Abstract
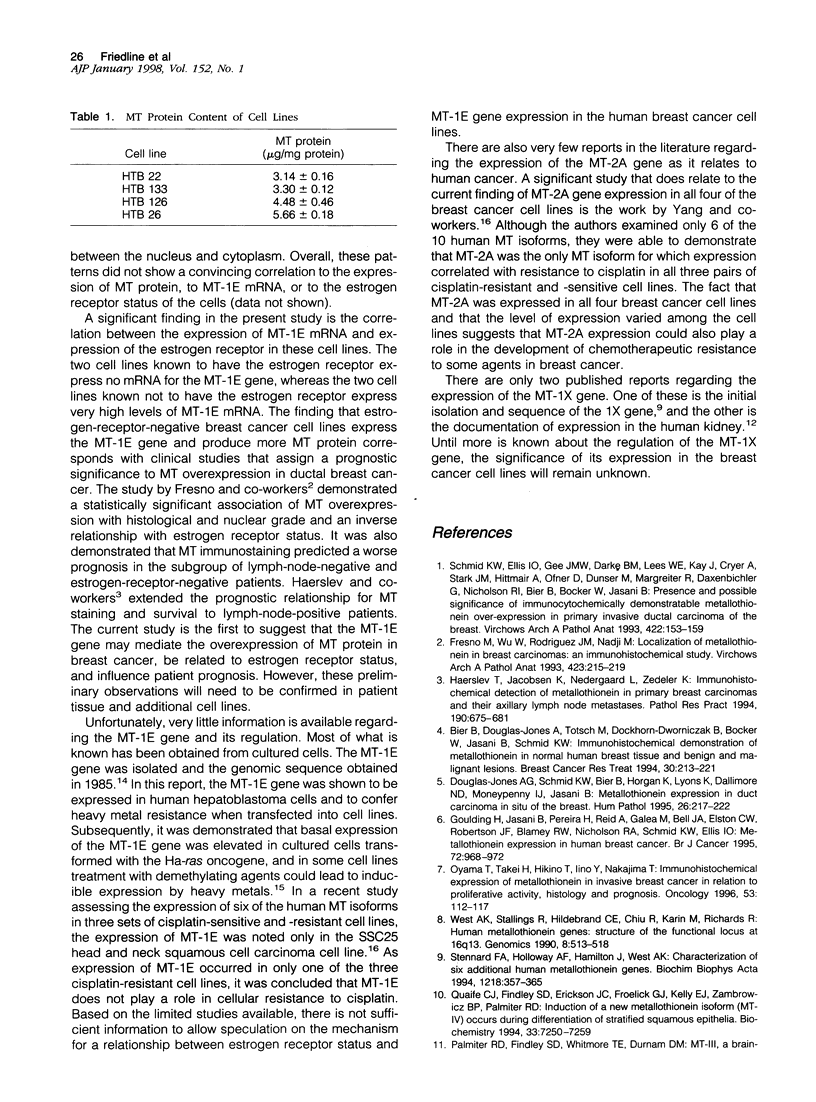
The goal of this study was to determine which of the 10 functional metallothionein (MT) genes are expressed in four human breast cancer cell lines and whether expression varies among the cell lines. Using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technology, it was shown that there was no expression of mRNA for the MT-1A, MT-1B, MT-1F, MT-1G, MT-1H, MT-3, and MT-4 genes in any of the four cell lines. All four cell lines were shown to express mRNA for the MT-2A and MT-1X genes. The expression level of mRNA for the MT-2A gene demonstrated modest differences among the cell lines, whereas expression of the MT-1X gene was consistent. In contrast, mRNA for the MT-1E gene was expressed in only two of the four cell lines and expression correlated to the estrogen receptor status of the cell lines. The two estrogen-receptor-positive cell lines showed no mRNA expression for the MT-1E gene. In the two estrogen-receptor-negative cell lines, mRNA expression for the MT-1E gene was elevated with expression levels similar to the housekeeping gene, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The cellular content of MT protein was also shown to be elevated in the estrogen-receptor-negative cell lines that express MT-1E mRNA. These results suggest a possible relationship between estrogen receptor status and MT-1E gene expression in human breast cancer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bier B., Douglas-Jones A., Tötsch M., Dockhorn-Dworniczak B., Böcker W., Jasani B., Schmid K. W. Immunohistochemical demonstration of metallothionein in normal human breast tissue and benign and malignant breast lesions. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;30(3):213–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00665963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas-Jones A. G., Schmid K. W., Bier B., Horgan K., Lyons K., Dallimore N. D., Moneypenny I. J., Jasani B. Metallothionein expression in duct carcinoma in situ of the breast. Hum Pathol. 1995 Feb;26(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresno M., Wu W., Rodriguez J. M., Nadji M. Localization of metallothionein in breast carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;423(3):215–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01614773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding H., Jasani B., Pereira H., Reid A., Galea M., Bell J. A., Elston C. W., Robertson J. F., Blamey R. W., Nicholson R. A. Metallothionein expression in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1995 Oct;72(4):968–972. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haerslev T., Jacobsen K., Nedergaard L., Zedeler K. Immunohistochemical detection of metallothionein in primary breast carcinomas and their axillary lymph node metastases. Pathol Res Pract. 1994 Aug;190(7):675–681. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80746-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mididoddi S., McGuirt J. P., Sens M. A., Todd J. H., Sens D. A. Isoform-specific expression of metallothionein mRNA in the developing and adult human kidney. Toxicol Lett. 1996 Apr;85(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(96)03632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzen C. A., Cartel N. J., Yu W. H., Fraser P. E., McLachlan D. R. Sensitive detection of metallothioneins-1, -2 and -3 in tissue homogenates by immunoblotting: a method for enhanced membrane transfer and retention. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1996 May 14;32(2):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(95)00044-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama T., Take H., Hikino T., Iino Y., Nakajima T. Immunohistochemical expression of metallothionein in invasive breast cancer in relation to proliferative activity, histology and prognosis. Oncology. 1996 Mar-Apr;53(2):112–117. doi: 10.1159/000227546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaife C. J., Findley S. D., Erickson J. C., Froelick G. J., Kelly E. J., Zambrowicz B. P., Palmiter R. D. Induction of a new metallothionein isoform (MT-IV) occurs during differentiation of stratified squamous epithelia. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 14;33(23):7250–7259. doi: 10.1021/bi00189a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K. W., Ellis I. O., Gee J. M., Darke B. M., Lees W. E., Kay J., Cryer A., Stark J. M., Hittmair A., Ofner D. Presence and possible significance of immunocytochemically demonstrable metallothionein over-expression in primary invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;422(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01607167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Cell specificity and an effect of ras on human metallothionein gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Jubier M. F., Hamer D. H. Structure and expression of two human metallothionein-I isoform genes and a related pseudogene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7731–7737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stennard F. A., Holloway A. F., Hamilton J., West A. K. Characterisation of six additional human metallothionein genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Aug 2;1218(3):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West A. K., Stallings R., Hildebrand C. E., Chiu R., Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes: structure of the functional locus at 16q13. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90038-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. Y., Woo E. S., Reese C. E., Bahnson R. R., Saijo N., Lazo J. S. Human metallothionein isoform gene expression in cisplatin-sensitive and resistant cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





