Abstract
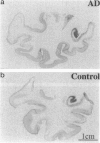
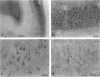
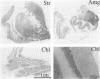
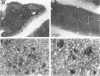
Cytokines mediate inflammatory responses through their receptors in the hematopoietic system. In a search for potential mediators of inflammatory responses in Alzheimer's disease, we examined brain for cytokine receptors. Herein we describe interleukin-8 receptor B (IL-8RB, also termed CXCR2) immunoreactivity in the central nervous system. Strong IL-8RB immunoreactivity is present in both Alzheimer's disease and control brains. Neurons, dendrites, and axons are clearly immunoreactive. In Alzheimer's disease, IL-8RB immunoreactivity is also present in some swollen dystrophic neurites of neuritic plaques. Double staining and confocal microscopic analysis reveals that these IL-8RB-positive neurites in plaques are neurofilament positive and are distinct from astrocytic or microglial processes. In general, these IL-8RB-positive neurities do not co-localize with PHF-1 or AT8 (hyperphosphorylated tau) immunoreactive neurites but instead co-localize with beta PP-positive neurites. These results demonstrate for the first time IL-8RB immunoreactivity in the central nervous system and imply a new role for this receptor outside the hematopoietic system. The strong presence of IL-8RB on neurons and the potential of glial cells to produce IL-8 suggest that this system might mediate neuronal-glial interactions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloisi F., Carè A., Borsellino G., Gallo P., Rosa S., Bassani A., Cabibbo A., Testa U., Levi G., Peschle C. Production of hemolymphopoietic cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, colony-stimulating factors) by normal human astrocytes in response to IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2358–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo D. M., Cotman C. W. Trophic effects of interleukin-4, -7 and -8 on hippocampal neuronal cultures: potential involvement of glial-derived factors. Brain Res. 1993 Jan 8;600(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90400-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B., Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines--CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behl C., Davis J. B., Lesley R., Schubert D. Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid beta protein toxicity. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):817–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz L. I., Perrone-Bizzozero N. I., Neve R. L., Rodriguez W. GAP-43 as a marker for structural plasticity in the mature CNS. Prog Brain Res. 1990;86:309–320. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz L. I., Perrone-Bizzozero N. I. The expression of GAP-43 in relation to neuronal growth and plasticity: when, where, how, and why? Prog Brain Res. 1991;89:69–87. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61716-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuntharapai A., Lee J., Hébert C. A., Kim K. J. Monoclonal antibodies detect different distribution patterns of IL-8 receptor A and IL-8 receptor B on human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 15;153(12):5682–5688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. W., Anderson K. J., Cotman C. W. Senile plaques as aberrant sprout-stimulating structures. Exp Neurol. 1986 Dec;94(3):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(86)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter B. D., Cox L. M., Rydel R. E., May P. C. Amyloid beta peptide potentiates cytokine secretion by interleukin-1 beta-activated human astrocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10738–10741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R., Vanmechelen E. Monoclonal antibody AT8 recognises tau protein phosphorylated at both serine 202 and threonine 205. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Apr 21;189(3):167–169. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11484-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P., Schein J. D., Binder L. I. Hydrofluoric acid-treated tau PHF proteins display the same biochemical properties as normal tau. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin W. S., Sheng J. G., Roberts G. W., Mrak R. E. Interleukin-1 expression in different plaque types in Alzheimer's disease: significance in plaque evolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1995 Mar;54(2):276–281. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199503000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley K., Carney J. M., Mattson M. P., Aksenova M., Harris M., Wu J. F., Floyd R. A., Butterfield D. A. A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3270–3274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Martin A., Hesselgesser J., Hadley T., Lu Z. H., Wang Z. X., Peiper S. C. The Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines: structural analysis and expression in the brain. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Jan;59(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Tanzi R. E., Marzloff K., Barbour R., Schenk D. Kunitz protease inhibitor-containing amyloid beta protein precursor immunoreactivity in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jan;51(1):76–83. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Wolf M., Qin S., Mackay C. R., Baggiolini M. Different functions for the interleukin 8 receptors (IL-8R) of human neutrophil leukocytes: NADPH oxidase and phospholipase D are activated through IL-8R1 but not IL-8R2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Harlow L. A., DiPietro L. A., Elner V. M., Elner S. G., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1798–1801. doi: 10.1126/science.1281554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Mallory M., Deerinck T., DeTeresa R., Lamont S., Miller A., Terry R. D., Carragher B., Ellisman M. Re-evaluation of the structural organization of neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Nov;52(6):619–632. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199311000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Mallory M., Hansen L., Alford M., Albright T., DeTeresa R., Terry R., Baudier J., Saitoh T. Patterns of aberrant sprouting in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Mallory M., Hansen L., Alford M., DeTeresa R., Terry R., Baudier J., Saitoh T. Localization of amyloid precursor protein in GAP43-immunoreactive aberrant sprouting neurites in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1992 Mar 6;574(1-2):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90831-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1995 Sep;21(2):195–218. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(95)00011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrak R. E., Sheng J. G., Griffin W. S. Glial cytokines in Alzheimer's disease: review and pathogenic implications. Hum Pathol. 1995 Aug;26(8):816–823. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90001-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney L. B., Mueller S. G., Bueno R., Peiper S. C., Richmond A. Distributions of melanoma growth stimulatory activity of growth-regulated gene and the interleukin-8 receptor B in human wound repair. Am J Pathol. 1995 Nov;147(5):1248–1260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta T., Allegretta M., Okumura K., Sato K., Steinman L. Neoplastic and reactive human astrocytes express interleukin-8 gene. Neurosurg Rev. 1992;15(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00345934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. Cytokines in Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Oct;5(5):642–646. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin S., LaRosa G., Campbell J. J., Smith-Heath H., Kassam N., Shi X., Zeng L., Buthcher E. C., Mackay C. R. Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin-8 receptors on subsets of T cells: correlation with transendothelial chemotactic potential. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Mar;26(3):640–647. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Villarete L. Regulation of cytokine gene expression by reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Apr;59(4):471–475. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Mufson E. J. Demonstrating immune-related antigens in Alzheimer's disease brain tissue. Neurobiol Aging. 1990 Jul-Aug;11(4):477–479. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(90)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meir E., Ceska M., Effenberger F., Walz A., Grouzmann E., Desbaillets I., Frei K., Fontana A., de Tribolet N. Interleukin-8 is produced in neoplastic and infectious diseases of the human central nervous system. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4297–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Ruffing N., Shi X., Newman W., Soler D., Mackay C. R., Qin S. Discrete steps in binding and signaling of interleukin-8 with its receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 6;271(49):31202–31209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.49.31202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]