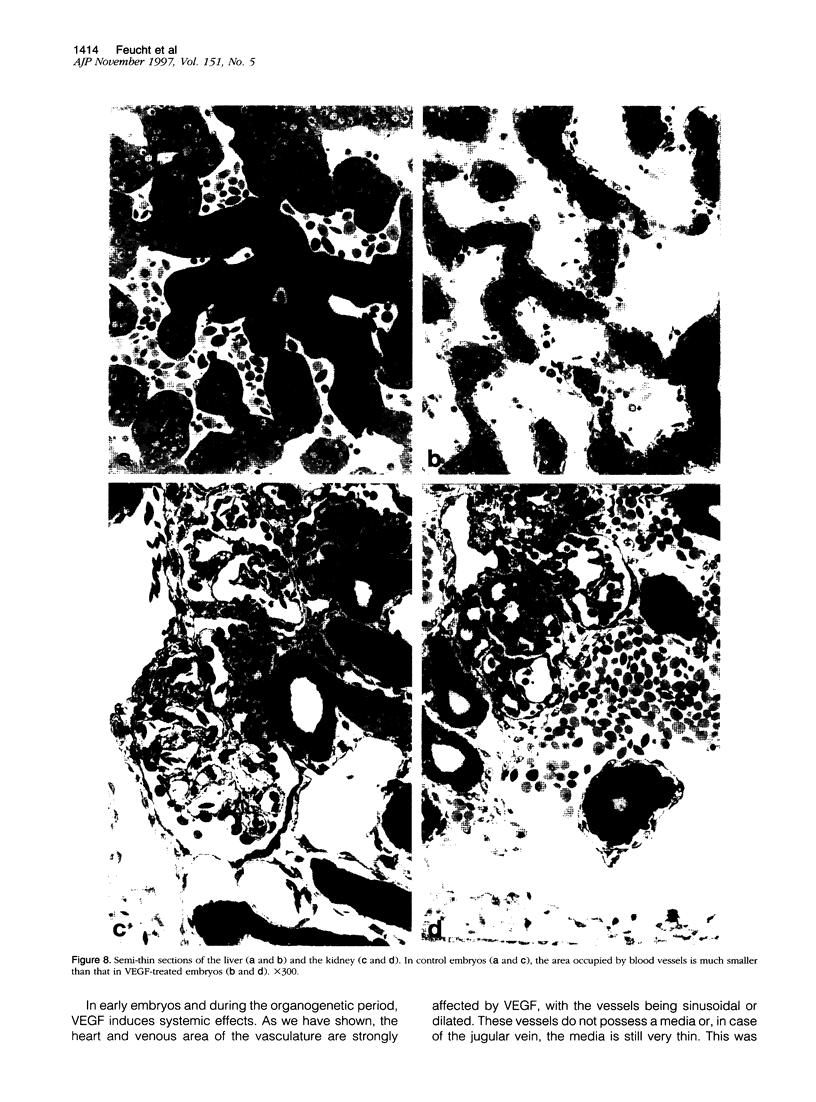
The essential function of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in embryonic angiogenesis has clearly been documented in murine embryos with targeted deletions of either VEGF or its receptors. The effects of VEGF in the organogenetic phase of development have not been studied to date. Therefore, we applied 0.7 to 0.9 microgram of VEGF via methylcellulose carriers into the midbrain or onto the right forelimb of 4.5-day-old quail embryos. Another group of embryos was treated with 1 microgram of platelet-derived growth factor and controls were carried out using carriers without any growth factor. VEGF-induced cardiovascular malformations resulted in embryonic lethality. The venous area of the vasculature was dilated in almost all organs. The heart was most seriously affected and showed typical characteristics of insufficiency. VEGF strongly increased endocardial cell proliferation and obviously induced impairment of the growth rates of myocardium and endocardium. The myocardium of the ventricles was extremely thin, and septation defects were observed. As a result of the disturbed outflow, the atria were extremely dilated and thin-walled. The morphology of the hearts was reminiscent of that observed in congenital malformations such as Uhl's and Osler's syndromes. Our results show that expression of VEGF has to be tightly controlled during development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber S., Hunter J. J., Ross J., Jr, Hongo M., Sansig G., Borg J., Perriard J. C., Chien K. R., Caroni P. MLP-deficient mice exhibit a disruption of cardiac cytoarchitectural organization, dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Cell. 1997 Feb 7;88(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81878-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenhäger R., Schneppe B., Röckl W., Wilting J., Weich H. A., McCarthy J. E. Synthesis and physiological activity of heterodimers comprising different splice forms of vascular endothelial growth factor and placenta growth factor. Biochem J. 1996 Jun 15;316(Pt 3):703–707. doi: 10.1042/bj3160703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Albrecht U., Sterrer S., Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):521–532. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Ferreira V., Breier G., Pollefeyt S., Kieckens L., Gertsenstein M., Fahrig M., Vandenhoeck A., Harpal K., Eberhardt C. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996 Apr 4;380(6573):435–439. doi: 10.1038/380435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Heuvelman D. M., Nelson R., Olander J. V., Eppley B. L., Delfino J. J., Siegel N. R., Leimgruber R. M., Feder J. Tumor vascular permeability factor stimulates endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1470–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI114322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake C. J., Little C. D. Exogenous vascular endothelial growth factor induces malformed and hyperfused vessels during embryonic neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7657–7661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont D. J., Fong G. H., Puri M. C., Gradwohl G., Alitalo K., Breitman M. L. Vascularization of the mouse embryo: a study of flk-1, tek, tie, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression during development. Dev Dyn. 1995 May;203(1):80–92. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann A., Marcelle C., Bréant C., Le Douarin N. M. Molecular cloning of Quek 1 and 2, two quail vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-like molecules. Gene. 1996 Sep 26;174(1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(96)00159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann A., Marcelle C., Bréant C., Le Douarin N. M. Two molecules related to the VEGF receptor are expressed in early endothelial cells during avian embryonic development. Mech Dev. 1993 Jul;42(1-2):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90096-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg R. N., Cafasso E. Macromolecular permeability of chick wing microvessels: an intravital confocal study. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1995 Apr;191(4):337–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00534686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Carver-Moore K., Chen H., Dowd M., Lu L., O'Shea K. S., Powell-Braxton L., Hillan K. J., Moore M. W. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature. 1996 Apr 4;380(6573):439–442. doi: 10.1038/380439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiebich B. L., Jäger B., Schöllmann C., Weindel K., Wilting J., Kochs G., Marmé D., Hug H., Weich H. A. Synthesis and assembly of functionally active human vascular endothelial growth factor homodimers in insect cells. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb19865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamme I., Breier G., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF receptor 2 (flk-1) are expressed during vasculogenesis and vascular differentiation in the quail embryo. Dev Biol. 1995 Jun;169(2):699–712. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamme I., von Reutern M., Drexler H. C., Syed-Ali S., Risau W. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor in the avian embryo induces hypervascularization and increased vascular permeability without alterations of embryonic pattern formation. Dev Biol. 1995 Oct;171(2):399–414. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., D'Amore P. A. Blood vessel formation: what is its molecular basis? Cell. 1996 Dec 27;87(7):1153–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81810-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong G. H., Rossant J., Gertsenstein M., Breitman M. L. Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):66–70. doi: 10.1038/376066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: A new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7123245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joukov V., Pajusola K., Kaipainen A., Chilov D., Lahtinen I., Kukk E., Saksela O., Kalkkinen N., Alitalo K. A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 15;15(2):290–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millauer B., Wizigmann-Voos S., Schnürch H., Martinez R., Møller N. P., Risau W., Ullrich A. High affinity VEGF binding and developmental expression suggest Flk-1 as a major regulator of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):835–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90573-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. J., Jeltsch M. M., Birkenhäger R., McCarthy J. E., Weich H. A., Christ B., Alitalo K., Wilting J. VEGF and VEGF-C: specific induction of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in the differentiated avian chorioallantoic membrane. Dev Biol. 1997 Aug 1;188(1):96–109. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardanaud L., Altmann C., Kitos P., Dieterlen-Lievre F., Buck C. A. Vasculogenesis in the early quail blastodisc as studied with a monoclonal antibody recognizing endothelial cells. Development. 1987 Jun;100(2):339–349. doi: 10.1242/dev.100.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGALL H. N. Parchment heart (Osler). Am Heart J. 1950 Dec;40(6):948–950. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(50)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Perruzzi C. A., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby F., Rossant J., Yamaguchi T. P., Gertsenstein M., Wu X. F., Breitman M. L., Schuh A. C. Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):62–66. doi: 10.1038/376062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Dougher-Vermazen M., Carrion M. E., Dimitrov D., Armellino D. C., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P. Identification of the KDR tyrosine kinase as a receptor for vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 30;187(3):1579–1586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHL H. S. M. A previously undescribed congenital malformation of the heart: almost total absence of the myocardium of the right ventricle. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952 Sep;91(3):197–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht R. J., Carmichael D. J., Gopal R., Philip G. Uhl's anomaly. Br Heart J. 1979 Jun;41(6):676–682. doi: 10.1136/hrt.41.6.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEEKLY clinicopathological exercise: cardiac dilatation of right heart, extreme, congenital. N Engl J Med. 1952 May 15;246(20):785–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195205152462007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller B. F., Smith E. R., Blackbourne B. D., Arce F. P., Sarkar N. N., Roberts W. C. Congenital hypoplasia of portions of both right and left ventricular myocardial walls. Clinical and necropsy observations in two patients with parchment heart syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1980 Nov;46(5):885–891. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(80)90444-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Birkenhäger R., Eichmann A., Kurz H., Martiny-Baron G., Marmé D., McCarthy J. E., Christ B., Weich H. A. VEGF121 induces proliferation of vascular endothelial cells and expression of flk-1 without affecting lymphatic vessels of chorioallantoic membrane. Dev Biol. 1996 May 25;176(1):76–85. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.9993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Brand-Saberi B., Huang R., Zhi Q., Köntges G., Ordahl C. P., Christ B. Angiogenic potential of the avian somite. Dev Dyn. 1995 Feb;202(2):165–171. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002020208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Christ B., Bokeloh M., Weich H. A. In vivo effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. Cell Tissue Res. 1993 Oct;274(1):163–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00327997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Christ B., Weich H. A. The effects of growth factors on the day 13 chorioallantoic membrane (CAM): a study of VEGF165 and PDGF-BB. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1992 Aug;186(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00174147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Eichmann A., Christ B. Expression of the avian VEGF receptor homologues Quek1 and Quek2 in blood-vascular and lymphatic endothelial and non-endothelial cells during quail embryonic development. Cell Tissue Res. 1997 May;288(2):207–223. doi: 10.1007/s004410050807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Kurz H., Brand-Saberi B., Steding G., Yang Y. X., Hasselhorn H. M., Epperlein H. H., Christ B. Kinetics and differentiation of somite cells forming the vertebral column: studies on human and chick embryos. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1994 Dec;190(6):573–581. doi: 10.1007/BF00190107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan F., Leunig M., Berk D. A., Jain R. K. Microvascular permeability of albumin, vascular surface area, and vascular volume measured in human adenocarcinoma LS174T using dorsal chamber in SCID mice. Microvasc Res. 1993 May;45(3):269–289. doi: 10.1006/mvre.1993.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]