Abstract
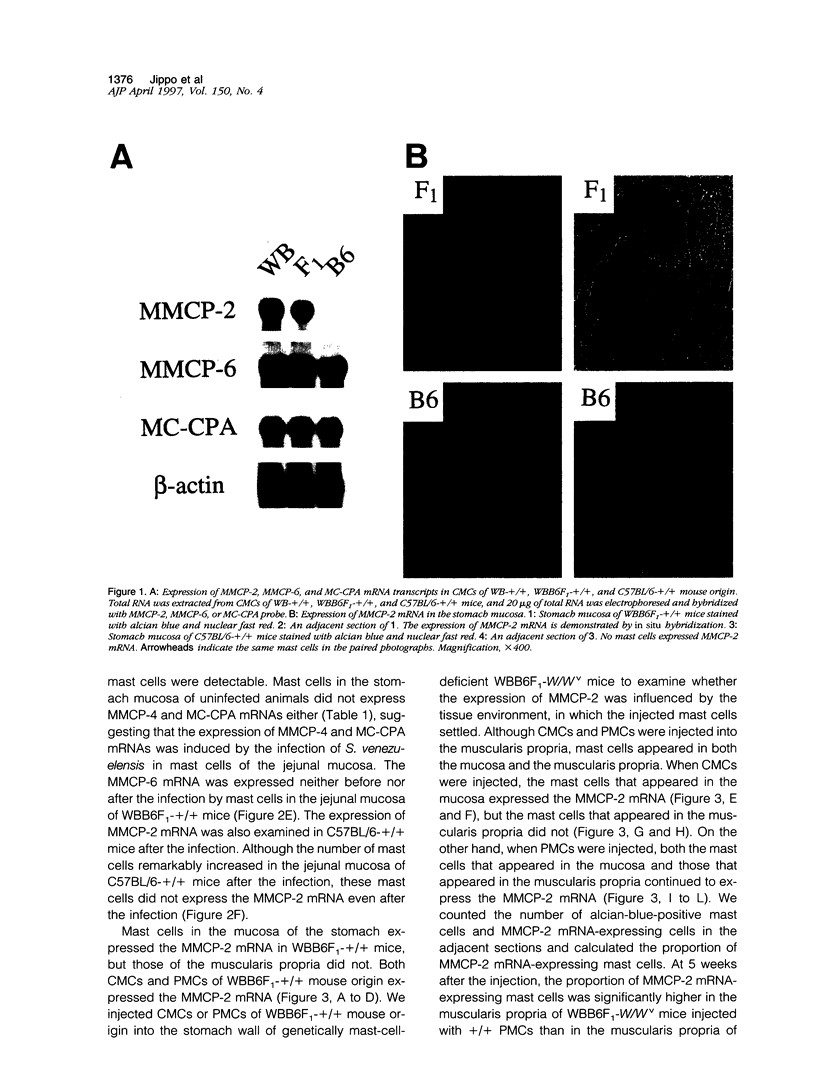
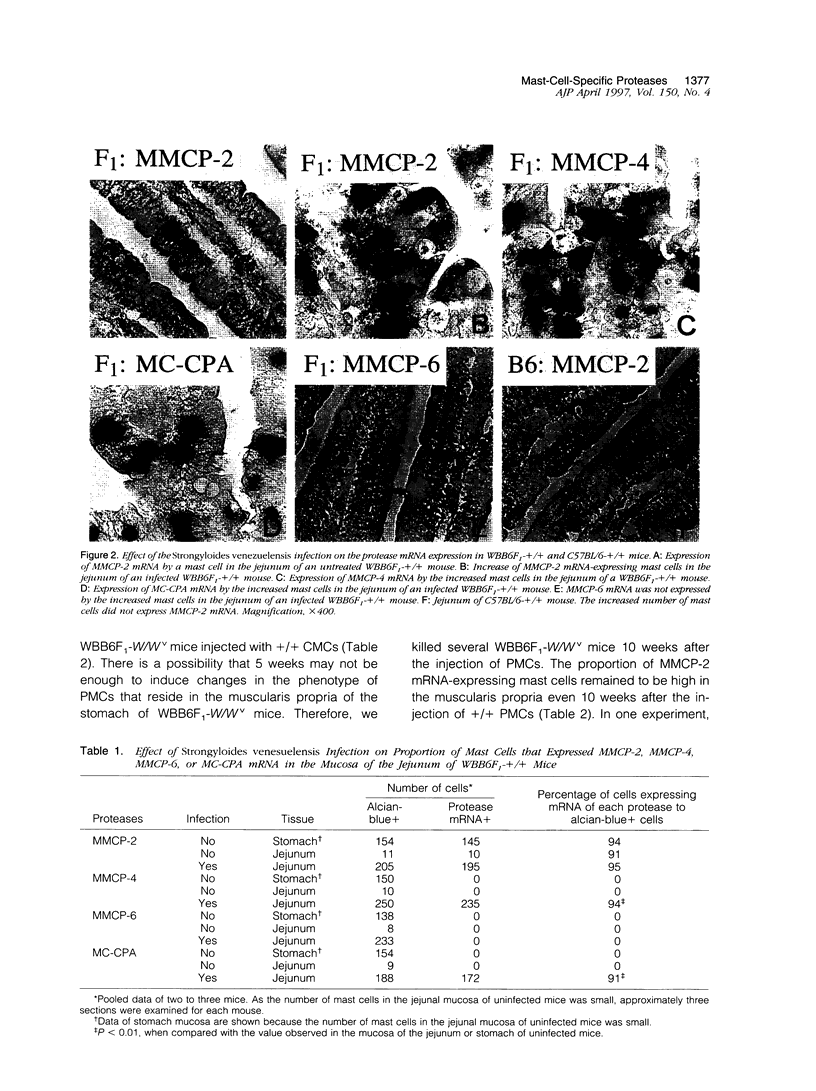
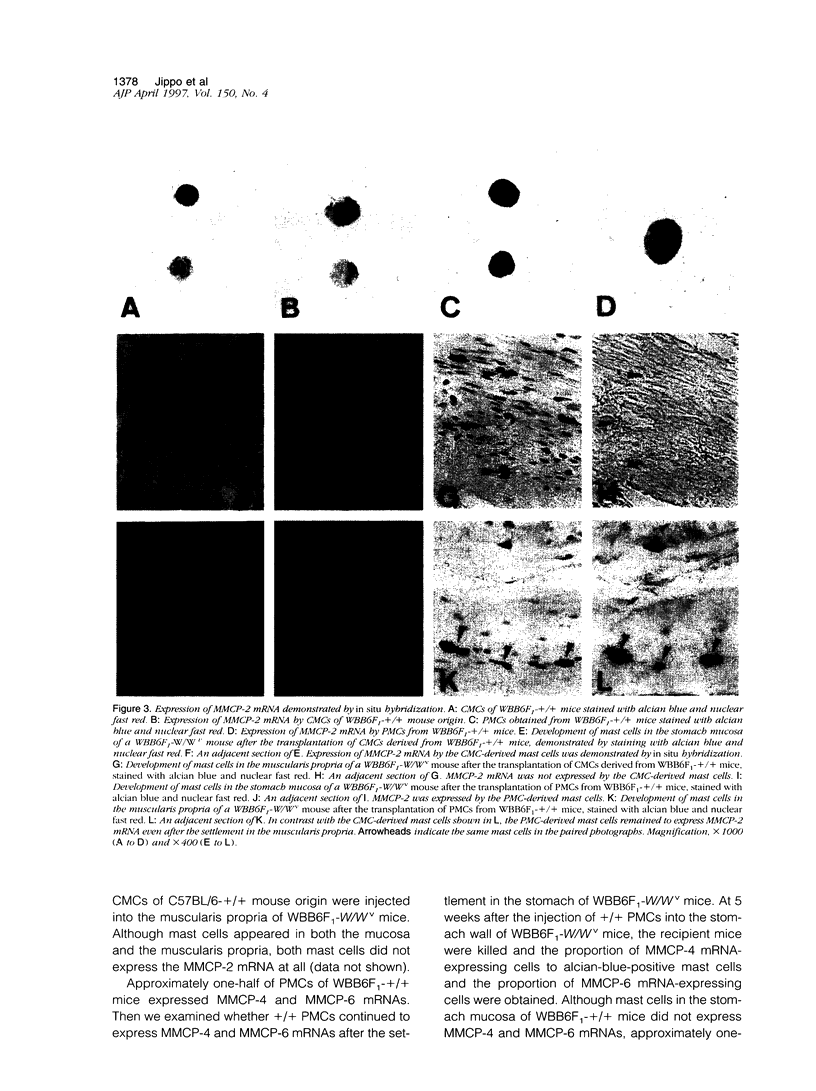
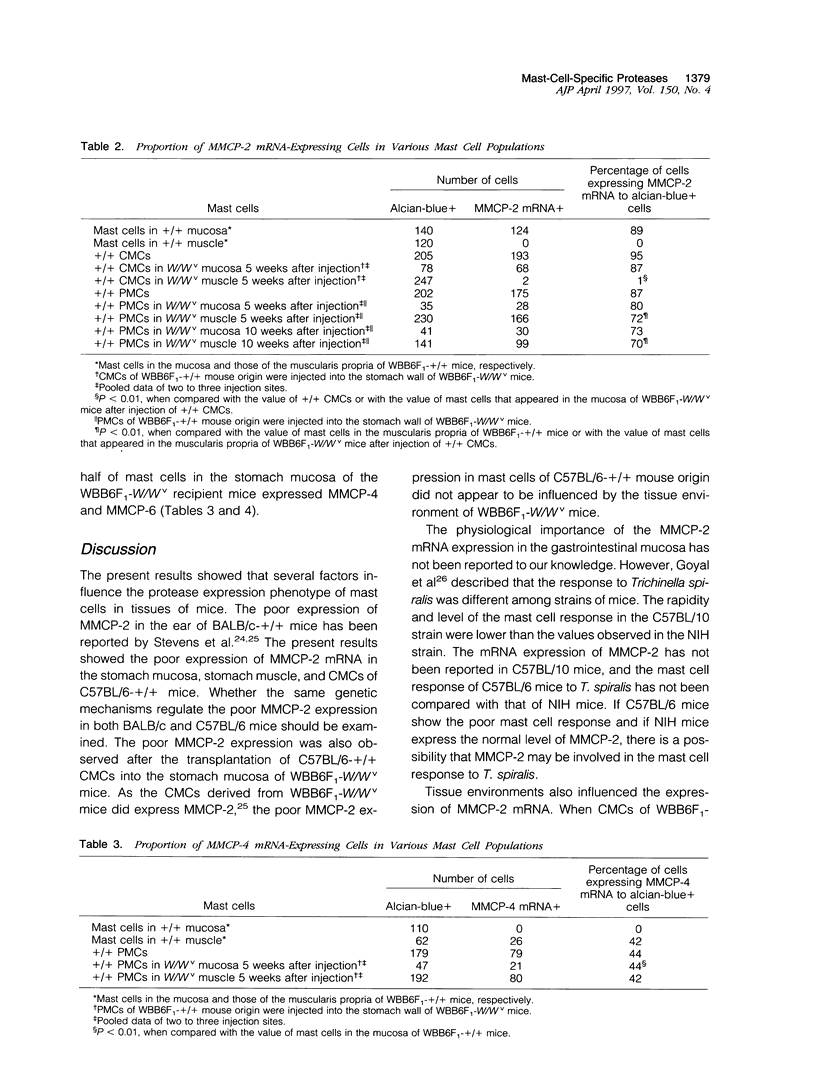
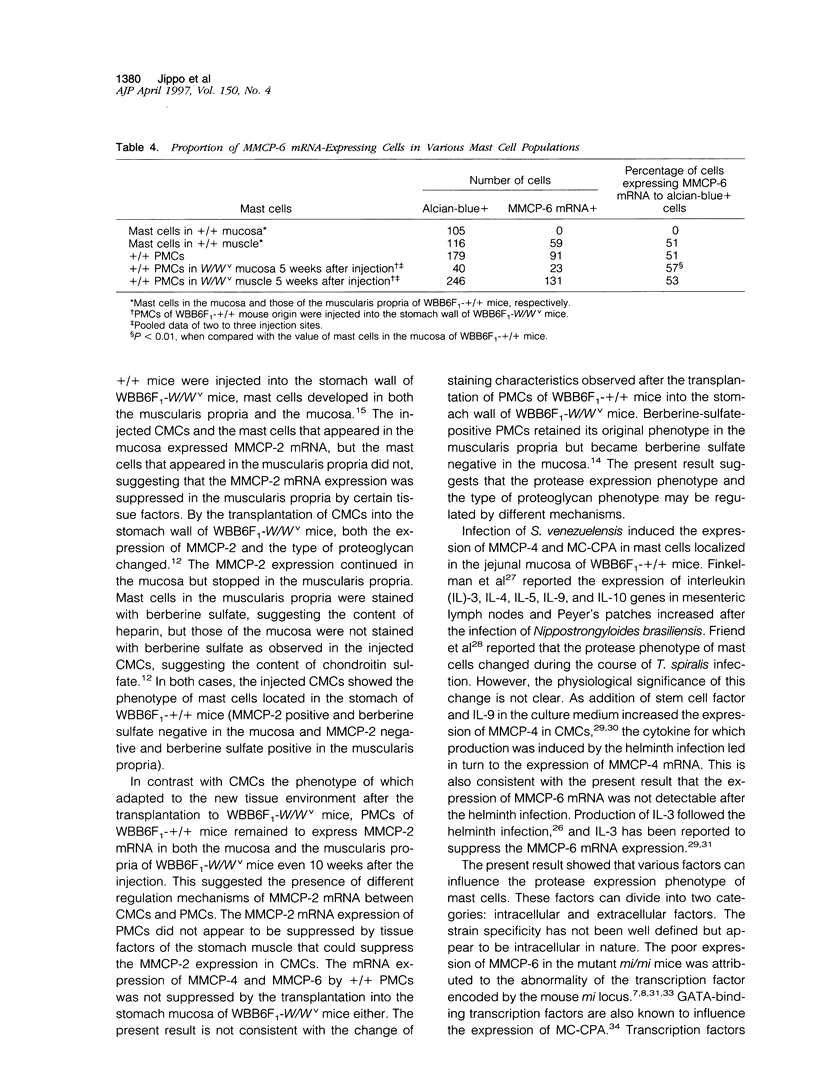
The protease mRNA expression phenotype of individual mast cells was studied by in situ hybridization. Mouse mast cell protease (MMCP)-2 mRNA was expressed by mast cells located in the mucosa of the stomach of WB(-)+/+ and (WB x C57BL/6)F1(-)+/+ (hereafter WBB6F1(-)+/+) mice but not by mast cells in the same tissue of C57BL/ 6(-)+/+ mice. Even in the stomach of WBB6F1(-)+/+ mice, mast cells located in the muscularis propria did not express MMCP-2 mRNA. The mRNAs of MMCP-4 and mouse mast cell carboxypeptidase A were not expressed by mast cells in the stomach mucosa of untreated WBB6F1(-)+/+ mice but were expressed after the infection of Strongyloides venezuelensis. We examined whether MMCP-2 mRNA expression varied by changing environments of mast cells. Cultured mast cells of WBB6F1(-)+/+ mice that expressed MMCP-2 mRNA were transplanted into the stomach wall of genetically mast-cell-deficient WBB6F1(-)W/Wv mice. Mast cells that appeared in the mucosa expressed the MMCP-2 mRNA, but mast cells that appeared in the muscularis propria did not, indicating the adaptation of cultured mast cells into a new environment. In contrast to cultured mast cells, peritoneal mast cells of WBB6F1(-)+/+ mice that expressed MMCP-2 mRNA as well did not adapt to the muscularis propria of WBB6F(1)-W/Wv mice. The MMCP-2 mRNA remained to be expressed after the settlement in either the mucosa or the muscularis propria. Furthermore, the peritoneal mast cells did not change the MMCP-4 and MMCP-6 mRNA expression phenotype after the settlement in either the mucosa or the muscularis propria of WBB6F(1)-W/Wv mice. The present result indicated that both intracellular factors such as strain specificity and source of mast cells and extracellular factors such as tissue specificity and helminth infection influenced the protease expression phenotypes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldenborg F., Enerbäck L. Histochemical heterogeneity of dermal mast cells in athymic and normal rats. Histochem J. 1988 Jan;20(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01745965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggaman R. A., Schechter N. M., Fraki J., Lazarus G. S. Degradation of the epidermal-dermal junction by proteolytic enzymes from human skin and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1027–1042. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebi Y., Kanakura Y., Jippo-Kanemoto T., Tsujimura T., Furitsu T., Ikeda H., Adachi S., Kasugai T., Nomura S., Kanayama Y. Low c-kit expression of cultured mast cells of mi/mi genotype may be involved in their defective responses to fibroblasts that express the ligand for c-kit. Blood. 1992 Sep 15;80(6):1454–1462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund K. K., Ghildyal N., Austen K. F., Friend D. S., Schiller V., Stevens R. L. Mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (mBMMC) obtained in vitro from mice that are mast cell-deficient in vivo express the same panel of granule proteases as mBMMC and serosal mast cells from their normal littermates. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):67–73. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund K. K., Ghildyal N., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Induction by IL-9 and suppression by IL-3 and IL-4 of the levels of chromosome 14-derived transcripts that encode late-expressed mouse mast cell proteases. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4266–4273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Madden K. B., Cheever A. W., Katona I. M., Morris S. C., Gately M. K., Hubbard B. R., Gause W. C., Urban J. F., Jr Effects of interleukin 12 on immune responses and host protection in mice infected with intestinal nematode parasites. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1563–1572. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Ghildyal N., Austen K. F., Gurish M. F., Matsumoto R., Stevens R. L. Mast cells that reside at different locations in the jejunum of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis exhibit sequential changes in their granule ultrastructure and chymase phenotype. J Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;135(1):279–290. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghildyal N., McNeil H. P., Stechschulte S., Austen K. F., Silberstein D., Gurish M. F., Somerville L. L., Stevens R. L. IL-10 induces transcription of the gene for mouse mast cell protease-1, a serine protease preferentially expressed in mucosal mast cells of Trichinella spiralis-infected mice. