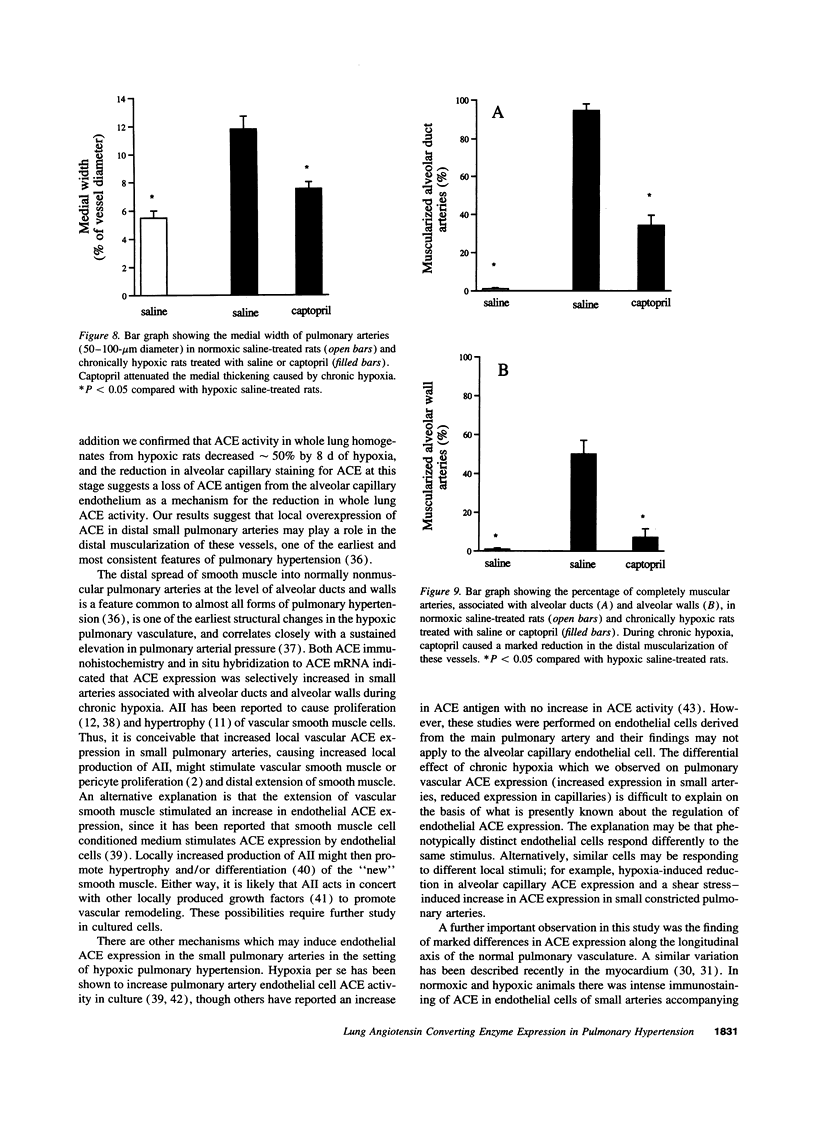
Abstract
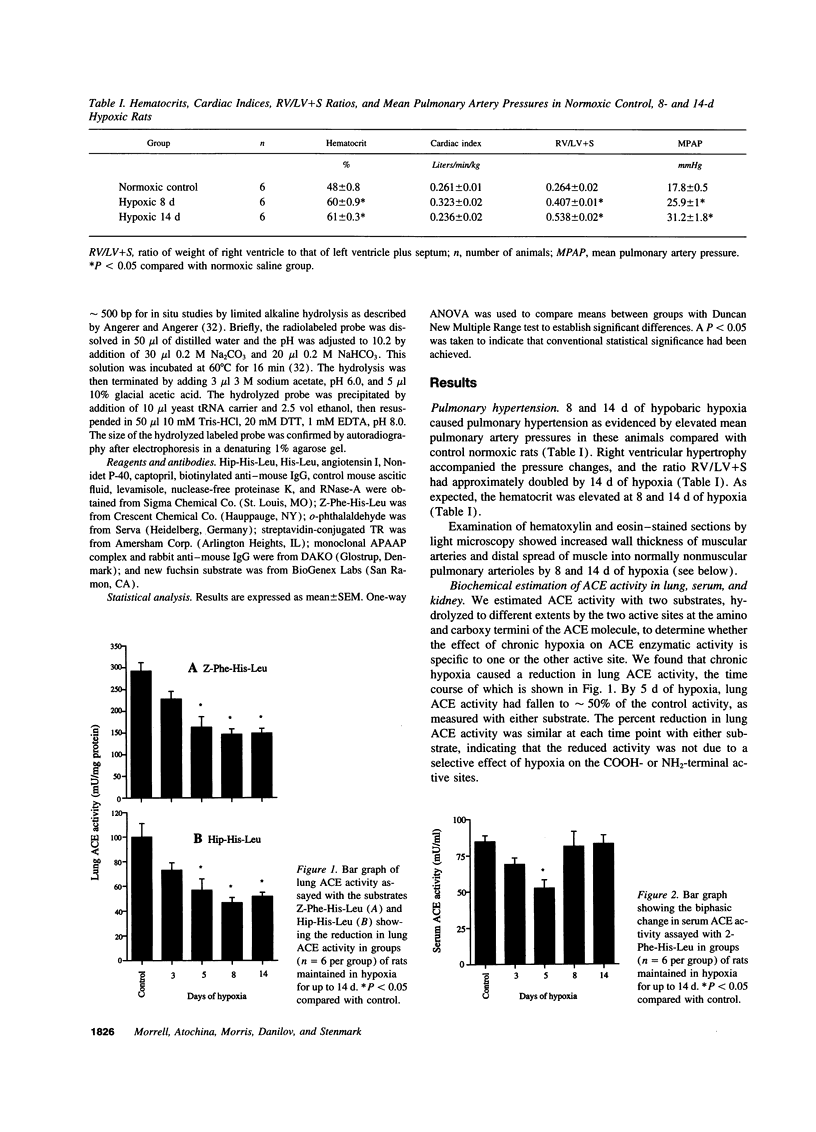
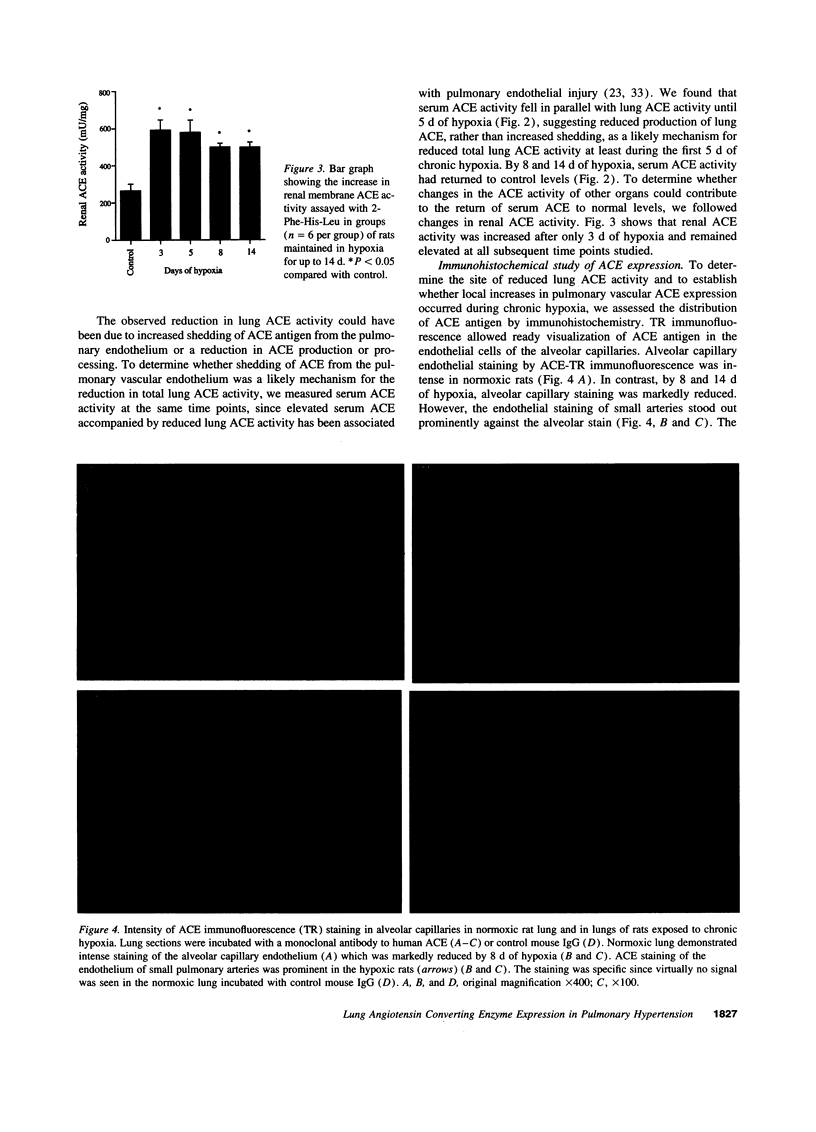
Previous studies suggest that while lung angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity is reduced during chronic hypoxia, inhibitors of ACE attenuate hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. In an attempt to explain this paradox we investigated the possibility that whole lung ACE activity may not reflect local pulmonary vascular ACE expression. The experimental approach combined in vivo hemodynamic studies in control and chronically hypoxic rats, measurement of whole lung ACE activity, and evaluation of local pulmonary vascular ACE expression by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Total lung ACE activity was reduced to 50% of control activity by 5 d of hypoxia and remained low for the duration of the study. Immunohistochemistry showed a marked reduction of ACE staining in alveolar capillary endothelium. However, an increase in ACE staining was observed in the walls of small newly muscularized pulmonary arteries at the level of alveolar ducts and walls. In situ hybridization studies showed increased signal for ACE mRNA in the same vessels. Inhibition of ACE by captopril during chronic hypoxia attenuated pulmonary hypertension and markedly reduced distal muscularization of small pulmonary arteries. In addition, we demonstrated marked longitudinal variation in ACE expression along the normal pulmonary vasculature with the highest levels found in small muscular arteries associated with terminal and respiratory bronchioles. We conclude that local ACE expression is increased in the walls of small pulmonary arteries during the development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension, despite a generalized reduction in alveolar capillary ACE expression, and we speculate that local arteriolar ACE may play a role in the vascular remodeling associated with pulmonary hypertension.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnal J. F., Battle T., Rasetti C., Challah M., Costerousse O., Vicaut E., Michel J. B., Alhenc-Gelas F. ACE in three tunicae of rat aorta: expression in smooth muscle and effect of renovascular hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 2):H1777–H1784. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.5.H1777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atochina E. N., Hiemisch H. H., Muzykantov V. R., Danilov S. M. Systemic administration of platelet-activating factor in rat reduces specific pulmonary uptake of circulating monoclonal antibody to angiotensin-converting enzyme. Lung. 1992;170(6):349–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00177581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell R. W., Blatteis C. M. Effect of chronic hypoxia on angiotensin-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction and converting enzyme activity in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Mar;172(3):346–350. doi: 10.3181/00379727-172-41568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Boswell M., Robertson A. L., Jr Effects of angiotensin II and vasopressin on human smooth muscle cells in vitro. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Oct;35(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clozel J. P., Saunier C., Hartemann D., Fischli W. Effects of cilazapril, a novel angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, on the structure of pulmonary arteries of rats exposed to chronic hypoxia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;17(1):36–40. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199101000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. G. Cardiac output by dye dilution in the conscious rat. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Sep;37(3):452–455. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilov S. M., Faerman A. I., Printseva OYu, Martynov A. V., Sakharov IYu, Trakht I. N. Immunohistochemical study of angiotensin-converting enzyme in human tissues using monoclonal antibodies. Histochemistry. 1987;87(5):487–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00496822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilov S., Jaspard E., Churakova T., Towbin H., Savoie F., Wei L., Alhenc-Gelas F. Structure-function analysis of angiotensin I-converting enzyme using monoclonal antibodies. Selective inhibition of the amino-terminal active site. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26806–26814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durmowicz A. G., Parks W. C., Hyde D. M., Mecham R. P., Stenmark K. R. Persistence, re-expression, and induction of pulmonary arterial fibronectin, tropoelastin, and type I procollagen mRNA expression in neonatal hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1994 Dec;145(6):1411–1420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenhahn M., Franke F., Bohle R. M., Zhu Y. C., Stauss H. M., Bachmann S., Danilov S., Unger T. Cellular distribution of angiotensin-converting enzyme after myocardial infarction. Hypertension. 1995 Feb;25(2):219–226. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R. S., Thourani V., Eisenberg S. J., Shai S. Y., Corson M. A., Nabel E. G., Bernstein K. E., Berk B. C. Fibroblast growth factor stimulates angiotensin converting enzyme expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Possible mediator of the response to vascular injury. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):377–387. doi: 10.1172/JCI117666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J., Silverstein E. A sensitive fluorimetric assay for serum angiotensin-converting enzyme. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;66(2):416–424. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.2.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer A. A., Peach M. J., Owens G. K. Angiotensin II induces hypertrophy, not hyperplasia, of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):749–756. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. H., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy vs. hyperplasia. Autocrine transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression determines growth response to angiotensin II. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):456–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI115881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goraya T. Y., Kessler S. P., Kumar R. S., Douglas J., Sen G. C. Identification of positive and negative transcriptional regulatory elements of the rabbit angiotensin-converting enzyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1194–1201. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. New findings in pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Oct;57(5):542–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber F., Sodal I. E., Weil J. V. On-line cardiac output by digital computer. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Feb;40(2):266–268. