Abstract
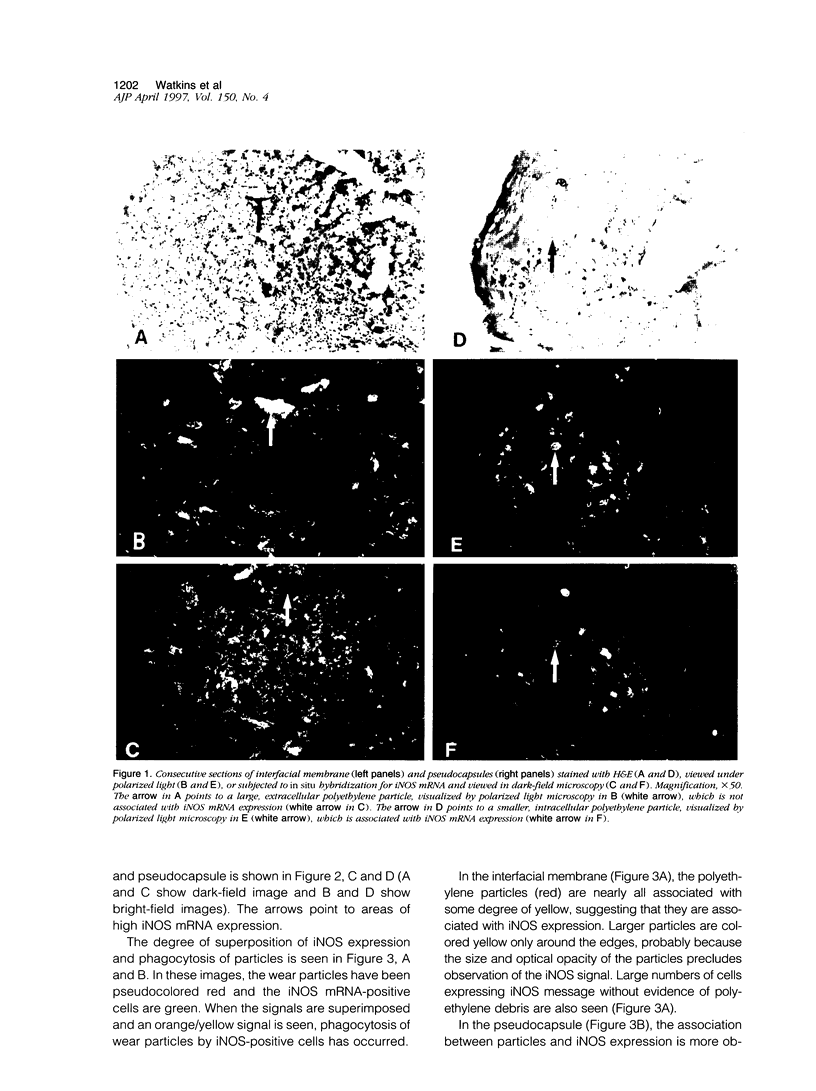
Exposure of rodent macrophages to certain cytokines and endotoxin results in the synthesis of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS or NOS-II) leading to the production of large amounts of nitric oxide (NO). Cultures of human macrophages, in contrast, do not produce iNOS after cytokine stimulation, and their ability to act as a physiological source of NO remains questionable. Here we have used immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization to demonstrate the presence of iNOS within human macrophages present in the interfacial membrane and pseudocapsule that surround failed prosthetic hip joints. Synovial tissue recovered from normal human joints did not express iNOS. Many of the iNOS-positive macrophages within the interfacial membrane had phagocytosed large amounts of polyethylene wear debris, suggesting a role for phagocytic stimuli in inducing iNOS in human macrophages. These findings additionally support a role for NO in modulating the localized bone resorption that accompanies the aseptic loosening of prosthetic joints.