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2123–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal P. K., Wakelin D. Influence of variation in host strain and parasite isolate on inflammatory and antibody responses to Trichinella spiralis in mice. Parasitology. 1993 May;106(Pt 4):371–378. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000067111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber B. L., Marchese M. J., Suzuki K., Schwartz L. B., Okada Y., Nagase H., Ramamurthy N. S. Synovial procollagenase activation by human mast cell tryptase dependence upon matrix metalloproteinase 3 activation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1657–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI114344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurish M. F., Ghildyal N., McNeil H. P., Austen K. F., Gillis S., Stevens R. L. Differential expression of secretory granule proteases in mouse mast cells exposed to interleukin 3 and c-kit ligand. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1003–1012. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann T., Ruoss S. J., Raymond W. W., Seuwen K., Caughey G. H. Human tryptase as a potent, cell-specific mitogen: role of signaling pathways in synergistic responses. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):L528–L534. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.5.L528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Tsujimura T., Moriyama Y., Yamatodani A., Kimura M., Tohya K., Morimoto M., Kitayama H., Kanakura Y., Kitamura Y. Transforming and differentiation-inducing potential of constitutively activated c-kit mutant genes in the IC-2 murine interleukin-3-dependent mast cell line. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jan;148(1):189–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isozaki K., Tsujimura T., Nomura S., Morii E., Koshimizu U., Nishimune Y., Kitamura Y. Cell type-specific deficiency of c-kit gene expression in mutant mice of mi/mi genotype. Am J Pathol. 1994 Oct;145(4):827–836. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jippo T., Ushio H., Hirota S., Mizuno H., Yamatodani A., Nomura S., Matsuda H., Kitamura Y. Poor response of cultured mast cells derived from mi/mi mutant mice to nerve growth factor. Blood. 