Abstract
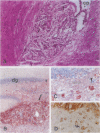
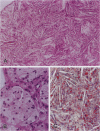
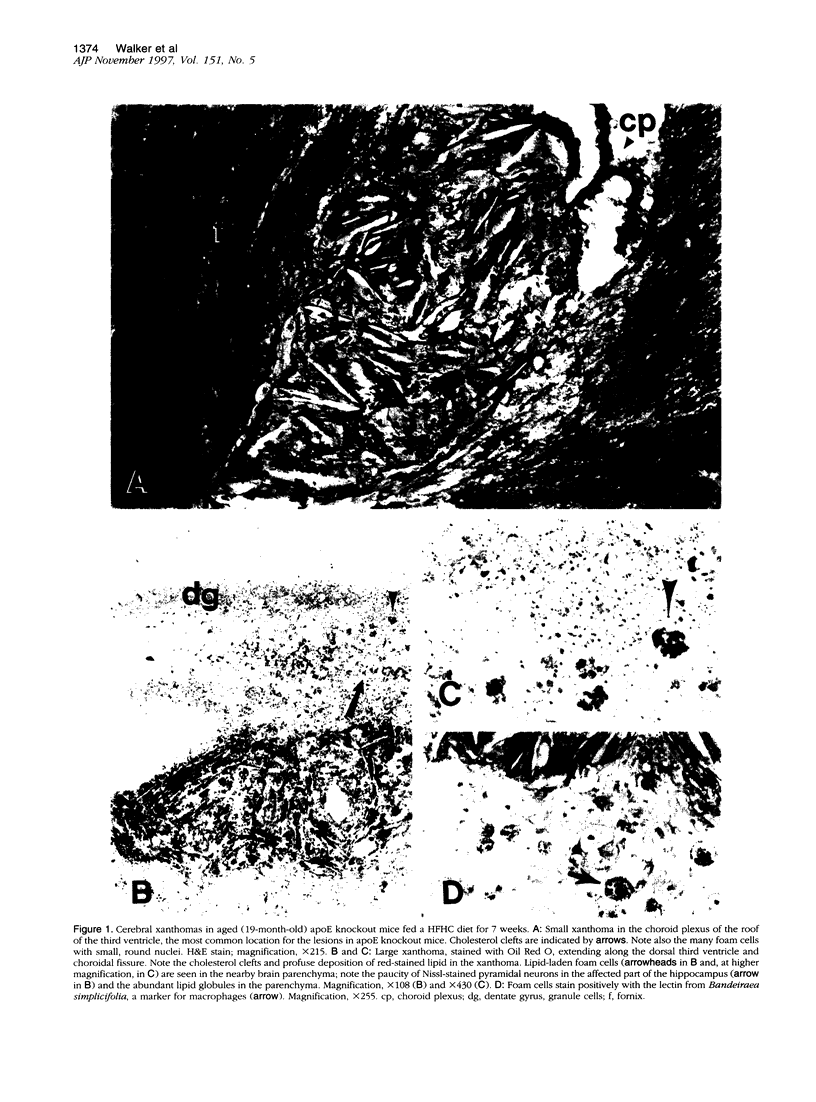
To assess the influence of age and diet on cerebral pathology in mice lacking apolipoprotein E (apoE), four male apoE knockout mice (epsilon -/-), and five male wild-type (epsilon +/+) littermate controls were placed on a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet for 7 weeks beginning at 17 months of age. All four aged knockout mice developed xanthomatous lesions in the brain consisting mostly of crystalline cholesterol clefts, lipid globules, and foam cells. Smaller xanthomas were confined mainly to the choroid plexus and ventral fornix in the roof of the third ventricle, occasionally extending subpially along the choroidal fissure and into the adjacent parenchyma. More advanced xanthomas disrupted adjoining neural tissue in the fornix, hippocampus, and dorsal diencephalon; in one case, over 60% of one telencephalic hemisphere, including nearly the entire neocortex, was obliterated by the lesion. No xanthomas were observed in aged wild-type controls fed the high-fat/high-cholesterol diet. Brains from 42 additional animals, fed only conventional chow, were examined; 3 of 15 aged (15- to 23-month-old) apoE knockout mice developed small choroidal xanthomas. In contrast, no lesions were observed in five young (2- to 4-month-old) apoE knockout mice or in any wild-type controls between the ages of 2 and 23 months. Our findings indicate that disorders of lipid metabolism can induce significant pathological changes in the central nervous system of aged apoE knockout mice, particularly those on a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet. It may be fruitful to seek potential interactions between genetic factors and diet in modulating the risk of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders in aged humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRUS S. B., MANN G. V. Xanthomatosis and atherosclerosis produced by diet in an adult rhesus monkey. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Oct;48(4):533–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AYRES W. W., HAYMAKER W. Xanthoma and cholesterol granuloma of the choroid plexus. Report of the pathological aspects in 29 cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1960 Apr;19:280–295. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196004000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Algoed L., Caemaert J., Achten E., van Aken J., de Reuck J. A large intracranial xanthoma in familial hypercholesterolemia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1994 Feb;96(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belza J., Rubinstein L. J., Maier N., Haimovici H. Experimental cerebral atherosclerosis in dogs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Nov 21;149(2):895–906. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb53845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner J. A., Heinecke J. W. The role of oxidized lipoproteins in atherogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;20(5):707–727. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(95)02173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodovitz S., Klein W. L. Cholesterol modulates alpha-secretase cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 23;271(8):4436–4440. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.8.4436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyles J. K., Zoellner C. D., Anderson L. J., Kosik L. M., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Hui D. Y., Mahley R. W., Gebicke-Haerter P. J., Ignatius M. J. A role for apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein A-I, and low density lipoprotein receptors in cholesterol transport during regeneration and remyelination of the rat sciatic nerve. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1015–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI113943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. Mouse models of atherosclerosis. Science. 1996 May 3;272(5262):685–688. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5262.