Abstract
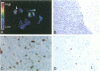
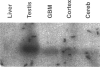
Deregulation of telomerase, a ribonucleoprotein polymerase that compensates progressive loss of telomeric (TTAGGG)n repeats during DNA replication, has been suggested to facilitate tumorigenesis and cellular immortality by providing unlimited proliferation capacity for cancer cells. We investigated the relationship between tumor proliferation activity and in situ expression of the telomerase RNA component in 46 human grade I to IV astrocytomas. Heterogeneously distributed telomerase RNA expression was detected from all of the tumor samples as well as from normal human brain tissue. However, expression of telomerase RNA was significantly increased in highly malignant tumors (P = 0.024) and in tumors that showed increased proliferation activity determined by MIB-1 immunohistochemistry (P = 0.014). Interestingly, increased telomerase RNA levels were observed in a subgroup of grade II astrocytomas that showed significant increase in proliferation activity (P = 0.047), indicating that the telomerase RNA component is up-regulated already in early states of astrocytoma malignancy. Telomeric repeats amplification assays revealed telomerase activity in 4 of 6 glioblastomas and in 1 rapidly proliferating grade II astrocytoma. These results suggest that increased tumor proliferation activity triggers telomerase activation via mechanisms that involve increased production of the telomerase RNA component.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco M. A., Rizen M., Greider C. W., Hanahan D. Differential regulation of telomerase activity and telomerase RNA during multi-stage tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 1996 Feb;12(2):200–204. doi: 10.1038/ng0296-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Funk W. D., Wang S. S., Weinrich S. L., Avilion A. A., Chiu C. P., Adams R. R., Chang E., Allsopp R. C., Yu J. The RNA component of human telomerase. Science. 1995 Sep 1;269(5228):1236–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.7544491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):458–460. doi: 10.1038/345458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Telomere loss: mitotic clock or genetic time bomb? Mutat Res. 1991 Mar-Nov;256(2-6):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim N. W., Piatyszek M. A., Prowse K. R., Harley C. B., West M. D., Ho P. L., Coviello G. M., Wright W. E., Weinrich S. L., Shay J. W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):2011–2015. doi: 10.1126/science.7605428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford L. A., Piatyszek M. A., Xu R., Schold S. C., Jr, Shay J. W. Telomerase activity in human brain tumours. Lancet. 1995 Nov 11;346(8985):1267–1268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91865-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. Z., Allsopp R. C., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W., Harley C. B. Telomere end-replication problem and cell aging. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):951–960. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachern M. J., Blackburn E. H. Runaway telomere elongation caused by telomerase RNA gene mutations. Nature. 1995 Aug 3;376(6539):403–409. doi: 10.1038/376403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyu M. S. Telomeres, telomerase, and immortality. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Jun 21;87(12):884–894. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.12.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallinen P. K., Haapasalo H. K., Visakorpi T., Helén P. T., Rantala I. S., Isola J. J., Helin H. J. Prognostication of astrocytoma patient survival by Ki-67 (MIB-1), PCNA, and S-phase fraction using archival paraffin-embedded samples. J Pathol. 1994 Dec;174(4):275–282. doi: 10.1002/path.1711740407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. S., Gottschling D. E. TLC1: template RNA component of Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomerase. Science. 1994 Oct 21;266(5184):404–409. doi: 10.1126/science.7545955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Shay J. W. Telomere positional effects and the regulation of cellular senescence. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90232-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]