Abstract
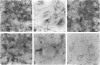
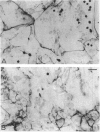
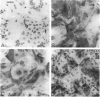
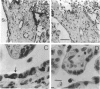
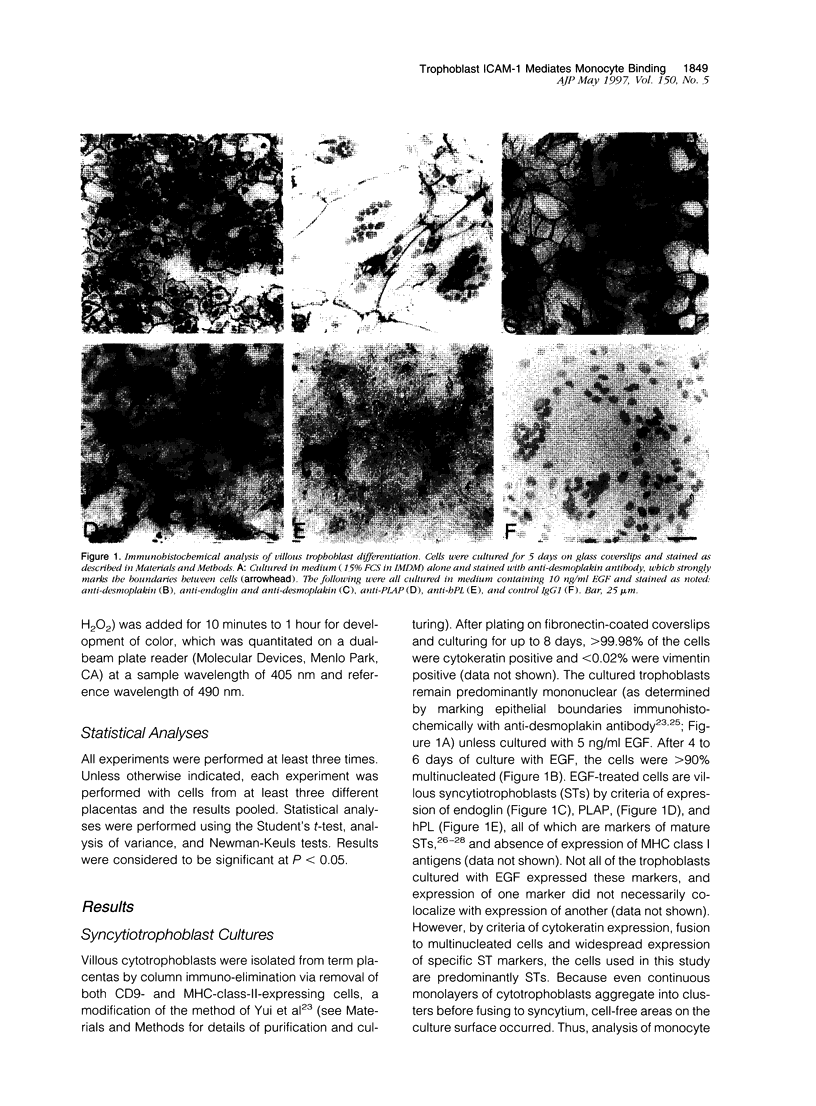
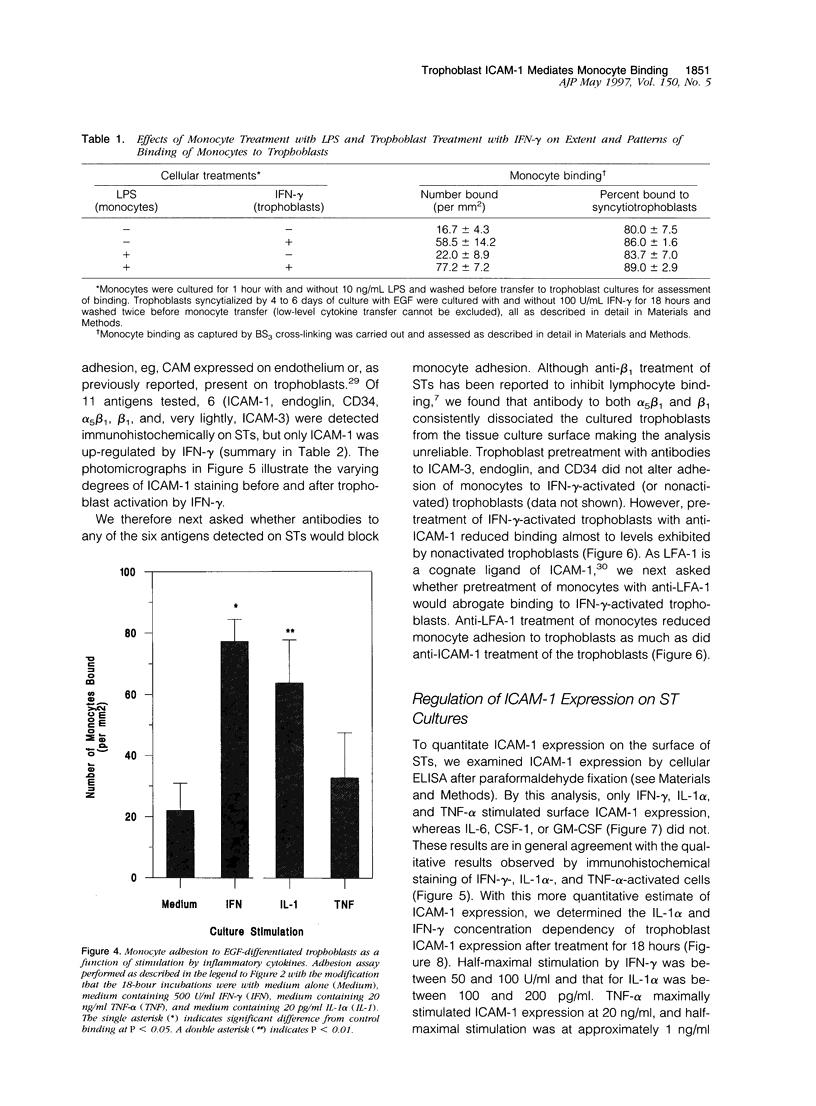
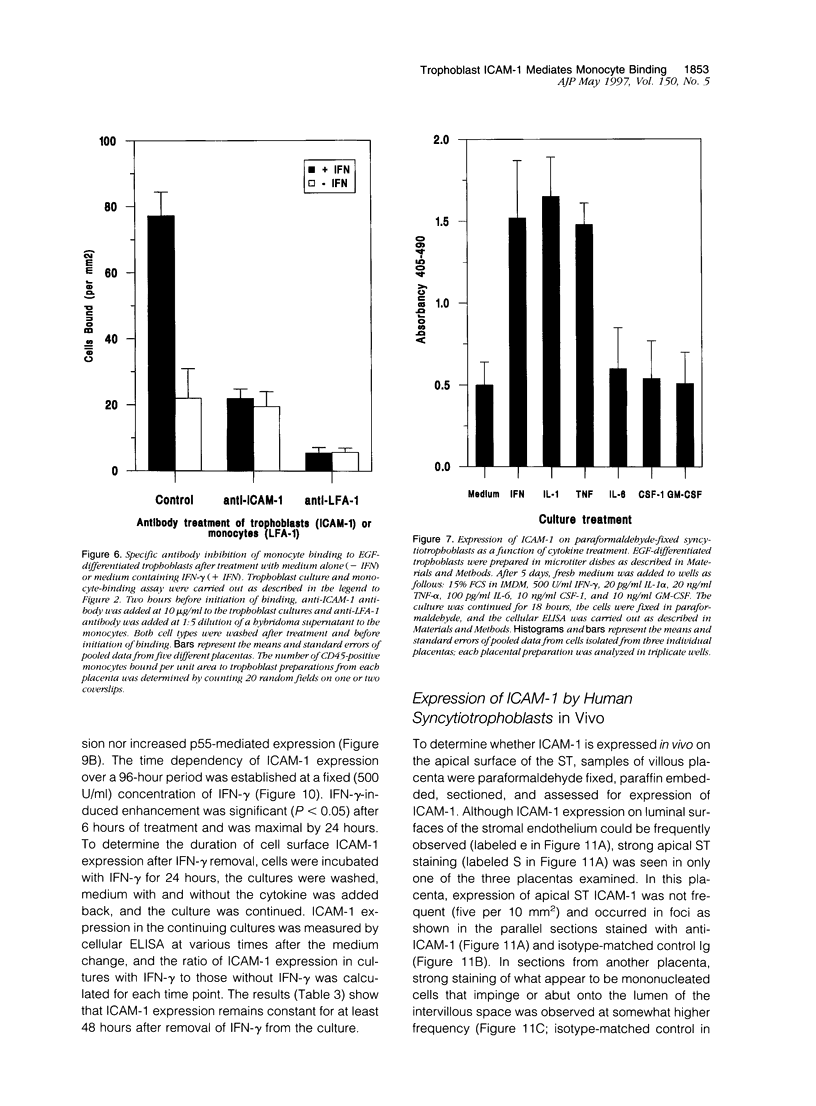
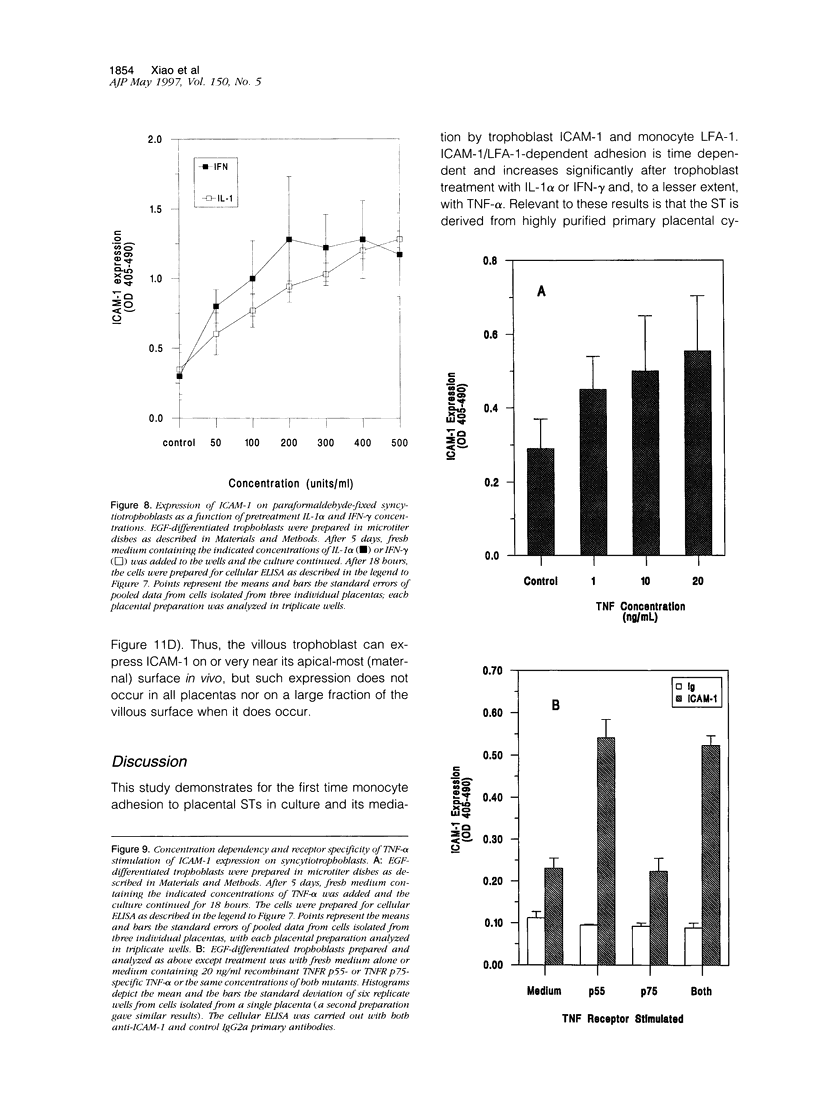
Accumulation of maternal monocytes in the villous/intervillous space (villitis) is associated with increased risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality and may initiate in utero transmission of cell-associated infectious agents such cytomegalovirus and HIV-1. We have developed an in vitro model of trophoblast syncytialization and have investigated the adhesive interactions between this tissue and peripheral blood monocytes. We show that monocytes strongly adhere to cultured syncytiotrophoblasts (STs) and that treatment with the inflammatory cytokines interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-1 alpha greatly increase the number bound. Pretreatment of STs with these cytokines upregulated apical expression of intercellular cell adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 but not E-or L-selection, ICAM-2 or -3, or various integrins. ICAM-1 expression was cytokine concentration dependent, significantly increased within 6 hours of treatment, peaked after 24 hours, and remained undiminished for 48 hours after cytokine removal from the cultures. Adhesion of monocytes to STs was inhibited > 80% by antibody to ICAM-1 or its cognate ligand LFA-1. ICAM-1 was detected immunohistochemically only in rare foci on intact term placental villi. These results suggest that villous trophoblast expression of ICAM-1 occurs only during an immune inflammatory reaction and that aberrant expression of this molecule may be an important pathological feature in those immunoinflammatory disorders of the placenta characterized by an excessive accumulation of leukocytes in the intervillous/villous space such as spontaneous abortion, perinatal hematogenous infections, and villitis of unknown etiology.
