Abstract
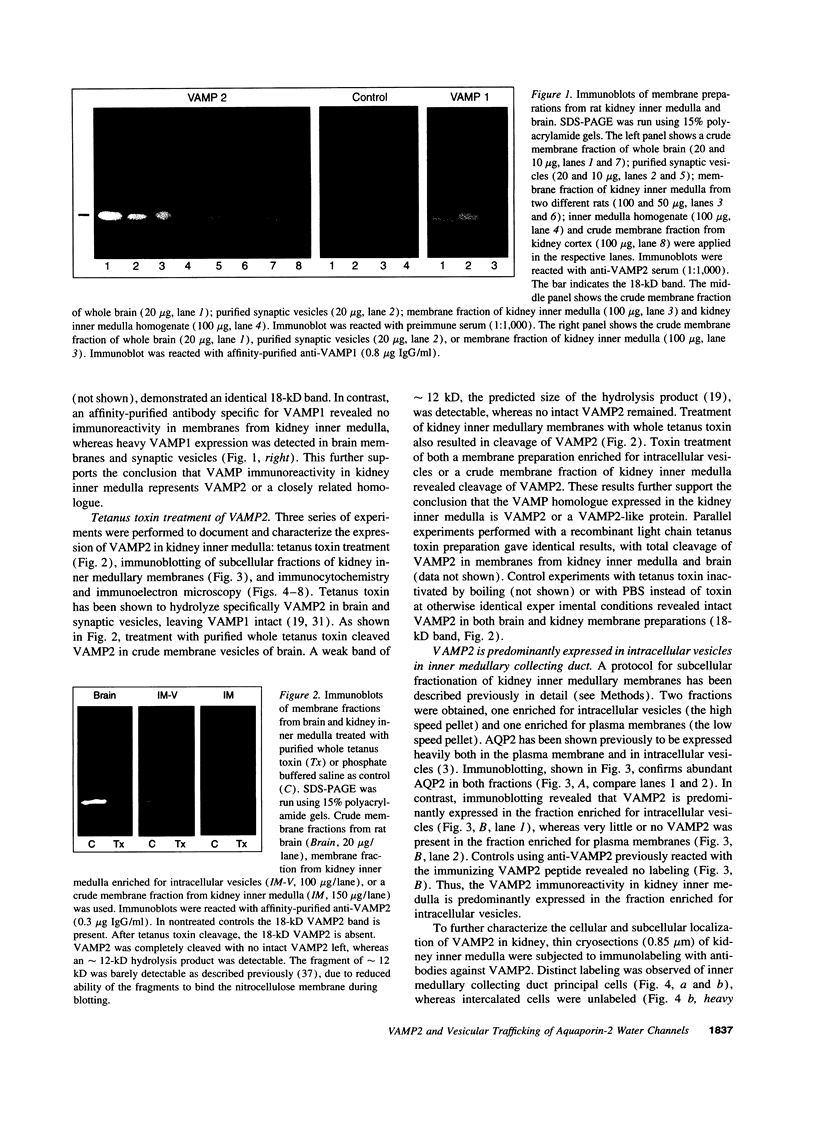
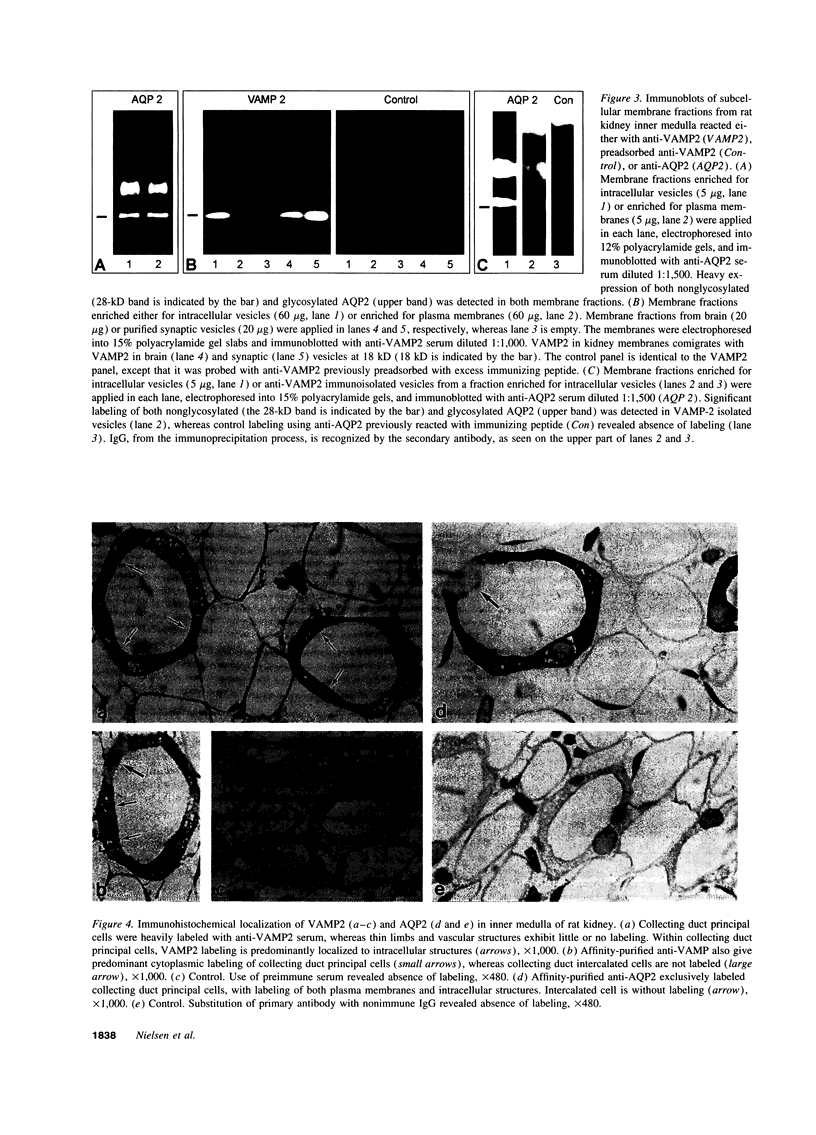
Body water balance is controlled by vasopressin, which regulates Aquaporin-2 (AQP2) water channels in kidney collecting duct cells by vesicular trafficking between intracellular vesicles and the plasma membrane. To examine the molecular apparatus involved in vesicle trafficking and vasopressin regulation of AQP2 in collecting duct cells, we tested if targeting proteins expressed in the synaptic vesicles, namely vesicle-associated membrane proteins 1 and 2 (VAMP1 and 2), are expressed in kidney collecting duct. Immunoblotting revealed specific labeling of VAMP2 (18-kD band) but not VAMP1 in membrane fractions prepared from kidney inner medulla. Controls using preadsorbed antibody or preimmune serum were negative. Bands of identical molecular size were detected in immunoblots of brain membrane vesicles and purified synaptic vesicles. VAMP2 in kidney membranes was cleaved by tetanus toxin, revealing a tetanus toxin-sensitive VAMP homologue. Similarly, tetanus toxin cleaved VAMP2 in synaptic vesicles. In kidney inner medulla, VAMP2 was predominantly expressed in the membrane fraction enriched for intracellular vesicles, with little or no VAMP2 in the plasma membrane enriched fraction. This was confirmed by immunocytochemistry using semithin cryosections, which showed mainly vesicular labeling in collecting duct principal cells, with no labeling of intercalated cells. VAMP2 immunolabeling colocalized with AQP2 labeling in intracellular vesicles, as determined by immunoelectron microscopy after double immunolabeling of isolated vesicles. Quantitative analysis of 1,310 vesicles revealed a highly significant association of both AQP2 and VAMP2 in the same vesicles (P < 0.0001). Furthermore, the presence of AQP2 in vesicles immunoisolated with anti-VAMP2 antibodies was confirmed by immunoblotting. In conclusion, VAMP2, a component of the neuronal SNARE complex, is expressed in vesicles carrying AQP2, suggesting a role in vasopressin-regulated vesicle trafficking of AQP2 water channels.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. C., Trimble W. S., Lienhard G. E. Members of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins are components of glucose transporter-containing vesicles from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11681–11684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Verdijk M. A., Knoers N. V., Wieringa B., Monnens L. A., van Os C. H., van Oost B. A. Requirement of human renal water channel aquaporin-2 for vasopressin-dependent concentration of urine. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiovanni S. R., Nielsen S., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A. Regulation of collecting duct water channel expression by vasopressin in Brattleboro rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8984–8988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Trimble W. S., Scheller R. H. Two vesicle-associated membrane protein genes are differentially expressed in the rat central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11061–11064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Jahn R. Vesicle fusion from yeast to man. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):191–193. doi: 10.1038/370191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamion B., Spring K. R. Water permeability of apical and basolateral cell membranes of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F986–F999. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaisano H. Y., Sheu L., Foskett J. K., Trimble W. S. Tetanus toxin light chain cleaves a vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) isoform 2 in rat pancreatic zymogen granules and inhibits enzyme secretion. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17062–17066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Sasaki S., Tsuganezawa H., Monkawa T., Kitajima W., Konishi K., Fushimi K., Marumo F., Saruta T. Expression and distribution of aquaporin of collecting duct are regulated by vasopressin V2 receptor in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):1778–1783. doi: 10.1172/JCI117525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. M., Bommert K., Charlton M. P., Kistner A., Habermann E., Augustine G. J., Betz H. A post-docking role for synaptobrevin in synaptic vesicle fusion. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1269–1279. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B. Cell biology. Snappy exocytoxins. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):104–105. doi: 10.1038/365104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Isolation of (Na+ plus K+)-ATPase. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:277–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepper M. A. The aquaporin family of molecular water channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6255–6258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link E., Edelmann L., Chou J. H., Binz T., Yamasaki S., Eisel U., Baumert M., Südhof T. C., Niemann H., Jahn R. Tetanus toxin action: inhibition of neurotransmitter release linked to synaptobrevin proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92305-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples D., Christensen S., Christensen E. I., Ottosen P. D., Nielsen S. Lithium-induced downregulation of aquaporin-2 water channel expression in rat kidney medulla. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1838–1845. doi: 10.1172/JCI117863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Chou C. L., Marples D., Christensen E. I., Kishore B. K., Knepper M. A. Vasopressin increases water permeability of kidney collecting duct by inducing translocation of aquaporin-CD water channels to plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1013–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., DiGiovanni S. R., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Harris H. W. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of vasopressin-regulated water channel in rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11663–11667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Agre P. Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7275–7279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyler G. A., Higgins G. A., Hart R. A., Battenberg E., Billingsley M., Bloom F. E., Wilson M. C. The identification of a novel synaptosomal-associated protein, SNAP-25, differentially expressed by neuronal subpopulations. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3039–3052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetto O., Schiavo G., Montecucco C., Poulain B., Deloye F., Lozzi L., Shone C. C. SNARE motif and neurotoxins. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):415–416. doi: 10.1038/372415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Benfenati F., Poulain B., Rossetto O., Polverino de Laureto P., DasGupta B. R., Montecucco C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):832–835. doi: 10.1038/359832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Poulain B., Rossetto O., Benfenati F., Tauc L., Montecucco C. Tetanus toxin is a zinc protein and its inhibition of neurotransmitter release and protease activity depend on zinc. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3577–3583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. L., Baumgarten R., Nielsen S., Raben D., Zeidel M. L., Agre P. Concurrent expression of erythroid and renal aquaporin CHIP and appearance of water channel activity in perinatal rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):2035–2041. doi: 10.1172/JCI116798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle membrane protein is conserved from mammals to Drosophila. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1475–1481. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc. 1986 Aug;143(Pt 2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S. Analysis of the structure and expression of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins. J Physiol Paris. 1993;87(2):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0928-4257(93)90004-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. VAMP-1: a synaptic vesicle-associated integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Gray T. S., Elferink L. A., Wilson M. C., Scheller R. H. Distinct patterns of expression of two VAMP genes within the rat brain. J Neurosci. 1990 Apr;10(4):1380–1387. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01380.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]