Abstract
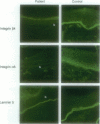
Epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia (EB-PA; OMIM 226730) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous autosomal recessive blistering disorder, including lethal and nonlethal variants. Recently, expression of alpha6beta4 integrin, a transmembrane protein of the epithelial basement membranes, has been shown to be altered in these patients. In this work, we have explored the molecular pathology of the lethal form of EB-PA, and we describe novel ITGB4 mutations in five alleles of three patients. The mutation detection strategy included polymerase chain reaction amplification of each exon of ITGB4, followed by heteroduplex analysis and direct nucleotide sequencing. The novel mutations included a homozygous 2-bp deletion in exon 34 (4501delTC), compound heterozygosity for a 2-bp deletion within the paternal allele (120delTG) within exon 3 and a cysteine substitution in the maternal allele (C245G) within exon 7, and the paternal nonsense mutation within exon 4 (Q73X). Thus, three of four distinct mutations predicted truncated polypeptide chains, whereas the missense mutation in the extracellular domain of beta4 integrin may affect ligand binding or dimerization of alpha6 and beta4 integrin subunits. These mutations emphasize the critical importance of the alpha6beta4 integrin in providing stability to the association of epidermis to the underlying dermis at the cutaneous basement membrane zone.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argraves W. S., Suzuki S., Arai H., Thompson K., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Amino acid sequence of the human fibronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., LaForgia S., Paller A. S., McGuire J., Shimizu H., Uitto J. Prenatal diagnosis for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in 10 families by mutation and haplotype analysis in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1). Mol Med. 1996 Jan;2(1):59–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Pulkkinen L., McGrath J. A., Uitto J. Mutation-based prenatal diagnosis of Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Prenat Diagn. 1997 Apr;17(4):343–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Uitto J. Molecular complexity of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Revelations from the paradigms of epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol. 1996 Feb;5(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Uitto J. Molecular diagnosis of inherited skin diseases: the paradigm of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Adv Dermatol. 1996;11:199–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden L. D., McLean W. H. Human keratin diseases: hereditary fragility of specific epithelial tissues. Exp Dermatol. 1996 Dec;5(6):297–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J., Yu Q. C., Fuchs E. Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;134(2):559–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltri M. L., Arona M., Scherer S. S., Wrabetz L. Cloning and sequence of the cDNA encoding the beta 4 integrin subunit in rat peripheral nerve. Gene. 1997 Feb 28;186(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00725-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. D., Bauer E. A., Briggaman R. A., Carter D. M., Eady R. A., Esterly N. B., Holbrook K. A., Hurwitz S., Johnson L., Lin A. Revised clinical and laboratory criteria for subtypes of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. A consensus report by the Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Classification of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Jan;24(1):119–135. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(91)70021-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Lo S. S., Phillips D. R. Protein sequence of endothelial glycoprotein IIIa derived from a cDNA clone. Identity with platelet glycoprotein IIIa and similarity to "integrin". J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3936–3939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly A., Rock M. J., Prockop D. J. Conformation-sensitive gel electrophoresis for rapid detection of single-base differences in double-stranded PCR products and DNA fragments: evidence for solvent-induced bends in DNA heteroduplexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10325–10329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges-Labouesse E., Messaddeq N., Yehia G., Cadalbert L., Dierich A., Le Meur M. Absence of integrin alpha 6 leads to epidermolysis bullosa and neonatal death in mice. Nat Genet. 1996 Jul;13(3):370–373. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil S. G., Brown T. A., Ryan M. C., Carter W. G. Junctional epidermolysis bullosis: defects in expression of epiligrin/nicein/kalinin and integrin beta 4 that inhibit hemidesmosome formation. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Nov;103(5 Suppl):31S–38S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12398953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Jones J. C. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes: structure and function of molecular components. FASEB J. 1996 Jun;10(8):871–881. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.10.8.8666164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto I., Schnyder U. W., Anton-Lamprecht I. Epidermolysis bullosa hereditaria with junctional blistering in an adult. Dermatologica. 1976;152(2):72–86. doi: 10.1159/000251166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintner H., Wolff K. Generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Arch Dermatol. 1982 Jun;118(6):375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., van Kessel A. G., Sonnenberg A. Molecular cloning of the human alpha 6 integrin subunit. Alternative splicing of alpha 6 mRNA and chromosomal localization of the alpha 6 and beta 4 genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):425–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., von dem Borne A. E., Sonnenberg A. Cloning and sequence analysis of beta-4 cDNA: an integrin subunit that contains a unique 118 kd cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):765–770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman M. F., de Jong M. C., Heeres K., Pas H. H., van der Meer J. B., Owaribe K., Martinez de Velasco A. M., Niessen C. M., Sonnenberg A. 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BP180) is deficient in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1345–1352. doi: 10.1172/JCI117785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Godfrey V., Ch'ang L. Y., Lankford T. K., Foote L. J., Makkinje A. The beta 4 subunit of the integrin family is displayed on a restricted subset of endothelium in mice. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):145–150. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Connor K., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Cloning of the beta subunit of the leukocyte adhesion proteins: homology to an extracellular matrix receptor defines a novel supergene family. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Vestal D. J., Cheresh D. A., Bodary S. C. cDNA sequence of the human integrin beta 5 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17126–17131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldgaard Lund A., Karlsmark T., Kobayasi T. Protein-losing enteropathy in a child with junctional epidermolysis bullosa and pyloric atresia. Acta Derm Venereol. 1995 Jan;75(1):59–61. doi: 10.2340/00015555755961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessen C. M., van der Raaij-Helmer M. H., Hulsman E. H., van der Neut R., Jonkman M. F., Sonnenberg A. Deficiency of the integrin beta 4 subunit in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia: consequences for hemidesmosome formation and adhesion properties. J Cell Sci. 1996 Jul;109(Pt 7):1695–1706. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.7.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault N., Vachon P. H., Beaulieu J. F. Appearance and distribution of laminin A chain isoforms and integrin alpha 2, alpha 3, alpha 6, beta 1, and beta 4 subunits in the developing human small intestinal mucosa. Anat Rec. 1995 Jun;242(2):242–250. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092420214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohla-Gubo G., Lazarova Z., Giudice G. J., Liebert M., Grassegger A., Hintner H., Yancey K. B. Diminished expression of the extracellular domain of bullous pemphigoid antigen 2 (BPAG2) in the epidermal basement membrane of patients with generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol. 1995 Aug;4(4 Pt 1):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1995.tb00245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulkkinen L., Kimonis V. E., Xu Y., Spanou E. N., McLean W. H., Uitto J. Homozygous alpha6 integrin mutation in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with congenital duodenal atresia. Hum Mol Genet. 1997 May;6(5):669–674. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.5.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulkkinen L., Kurtz K., Xu Y., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Uitto J. Genomic organization of the integrin beta 4 gene (ITGB4): a homozygous splice-site mutation in a patient with junctional epidermolysis bullosa associated with pyloric atresia. Lab Invest. 1997 Jun;76(6):823–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzzi L., Gagnoux-Palacios L., Pinola M., Belli S., Meneguzzi G., D'Alessio M., Zambruno G. A homozygous mutation in the integrin alpha6 gene in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. J Clin Invest. 1997 Jun 15;99(12):2826–2831. doi: 10.1172/JCI119474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D., Rozzo C., Starr L., Quaranta V., Erle D. J., Pytela R. Complete amino acid sequence of a novel integrin beta subunit (beta 6) identified in epithelial cells using the polymerase chain reaction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11502–11507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Suzumori K., Hatta N., Nishikawa T. Absence of detectable alpha 6 integrin in pyloric atresia-junctional epidermolysis bullosa syndrome. Application for prenatal diagnosis in a family at risk for recurrence. Arch Dermatol. 1996 Aug;132(8):919–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., Daams H., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Aplin J. D., Baker J., Loizidou M. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):907–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa Y., Shimizu H., Nishikawa T., Hatta N., Pulkkinen L., Uitto J. Novel ITGB4 mutations in a patient with junctional epidermolysis bullosa-pyloric atresia syndrome and altered basement membrane zone immunofluorescence for the alpha6beta4 integrin. J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Jun;108(6):943–946. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12296240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Christiano A. M. Molecular basis for the dystrophic forms of epidermolysis bullosa: mutations in the type VII collagen gene. Arch Dermatol Res. 1994;287(1):16–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00370713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Christiano A. M. Molecular genetics of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Perspectives on epidermolysis bullosa and other blistering skin diseases. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):687–692. doi: 10.1172/JCI115938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Pulkkinen L., McLean W. H. Epidermolysis bullosa: a spectrum of clinical phenotypes explained by molecular heterogeneity. Mol Med Today. 1997 Oct;3(10):457–465. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(97)01112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Pulkkinen L. Molecular complexity of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Mol Biol Rep. 1996;23(1):35–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00357071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Pulkkinen L., Smith F. J., McLean W. H. Plectin and human genetic disorders of the skin and muscle. The paradigm of epidermolysis bullosa with muscular dystrophy. Exp Dermatol. 1996 Oct;5(5):237–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal F., Aberdam D., Miquel C., Christiano A. M., Pulkkinen L., Uitto J., Ortonne J. P., Meneguzzi G. Integrin beta 4 mutations associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nat Genet. 1995 Jun;10(2):229–234. doi: 10.1038/ng0695-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee G. H., Hynes R. O. A novel, tissue-specific integrin subunit, beta nu, expressed in the midgut of Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):845–858. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Q. A., Jiang W. M., Krissansen G. W., Watson J. D. Cloning and sequence analysis of a novel beta 2-related integrin transcript from T lymphocytes: homology of integrin cysteine-rich repeats to domain III of laminin B chains. Int Immunol. 1990;2(11):1097–1108. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.11.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Neut R., Krimpenfort P., Calafat J., Niessen C. M., Sonnenberg A. Epithelial detachment due to absence of hemidesmosomes in integrin beta 4 null mice. Nat Genet. 1996 Jul;13(3):366–369. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]