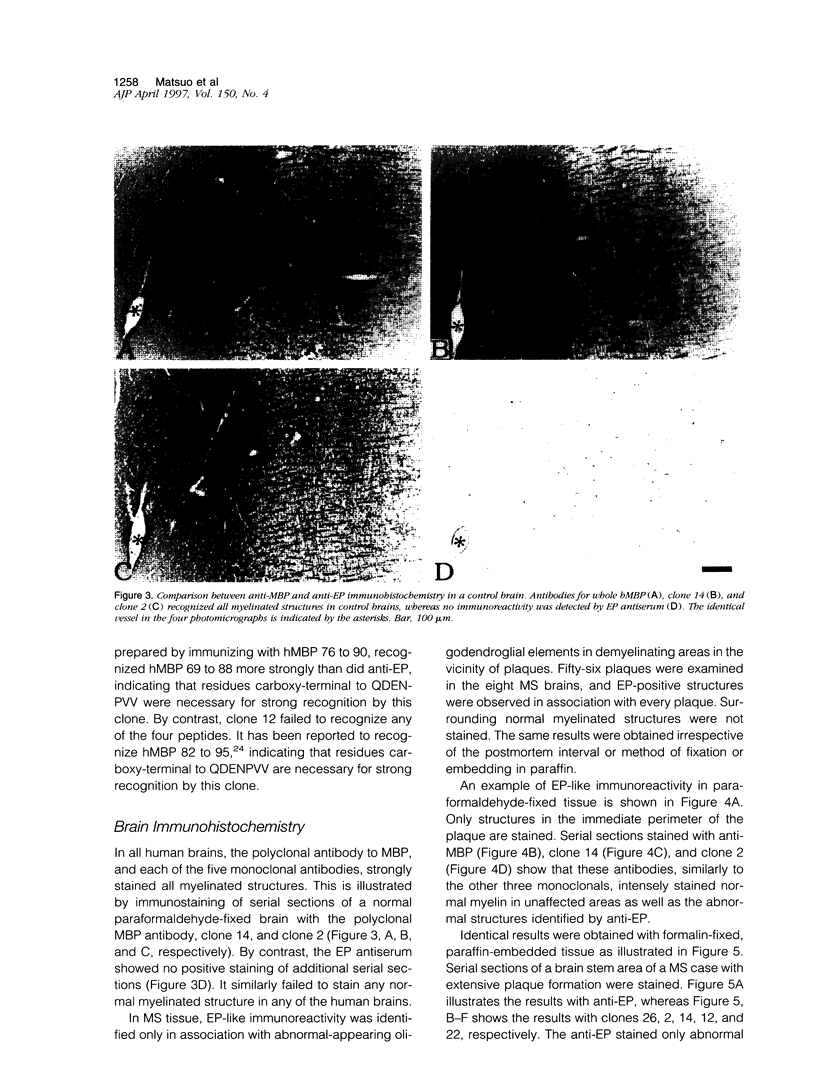
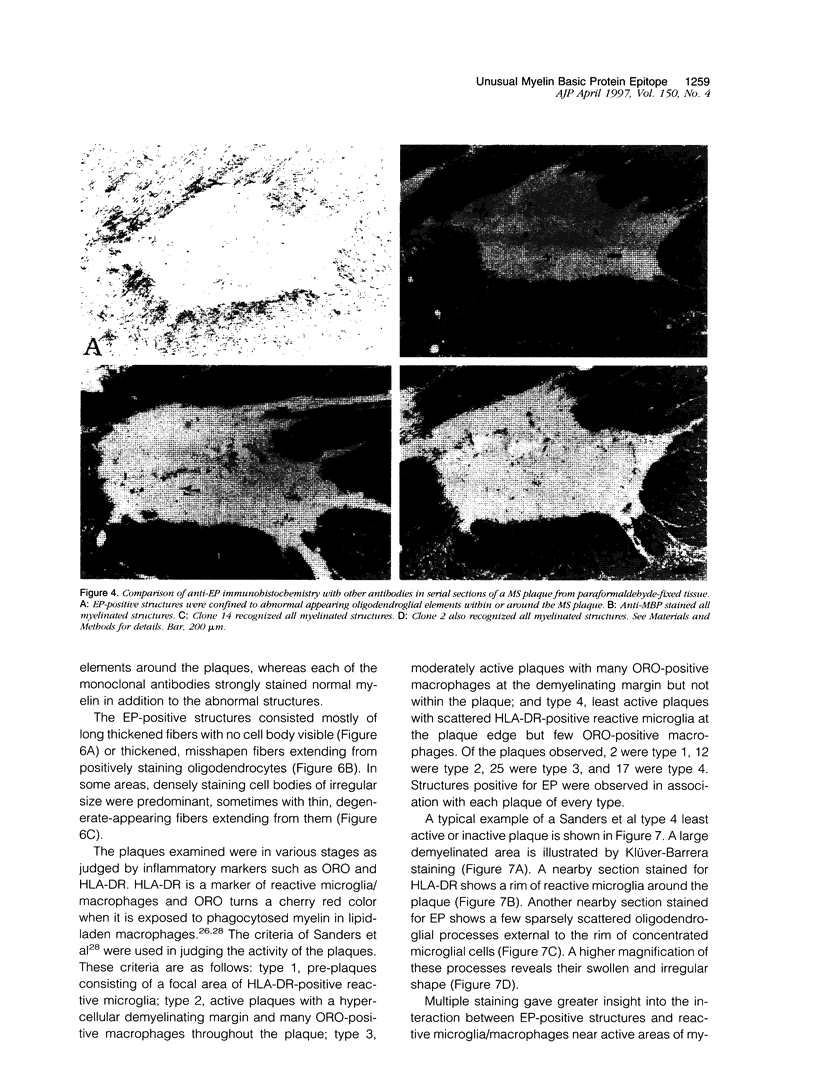
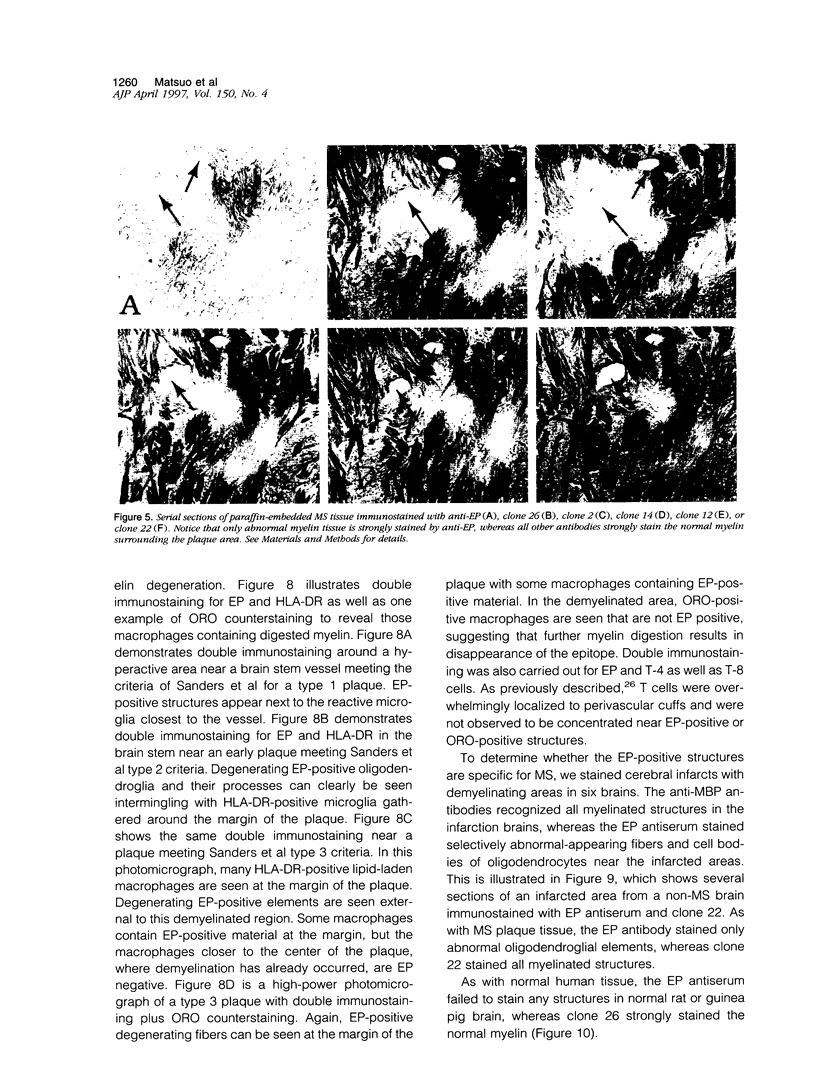
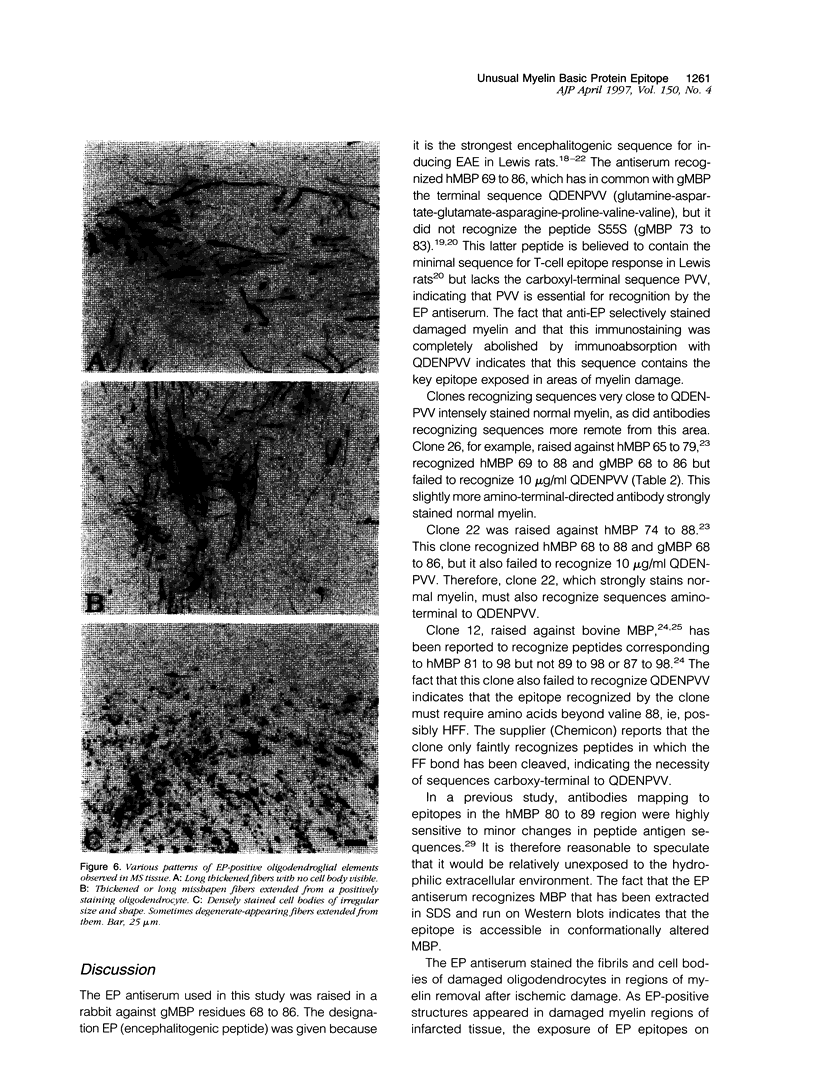
Abstract
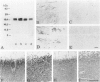
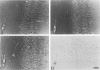
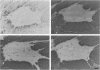
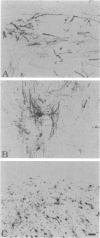
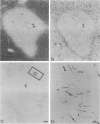
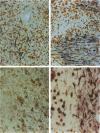
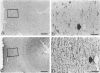
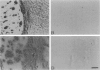
A rabbit antiserum (anti-EP), induced against a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues 68 to 86 of guinea pig myelin basic protein, powerfully immunostained abnormal-appearing oligodendrocytic processes and cell bodies in demyelinating areas associated with multiple sclerosis plaques. However, it failed to recognize any structures in normal human, rat, or guinea pig brain. The antiserum recognized the synthetic peptide QDENPVV, which corresponds to human myelin basic protein residues 82 to 88. Immunoabsorption with this peptide eliminated immunohistochemical staining. By contrast, several commercial antibodies recognizing nearby sequences of human myelin basic protein intensely stained all myelinated structures in both normal and multiple sclerosis tissue. The unusual epitope recognized by anti-EP appears to be accessible only in areas of myelin degeneration. If insults occur that repeatedly expose a region of MBP normally sheltered from immunosurveillance, a self-sustaining immune reaction might result.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle E. A., McGeer P. L. Cellular immune response in multiple sclerosis plaques. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):575–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. H., Fritz R. B., Chou F. C., Kibler R. F. The immune response of Lewis rats to peptide 68-88 of guinea pig myelin basic protein. I. T cell determinants. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1540–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. K., Jones R. E., Bourdette D., Whitham R., Hashim G., Atherton J., Offner H., Vandenbark A. A. Human myelin basic protein (MBP) epitopes recognized by mouse MBP-selected T cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Jan;49(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritse K., Deen C., Fasbender M., Ravid R., Boersma W., Claassen E. The involvement of specific anti myelin basic protein antibody-forming cells in multiple sclerosis immunopathology. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Jan;49(1-2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groome N. P., Dawkes A., Gales M., Hruby S., Alvord E. C., Jr Region-specific immunoassays for human myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Oct;12(4):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groome N., Dawkes A., Barry R., Hruby S., Alvord E., Jr New monoclonal antibodies reactive with defined sequential epitopes in human myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Oct;19(4):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashim G. A., Day E. D., Carvalho E., Abdelaal A. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE): role of B cell and T cell epitopes in the development of EAE in Lewis rats. J Neurosci Res. 1987;17(4):375–383. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490170408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashim G. A. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats: chemical synthesis of disease-inducing determinant. Science. 1977 Jun 10;196(4295):1219–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.67639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby S., Alvord E. C., Jr, Groome N. P., Dawkes A., Martenson R. E. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with myelin basic protein. Mol Immunol. 1987 Dec;24(12):1359–1364. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamholz J., de Ferra F., Puckett C., Lazzarini R. Identification of three forms of human myelin basic protein by cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4962–4966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlero De Rosbo N., Carnegie P. R., Bernard C. C., Linthicum D. S. Detection of various forms of brain myelin basic protein in vertebrates by electroimmunoblotting. Neurochem Res. 1984 Oct;9(10):1359–1369. doi: 10.1007/BF00964663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannie M. D., Paterson P. Y., U'Prichard D. C., Flouret G. Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats with purified synthetic peptides: delineation of antigenic determinants for encephalitogenicity, in vitro activation of cellular transfer, and proliferation of lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5515–5519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Whitaker J., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. Fine specificity and HLA restriction of myelin basic protein-specific cytotoxic T cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients and healthy individuals. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., McFarland H. F. Immunological aspects of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1995;32(2):121–182. doi: 10.3109/10408369509084683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:153–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino G., Olsson T., Fredrikson S., Hojeberg B., Kostulas V., Grimaldi L. M., Link H. Cells producing antibodies specific for myelin basic protein region 70-89 are predominant in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):2971–2976. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaurin J. A., Hafler D. A., Antel J. P. Reactivity of normal T-cell lines to MBP isolated from normal and multiple sclerosis white matter. J Neurol Sci. 1995 Feb;128(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)00224-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders V., Conrad A. J., Tourtellotte W. W. On classification of post-mortem multiple sclerosis plaques for neuroscientists. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jul;46(1-2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90251-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Autoantibodies to myelin basic protein within multiple sclerosis central nervous system tissue. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Apr;115(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90221-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Increased synthetic peptide specificity of tissue-CSF bound anti-MBP in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Mar;43(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90078-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Relative frequency of autoantibodies to myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein in optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Sci. 1994 Jan;121(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I., Steinman L. Fine specificity of the antibody response to myelin basic protein in the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis: the minimal B-cell epitope and a model of its features. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 21;92(24):11061–11065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.11061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Synthetic peptide specificity of anti-myelin basic protein from multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Jul;39(1-2):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90177-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Layton B. A., Herman P. K., Kachelhofer R. D., Burgard S., Bartolucci A. A. Correlation of myelin basic protein-like material in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients with their response to glucocorticoid treatment. Ann Neurol. 1993 Jan;33(1):10–17. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Moscarello M. A., Herman P. K., Epand R. M., Surewicz W. K. Conformational correlates of the epitopes of human myelin basic protein peptide 80-89. J Neurochem. 1990 Aug;55(2):568–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N. The presence of immunoreactive myelin basic protein peptide in urine of persons with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1987 Nov;22(5):648–655. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Williams P. H., Layton B. A., McFarland H. F., Stone L. A., Smith M. E., Kachelhofer R. D., Bradley E. L., Burgard S., Zhao G. Correlation of clinical features and findings on cranial magnetic resonance imaging with urinary myelin basic protein-like material in patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994 May;35(5):577–585. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Hafler D. A., Strominger J. L. Structure of human T-cell receptors specific for an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide: positioning of T-cell receptors on HLA-DR2/peptide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8896–8900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]