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. M., Narkates A. J., Oparil S. Impaired pulmonary conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II in rats exposed to chronic hypoxia. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Apr;60(4):1121–1127. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.4.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Keane P. M., Suyama K. L., Gauthier D. Angiotensin converting enzyme activity and evolution of pulmonary vascular disease in rats with monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension. Thorax. 1982 Feb;37(2):88–96. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.2.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane P. M., Kay J. M., Suyama K. L., Gauthier D., Andrew K. Lung angiotensin converting enzyme activity in rats with pulmonary hypertension. Thorax. 1982 Mar;37(3):198–204. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.3.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kentera D., Susić D., Cvetković A., Djordjević G. Effects of SQ 14.225, an orally active inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme, on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy in rats. Basic Res Cardiol. 1981 May-Jun;76(3):344–351. doi: 10.1007/BF01907777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kifor I., Dzau V. J. Endothelial renin-angiotensin pathway: evidence for intracellular synthesis and secretion of angiotensins. Circ Res. 1987 Mar;60(3):422–428. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.3.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. J., Booyse F. M., Lin P. H., Traylor M., Narkates A. J., Oparil S. Hypoxia stimulates endothelial cell angiotensin-converting enzyme antigen synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1231–C1238. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulewitz A. H., Fanburg B. L. The effect of oxygen tension on the in vitro production and release of angiotensin-converting enzyme by bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):866–869. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O., Perkett E. A. The sequence of cellular and hemodynamic changes of chronic pulmonary hypertension induced by hypoxia and other stimuli. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Nov;140(5):1486–1489. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.5.1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Hypoxia and incorporation of 3H-thymidine by cells of the rat pulmonary arteries and alveolar wall. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):51–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzykantov V. R., Danilov S. M. A new approach to the investigation of oxidative injury to the pulmonary endothelium: use of angiotensin-converting enzyme as a marker. Biomed Sci. 1991;2(1):11–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Yamada T., Setoguchi M. Prolonged inhibition of local angiotensin-converting enzyme after single or repeated treatment with quinapril in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;19(1):102–107. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199201000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S., Narkates A. J., Jackson R. M., Ann H. S. Altered angiotensin-converting enzyme in lung and extrapulmonary tissues of hypoxia-adapted rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jul;65(1):218–227. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.1.