Full text
PDF


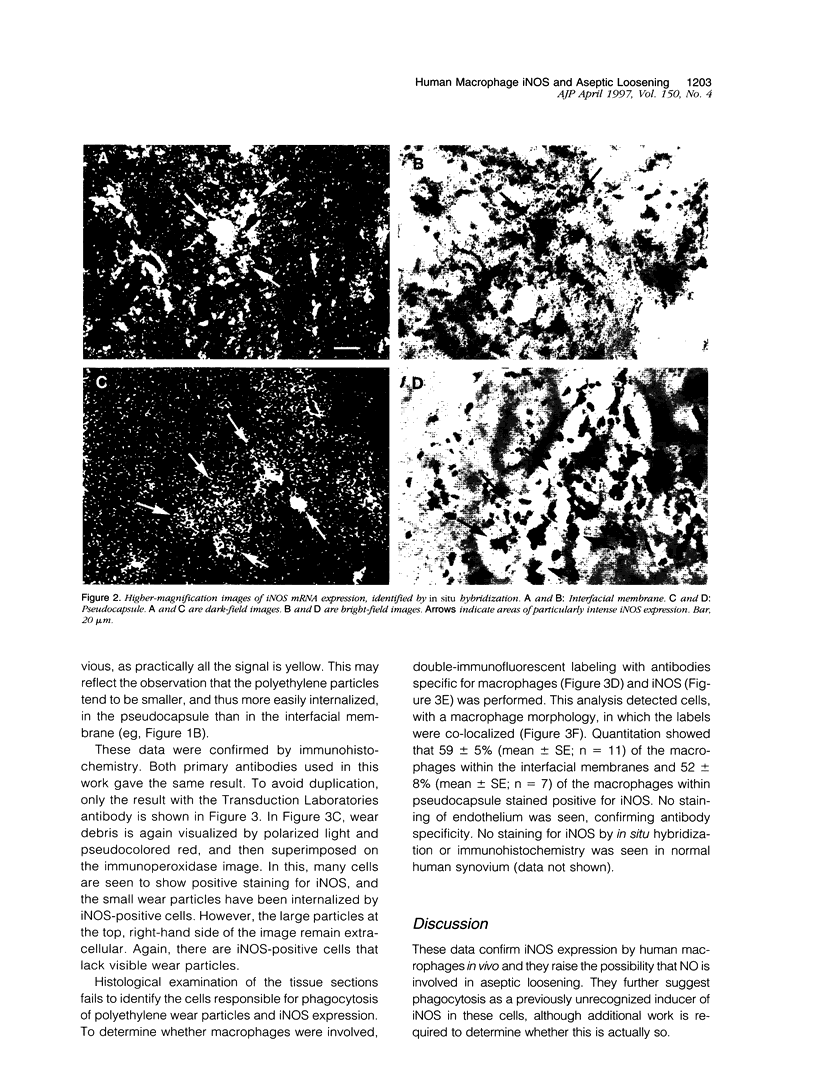
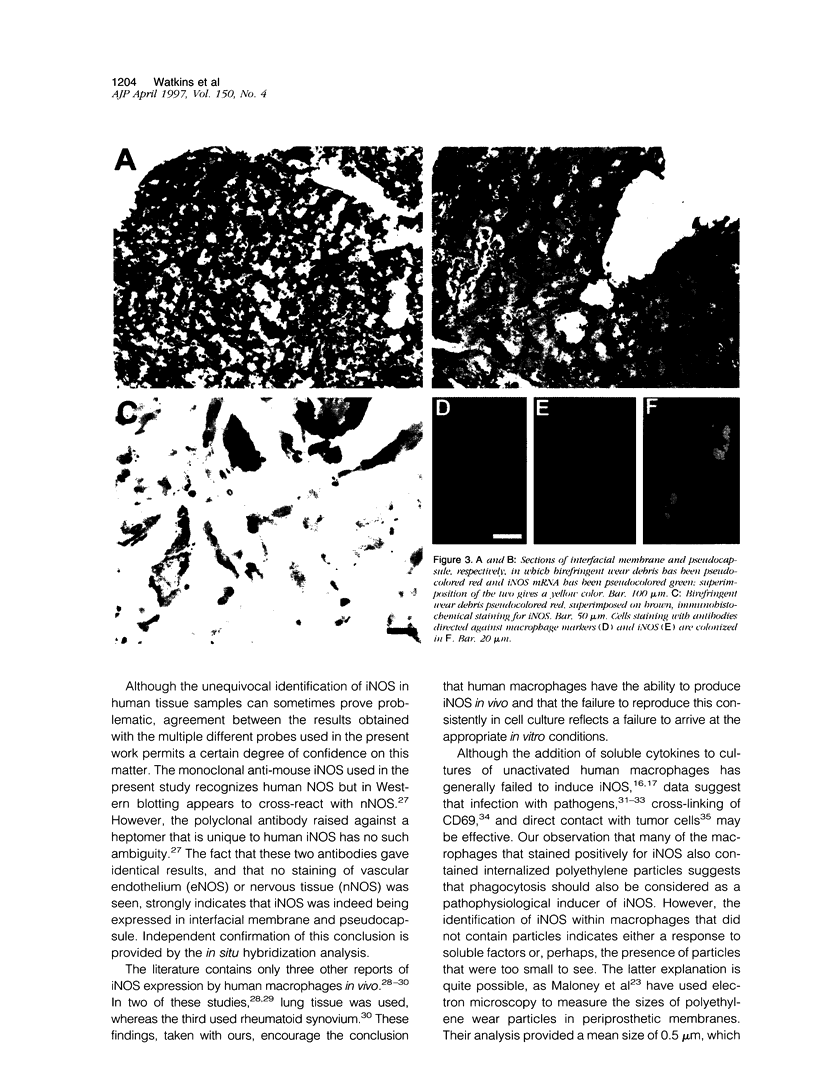


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albina J. E. On the expression of nitric oxide synthase by human macrophages. Why no NO? J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Dec;58(6):643–649. doi: 10.1002/jlb.58.6.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin A. R., Di Cesare P. E., Vyas P., Attur M., Tzeng E., Billiar T. R., Stuchin S. A., Abramson S. B. The expression and regulation of nitric oxide synthase in human osteoarthritis-affected chondrocytes: evidence for up-regulated neuronal nitric oxide synthase. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):2097–2102. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Nottet H. S., Schmidtmayerova H., Dubrovsky L., Flanagan C. R., Mullins M. E., Lipton S. A., Gendelman H. E. Regulation of nitric oxide synthase activity in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected monocytes: implications for HIV-associated neurological disease. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):735–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charosky C. B., Bullough P. G., Wilson P. D., Jr Total hip replacement failures. A histological evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973 Jan;55(1):49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Sweetland M. A., Wang J. L., Lancaster J. R., Jr, McDaniel M. L. Nitric oxide mediates cytokine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by human islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damoulis P. D., Hauschka P. V. Cytokines induce nitric oxide production in mouse osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jun 15;201(2):924–931. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maria R., Cifone M. G., Trotta R., Rippo M. R., Festuccia C., Santoni A., Testi R. Triggering of human monocyte activation through CD69, a member of the natural killer cell gene complex family of signal transducing receptors. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1999–2004. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Human monocytes/macrophages: NO or no NO? J Leukoc Biol. 1994 May;55(5):682–684. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor stimulate human macrophages to restrict growth of virulent Mycobacterium avium and to kill avirulent M. avium: killing effector mechanism depends on the generation of reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Apr;49(4):380–387. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. H., Mazzocchi R. A., Nelson D. D., Rubash H. E. Experimental arthritis induced by intraarticular injection of allogenic cartilaginous particles into rabbit knees. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):200–207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. H., Mears D. C., McKnight J. L. A preliminary ferrographic survey of the wear particles in human synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jul;24(7):912–918. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. H., Stefanovic-Racic M., Lancaster J. Nitric oxide and its role in orthopaedic disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995 Mar;(312):275–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Closs E. I., Pollock J. S., Nakane M., Schwarz P., Gath I., Kleinert H. Nitric oxide synthase isozymes. Characterization, purification, molecular cloning, and functions. Hypertension. 1994 Jun;23(6 Pt 2):1121–1131. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.23.6.