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cali J. J., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Russell D. W. Mutations in the bile acid biosynthetic enzyme sterol 27-hydroxylase underlie cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7779–7783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Pericak-Vance M. A., Roses A. D. There is a pathologic relationship between ApoE-epsilon 4 and Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1995 Jul;52(7):650–651. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1995.00540310012003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Roselaar S. E. Lipoprotein oxidation as a mediator of atherogenesis: insights from pharmacological studies. Cardiovasc Res. 1995 Mar;29(3):297–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstl H., Czech C., Sattel H., Geiger-Kabisch C., Besthorn C., Kreger S., Mönning U., Hartmann T., Masters C., Beyreuther K. Apolipoprotein E und Alzheimer-Demenz. Eigene Ergebnisse und kurze Literaturübersicht. Nervenarzt. 1994 Nov;65(11):780–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genis I., Gordon I., Sehayek E., Michaelson D. M. Phosphorylation of tau in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Oct 13;199(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)12007-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Isla T., West H. L., Rebeck G. W., Harr S. D., Growdon J. H., Locascio J. J., Perls T. T., Lipsitz L. A., Hyman B. T. Clinical and pathological correlates of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1996 Jan;39(1):62–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. M., Rebeck G. W., Vonsattel J. P., Gomez-Isla T., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 and cerebral hemorrhage associated with amyloid angiopathy. Ann Neurol. 1995 Aug;38(2):254–259. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. R., Mackenzie I. R. Xanthoma disseminatum with massive intracranial involvement. Clin Neuropathol. 1995 Nov-Dec;14(6):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks M. J., Albrecht S., Trask T., Byrne M. E., Narayan R. K., Goodman J. C. Symptomatic choroid plexus xanthogranuloma of the lateral ventricle. Case report and brief critical review of xanthogranulomatous lesions of the brain. Clin Neuropathol. 1993 Mar-Apr;12(2):92–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman A., Ott A., Breteler M. M., Bots M. L., Slooter A. J., van Harskamp F., van Duijn C. N., Van Broeckhoven C., Grobbee D. E. Atherosclerosis, apolipoprotein E, and prevalence of dementia and Alzheimer's disease in the Rotterdam Study. Lancet. 1997 Jan 18;349(9046):151–154. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)09328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., West H. L., Rebeck G. W., Buldyrev S. V., Mantegna R. N., Ukleja M., Havlin S., Stanley H. E. Quantitative analysis of senile plaques in Alzheimer disease: observation of log-normal size distribution and molecular epidemiology of differences associated with apolipoprotein E genotype and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3586–3590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Herz J., Burns D. K. Massive xanthomatosis and atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed low density lipoprotein receptor-negative mice. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):1885–1893. doi: 10.1172/JCI117179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaer O., Loken A. C., Nesbakken R. Hydrocephalus due to xanthogranuloma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1973 Nov;39(5):659–661. doi: 10.3171/jns.1973.39.5.0659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz A., Lautenschlager N., Haupt M., Zimmer R., von Thülen B., Altland K., Lauter H., Müller U. Das Apolipoprotein E-epsilon 4-Allel ist ein Risikofaktor für die Alzheimer-Krankheit mit frühem und spätem Beginn. Nervenarzt. 1994 Nov;65(11):774–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovirta M., Laakso M. P., Soininen H., Helisalmi S., Mannermaa A., Helkala E. L., Partanen K., Ryynänen M., Vainio P., Hartikainen P. Volumes of hippocampus, amygdala and frontal lobe in Alzheimer patients with different apolipoprotein E genotypes. Neuroscience. 