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orton E. C., LaRue S. M., Ensley B., Stenmark K. Bromodeoxyuridine labeling and DNA content of pulmonary arterial medial cells from hypoxia-exposed and nonexposed healthy calves. Am J Vet Res. 1992 Oct;53(10):1925–1930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piquilloud Y., Reinharz A., Roth M. Studies on the angiotensin converting enzyme with different substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 22;206(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Clozel J. P., Müller R. K., Kuhn H., Hefti F., Hosang M., Baumgartner H. R. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2526370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser I. W., Stenmark K. R., Suthar M., Crouch E. C., Mecham R. P., Parks W. C. Regional heterogeneity of elastin and collagen gene expression in intralobar arteries in response to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension as demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1073–1088. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Gamble W., Nadas A. S., Miettinen O. S., Reid L. Rat pulmonary circulation after chronic hypoxia: hemodynamic and structural features. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):H818–H827. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakugi H., Kim D. K., Krieger J. E., Wang D. S., Dzau V. J., Pratt R. E. Induction of angiotensin converting enzyme in the neointima after vascular injury. Possible role in restenosis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):339–346. doi: 10.1172/JCI116965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota N., Miyazaki M., Okunishi H. Increase of angiotensin converting enzyme gene expression in the hypertensive aorta. Hypertension. 1992 Aug;20(2):168–174. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibony M., Gasc J. M., Soubrier F., Alhenc-Gelas F., Corvol P. Gene expression and tissue localization of the two isoforms of angiotensin I converting enzyme. Hypertension. 1993 Jun;21(6 Pt 1):827–835. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.21.6.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark K. R., Durmowicz A. G., Roby J. D., Mecham R. P., Parks W. C. Persistence of the fetal pattern of tropoelastin gene expression in severe neonatal bovine pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1234–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI117077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turla M. B., Thompson M. M., Corjay M. H., Owens G. K. Mechanisms of angiotensin II- and arginine vasopressin-induced increases in protein synthesis and content in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Evidence for selective increases in smooth muscle isoactin expression. Circ Res. 1991 Jan;68(1):288–299. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.1.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L., Alhenc-Gelas F., Corvol P., Clauser E. The two homologous domains of human angiotensin I-converting enzyme are both catalytically active. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9002–9008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. S., Lee S. L., Fanburg B. L. Smooth muscle cell conditioned medium elevates angiotensin-converting enzyme of bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Nov;1(5):401–405. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.5.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakheim R. M., Mattioli L., Molteni A., Mullis K. B., Bartley J. Prevention of pulmonary vascular changes of chronic alveolar hypoxia by inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme in the rat. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]