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galante J. O., Lemons J., Spector M., Wilson P. D., Jr, Wright T. M. The biologic effects of implant materials. J Orthop Res. 1991 Sep;9(5):760–775. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100090516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring S. R., Schiller A. L., Roelke M., Rourke C. M., O'Neil D. A., Harris W. H. The synovial-like membrane at the bone-cement interface in loose total hip replacements and its proposed role in bone lysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983 Jun;65(5):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greis P. E., Georgescu H. I., Fu F. H., Evans C. H. Particle-induced synthesis of collagenase by synovial fibroblasts: an immunocytochemical study. J Orthop Res. 1994 Mar;12(2):286–293. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100120219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruen T. A., McNeice G. M., Amstutz H. C. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979 Jun;(141):17–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. H., Sledge C. B. Total hip and total knee replacement (1). N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 13;323(11):725–731. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009133231106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasten T. P., Collin-Osdoby P., Patel N., Osdoby P., Krukowski M., Misko T. P., Settle S. L., Currie M. G., Nickols G. A. Potentiation of osteoclast bone-resorption activity by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Chiba J., Rubash H. E. In vivo and in vitro analysis of membranes from hip prostheses inserted without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994 Feb;76(2):172–180. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199402000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide as a signal in blood vessels. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90008-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 1;298(Pt 2):249–258. doi: 10.1042/bj2980249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobzik L., Bredt D. S., Lowenstein C. J., Drazen J., Gaston B., Sugarbaker D., Stamler J. S. Nitric oxide synthase in human and rat lung: immunocytochemical and histochemical localization. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;9(4):371–377. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.4.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre I., Zaidi M., Alam A. S., Datta H. K., Moonga B. S., Lidbury P. S., Hecker M., Vane J. R. Osteoclastic inhibition: an action of nitric oxide not mediated by cyclic GMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney W. J., Smith R. L., Schmalzried T. P., Chiba J., Huene D., Rubash H. Isolation and characterization of wear particles generated in patients who have had failure of a hip arthroplasty without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995 Sep;77(9):1301–1310. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton S. J., Shorthouse M., Hunter J. O. Increased nitric oxide synthesis in ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1993 Feb 20;341(8843):465–466. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. M., Jr, Billiar T. R. New insights into the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):E829–E839. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.266.6.E829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S., Bonecini-Almeida M. da G., Lapa e Silva J. R., Nathan C., Xie Q. W., Mumford R., Weidner J. R., Calaycay J., Geng J., Boechat N. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in pulmonary alveolar macrophages from patients with tuberculosis. J Exp Med. 1996 May 1;183(5):2293–2302. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.5.2293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussler A. K., Billiar T. R. Inflammation, immunoregulation, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Aug;54(2):171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. J., Kang J. D., Fu F. H., Georgescu H. I., Mason G. C., Evans C. H. The biochemical and histological effects of artificial ligament wear particles: in vitro and in vivo studies. Am J Sports Med. 1988 Nov-Dec;16(6):558–570. doi: 10.1177/036354658801600602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston S. H., Todd D., Helfrich M., Benjamin N., Grabowski P. S. Human osteoblast-like cells produce nitric oxide and express inducible nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1994 Jul;135(1):330–336. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.1.7516867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai H., Kohsaka H., Liu M. F., Higashiyama H., Hirata Y., Kanno K., Saito I., Miyasaka N. Nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in inflammatory arthritides. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2357–2363. doi: 10.1172/JCI118292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. P., Loro M. L., Wong V. Z., Tashkin D. P. Cytokine- and Pneumocystis carinii- induced L-arginine oxidation by murine and human pulmonary alveolar macrophages. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):234S–236S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Stefanovic-Racic M., Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., McIntyre L. A., Georgescu H. I., Simmons R. L., Evans C. H. Articular chondrocytes synthesize nitric oxide in response to cytokines and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3915–3920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic-Racic M., Stadler J., Evans C. H. Nitric oxide and arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1036–1044. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic-Racic M., Stadler J., Georgescu H. I., Evans C. H. Nitric oxide synthesis and its regulation by rabbit synoviocytes. J Rheumatol. 1994 Oct;21(10):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey W. R., Xue C., Klinghofer V., Barlow J., Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Johns R. A. Immunochemical detection of inducible NO synthase in human lung. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L722–L727. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willert H. G., Ludwig J., Semlitsch M. Reaction of bone to methacrylate after hip arthroplasty: a long-term gross, light microscopic, and scanning electron microscopic study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 Oct;56(7):1368–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q., Nathan C. The high-output nitric oxide pathway: role and regulation. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Nov;56(5):576–582. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.5.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembala M., Siedlar M., Marcinkiewicz J., Pryjma J. Human monocytes are stimulated for nitric oxide release in vitro by some tumor cells but not by cytokines and lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Feb;24(2):435–439. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]