1994 Nov 1;84(9):2977–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasugai T., Oguri K., Jippo-Kanemoto T., Morimoto M., Yamatodani A., Yoshida K., Ebi Y., Isozaki K., Tei H., Tsujimura T. Deficient differentiation of mast cells in the skin of mi/mi mice. Usefulness of in situ hybridization for evaluation of mast cell phenotype. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1337–1347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. I., Horii Y., Tiuria R., Sato Y., Nawa Y. Mucosal mast cells and the expulsive mechanisms of mice against Strongyloides venezuelensis. Int J Parasitol. 1993 Aug;23(5):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(93)90159-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S., Hatanaka K. Decrease of mast cells in W/Wv mice and their increase by bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Austen K. F., Somerville L. L., Gurish M. F., Stevens R. L. Molecular cloning of the mouse mast cell protease-5 gene. A novel secretory granule protease expressed early in the differentiation of serosal mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20316–20322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Reynolds D. S., Schiller V., Ghildyal N., Gurley D. S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Isolation, characterization, and transcription of the gene encoding mouse mast cell protease 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11174–11178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H., Schechter N., Lazarus G., Black R. A., Kupper T. S. Rapid and specific conversion of precursor interleukin 1 beta (IL-1 beta) to an active IL-1 species by human mast cell chymase. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):821–825. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii E., Takebayashi K., Motohashi H., Yamamoto M., Nomura S., Kitamura Y. Loss of DNA binding ability of the transcription factor encoded by the mutant mi locus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 15;205(2):1299–1304. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii E., Tsujimura T., Jippo T., Hashimoto K., Takebayashi K., Tsujino K., Nomura S., Yamamoto M., Kitamura Y. Regulation of mouse mast cell protease 6 gene expression by transcription factor encoded by the mi locus. Blood. 1996 Oct 1;88(7):2488–2494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Spicer S. S., Cantey J. R., Ogawa M. Clonal assay of mouse mast cell colonies in methylcellulose culture. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):352–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Sonoda T., Hayashi C., Yamatodani A., Kanayama Y., Yamamura T., Asai H., Yonezawa T., Kitamura Y., Galli S. J. Fate of bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells after intracutaneous, intraperitoneal, and intravenous transfer into genetically mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. Evidence that cultured mast cells can give rise to both connective tissue type and mucosal mast cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1025–1043. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Wills A. J., Edwards D. R., Heath J. K., Hogan B. L. Developmental expression of 2ar (osteopontin) and SPARC (osteonectin) RNA as revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):441–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu K., Nakano T., Kanakura Y., Asai H., Katz H. R., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L., Galli S. J., Kitamura Y. Phenotypic changes of bone marrow-derived mast cells after intraperitoneal transfer into W/Wv mice that are genetically deficient in mast cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):615–627. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Gurley D. S., Austen K. F., Serafin W. E. Cloning of the cDNA and gene of mouse mast cell protease-6. Transcription by progenitor mast cells and mast cells of the connective tissue subclass. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3847–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Stevens R. L., Gurley D. S., Lane W. S., Austen K. F., Serafin W. E. Isolation and molecular cloning of mast cell carboxypeptidase A. A novel member of the carboxypeptidase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20094–20099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Toma H. Strongyloides venezuelensis infections in mice. Int J Parasitol. 1990 Feb;20(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(90)90173-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Bradford T. R., Littman B. H., Wintroub B. U. The fibrinogenolytic activity of purified tryptase from human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2762–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafin W. E., Reynolds D. S., Rogelj