1995 Jul;67(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00014-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Mallory M., Ge N., Alford M., Veinbergs I., Roses A. D. Neurodegeneration in the central nervous system of apoE-deficient mice. Exp Neurol. 1995 Dec;136(2):107–122. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1995.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Samuel W., Veinbergs I., Mallory M., Mante M., Saitoh T. Neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment in apoE-deficient mice is ameliorated by infusion of recombinant apoE. Brain Res. 1997 Mar 21;751(2):307–314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(96)01420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken L., Brion J. P. Phosphorylation of tau protein is not affected in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Neuroreport. 1995 Nov 27;6(17):2381–2384. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199511270-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura Y., Kuriyama M., Tokimura Y., Fujiyama J., Osame M., Takesako K., Tanaka N. Treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-apheresis. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Feb;114(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90303-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata M., Smith J. D. Apolipoprotein E allele-specific antioxidant activity and effects on cytotoxicity by oxidative insults and beta-amyloid peptides. Nat Genet. 1996 Sep;14(1):55–61. doi: 10.1038/ng0996-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montine K. S., Olson S. J., Amarnath V., Whetsell W. O., Jr, Graham D. G., Montine T. J. Immunohistochemical detection of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal adducts in Alzheimer's disease is associated with inheritance of APOE4. Am J Pathol. 1997 Feb;150(2):437–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Higuchi S., Arai H., Sasaki H., Yamada K., Hayashida M., Trojanowski J. Q. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distribution in alcoholic dementia and in Alzheimer's disease in Japan. Ann Neurol. 1994 Nov;36(5):797–799. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z., Esiri M. M., Jobst K. A., Johnston C., Litchfield S., Sim E., Smith A. D. Influence of the apolipoprotein E genotype on amyloid deposition and neurofibrillary tangle formation in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience. 1995 Dec;69(3):757–761. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00331-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Plump A. S., Raines E. W., Breslow J. L., Ross R. ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jan;14(1):133–140. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina P. M., Verstuyft J., Paigen B. Synthetic low and high fat diets for the study of atherosclerosis in the mouse. J Lipid Res. 1990 May;31(5):859–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohm T. G., Kirca M., Bohl J., Scharnagl H., Gross W., März W. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism influences not only cerebral senile plaque load but also Alzheimer-type neurofibrillary tangle formation. Neuroscience. 1995 Jun;66(3):583–587. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00596-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedrahita J. A., Zhang S. H., Hagaman J. R., Oliver P. M., Maeda N. Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setälä K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90362-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J. Apolipoprotein E in animal models of CNS injury and in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polano M. K. Xanthoma types in relation to the type of hyperlipoproteinemia. Nutr Metab. 1973;15(1):107–118. doi: 10.1159/000175427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polvikoski T., Sulkava R., Haltia M., Kainulainen K., Vuorio A., Verkkoniemi A., Niinistö L., Halonen P., Kontula K. Apolipoprotein E, dementia, and cortical deposition of beta-amyloid protein. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 9;333(19):1242–1247. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511093331902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar D. R., Cohen D. L., Hedera P., Friedland R. P., Kalaria R. N. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon4 alleles in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and cerebrovascular pathology associated with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):2083–2095. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck G. W., Reiter J. S., Strickland D. K., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E in sporadic Alzheimer's disease: allelic variation and receptor interactions. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiman E. M., Caselli R. J., Yun L. S., Chen K., Bandy D., Minoshima S., Thibodeau S. N., Osborne D. Preclinical evidence of Alzheimer's disease in persons homozygous for the epsilon 4 allele for apolipoprotein E. N Engl J Med. 1996 Mar 21;334(12):752–758. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199603213341202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayre L. M., Zelasko D. A., Harris P. L., Perry G., Salomon R. G., Smith M. A. 4-Hydroxynonenal-derived advanced lipid peroxidation end products are increased in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1997 May;68(5):2092–2097. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.68052092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Crain B. J., Hulette C. M., Joo S. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9649–9653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slooter A. J., Tang M. X., van Duijn C. M., Stern Y., Ott A., Bell K., Breteler M. M., Van Broeckhoven C., Tatemichi T. K., Tycko B. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 and the risk of dementia with stroke. A population-based investigation. JAMA. 1997 Mar 12;277(10):818–821. doi: 10.1001/jama.277.10.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Richey Harris P. L., Sayre L. M., Beckman J. S., Perry G. Widespread peroxynitrite-mediated damage in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1997 Apr 15;17(8):2653–2657. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-08-02653.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowdon D. A., Greiner L. H., Mortimer J. A., Riley K. P., Greiner P. A., Markesbery W. R. Brain infarction and the clinical expression of Alzheimer disease. The Nun Study. JAMA. 1997 Mar 12;277(10):813–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks D. L., Scheff S. W., Hunsaker J. C., 3rd, Liu H., Landers T., Gross D. R. Induction of Alzheimer-like beta-amyloid immunoreactivity in the brains of rabbits with dietary cholesterol. Exp Neurol. 1994 Mar;126(1):88–94. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verchere C. B., D'Alessio D. A., Palmiter R. D., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S., Baskin D. G., Kahn S. E. Islet amyloid formation associated with hyperglycemia in transgenic mice with pancreatic beta cell expression of human islet amyloid polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3492–3496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF A., COWEN D., GRAHAM S. Xanthomas of the choroid plexus in man. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1950 Jul;9(3):286–297. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195007000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E distribution among human plasma lipoproteins: role of the cysteine-arginine interchange at residue 112. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1503–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. W., Schaefer E. J., Larson M. G., Ordovas J. M. Apolipoprotein E alleles and risk of coronary disease. A meta-analysis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):1250–1255. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.16.10.1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Role of oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI115499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ree J. H., Gijbels M. J., van den Broek W. J., Hofker M. H., Havekes L. M. Atypical xanthomatosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice after cholesterol feeding. Atherosclerosis. 1995 Jan 20;112(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)05419-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]