S., Lane W. S., Conder G. A., Johnson S. S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Identification and molecular cloning of a novel mouse mucosal mast cell serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafin W. E., Sullivan T. P., Conder G. A., Ebrahimi A., Marcham P., Johnson S. S., Austen K. F., Reynolds D. S. Cloning of the cDNA and gene for mouse mast cell protease 4. Demonstration of its late transcription in mast cell subclasses and analysis of its homology to subclass-specific neutral proteases of the mouse and rat. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1934–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda S., Sonoda T., Nakano T., Kanayama Y., Kanakura Y., Asai H., Yonezawa T., Kitamura Y. Development of mucosal mast cells after injection of a single connective tissue-type mast cell in the stomach mucosa of genetically mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1319–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Friend D. S., McNeil H. P., Schiller V., Ghildyal N., Austen K. F. Strain-specific and tissue-specific expression of mouse mast cell secretory granule proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):128–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Kaempfer C. E., Schechter N. M., Proud D. A human lung mast cell chymotrypsin-like enzyme. Identification and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):196–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI112276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura T., Nakano T., Fukuzumi T., Waki N., Asai H., Yoshikawa K., Kitamura Y. Electron microscopic changes of bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells after injection into the skin of genetically mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Sep;91(3):269–273. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurt R. W., Leid R. W., Jr, Austen K. F. Native heparin from rat peritoneal mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):518–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Gurish M. F., Stevens R. L., Mather C., Reynolds D. S., Austen K. F., Orkin S. H. GATA-binding transcription factors in mast cells regulate the promoter of the mast cell carboxypeptidase A gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22948–22953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]