Full text
PDF






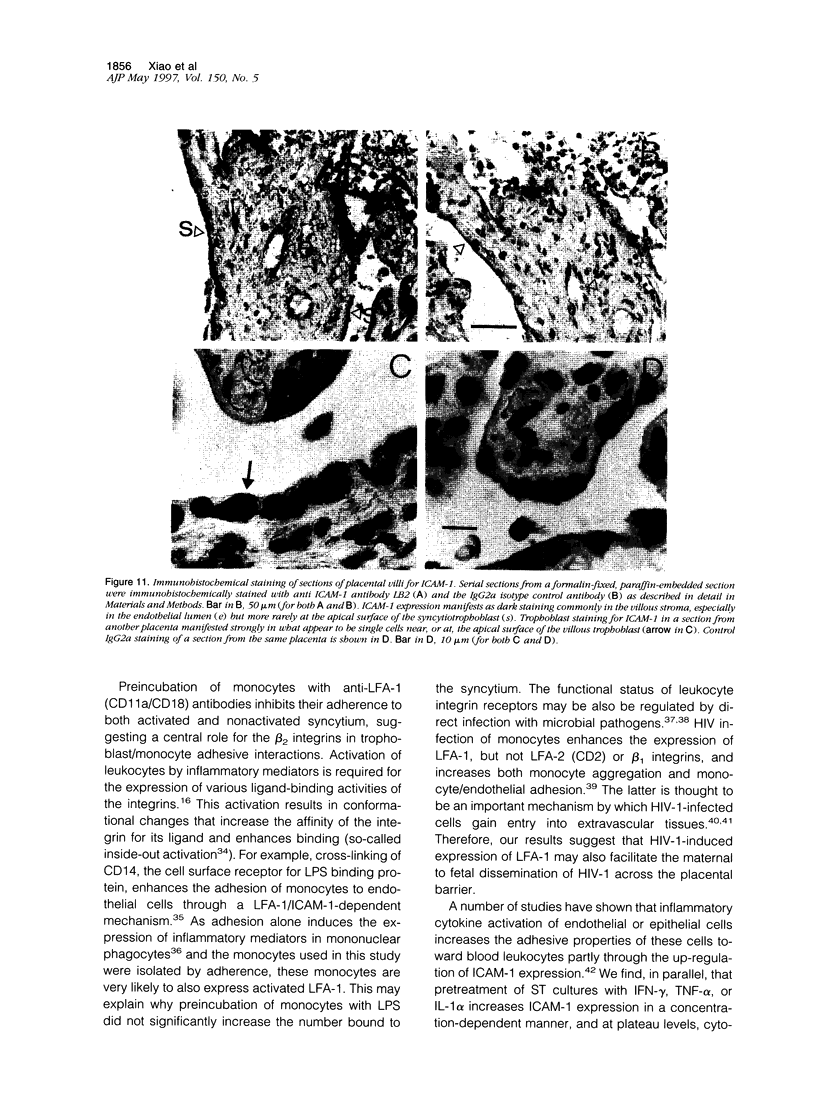




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M. Endothelial and epithelial cell adhesion molecules. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;4(3):195–203. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.3.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemani A. M. Immunohistochemical study of the inflammatory infiltrate in villitis of unknown etiology. A qualitative and quantitative analysis. Pathol Res Pract. 1992 Apr;188(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)81208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altshuler G., Russell P. The human placental villitides: a review of chronic intrauterine infection. Curr Top Pathol. 1975;60:64–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumheter S., Singer M. S., Henzel W., Hemmerich S., Renz M., Rosen S. D., Lasky L. A. Binding of L-selectin to the vascular sialomucin CD34. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):436–438. doi: 10.1126/science.7692600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekhuizen H., Blokland I., van Furth R. Cross-linking of CD14 molecules on monocytes results in a CD11/CD18- and ICAM-1-dependent adherence to cytokine-stimulated human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):950–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekhuizen H., van Furth R. Monocyte adherence to human vascular endothelium. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Oct;54(4):363–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourinbaiar A. S., Tan X. Inhibitory effect of choriocarcinoma-derived high molecular weight factor (HMWF) on lymphocyte proliferation and adhesion to trophoblasts. J Reprod Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(93)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butini L., De Fougerolles A. R., Vaccarezza M., Graziosi C., Cohen D. I., Montroni M., Springer T. A., Pantaleo G., Fauci A. S. Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-1 ICAM-2 and ICAM-3 function as counter-receptors for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 in human immunodeficiency virus-mediated syncytia formation. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Sep;24(9):2191–2195. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan S., Weeks B. S., Soderland C., Schnaper H. W., Toro L. A., Asthana S. P., Hewlett I. K., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M. HIV-1 infection alters monocyte interactions with human microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):422–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divers M. J., Bulmer J. N., Miller D., Lilford R. J. Beta 1 integrins in third trimester human placentae: no differential expression in pathological pregnancy. Placenta. 1995 Apr;16(3):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(95)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas G. C., Hu J., Thirkill T. L., Hovanes K., Sharma S., King B. F. Effect of cytokines and anti-adhesion molecule antibodies on the adhesion of lymphocytic cells to human syncytiotrophoblast. J Reprod Immunol. 1994 Aug;27(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(94)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas G. C., King B. F. Differentiation of human trophoblast cells in vitro as revealed by immunocytochemical staining of desmoplakin and nuclei. J Cell Sci. 1990 May;96(Pt 1):131–141. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Lloret M. I., Yui J., Winkler-Lowen B., Guilbert L. J. Epidermal growth factor inhibits cytokine-induced apoptosis of primary human trophoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1996 May;167(2):324–332. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199605)167:2<324::AID-JCP17>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendron R. L., Nestel F. P., Lapp W. S., Baines M. G. Lipopolysaccharide-induced fetal resorption in mice is associated with the intrauterine production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha. J Reprod Fertil. 1990 Nov;90(2):395–402. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0900395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Pahal G. S., Akbar A. N. Increased adherence of CD2 peripheral blood lymphocytes to cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts is blocked by anti-LFA-3 antibody. Immunology. 1993 Mar;78(3):413–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes M. K., Jackson L. G., Tuan R. S., Shepley K. J., Smith J. B. Cytokine production in first trimester chorionic villi: detection of mRNAs and protein products in situ. Cell Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(2):300–308. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. A., Polgar K., Anderson D. J. T-helper 1-type immunity to trophoblast in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion. JAMA. 1995 Jun 28;273(24):1933–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz A. A., Berman J. W., Lyman W. D. The role of the blood-brain barrier in HIV infection of the central nervous system. Adv Neuroimmunol. 1994;4(3):249–256. doi: 10.1016/s0960-5428(06)80263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarousseau A. C., Thibault G., Reverdiau P., Rodriguez A. M., Lacord M., de Russe J., Watier H., Degenne D., Lebranchu Y., Gruel Y. Adhesive properties of choriocarcinoma cells toward lymphocytes activated or not by interleukin-2. Cell Immunol. 1994 Aug;157(1):38–47. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Keist R., Joller P. Macrophage response to microbial pathogens: modulation of the expression of adhesion, CD14, and MHC class II molecules by viruses, bacteria, protozoa and fungi. Scand J Immunol. 1995 Sep;42(3):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1995.tb03665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Nestler J. E., Sermasi E., Sanger J. M., Strauss J. F., 3rd Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placentae. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1567–1582. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan L., Guilbert L. J., Wegmann T. G., Belosevic M., Mosmann T. R. T helper 1 response against Leishmania major in pregnant C57BL/6 mice increases implantation failure and fetal resorptions. Correlation with increased IFN-gamma and TNF and reduced IL-10 production by placental cells. J Immunol. 1996 Jan 15;156(2):653–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarrere C. A., Faulk W. P., McIntyre J. A. Villitis in normal term human placentae: frequency of the lesion determined by monoclonal antibody to HLA-DR antigen. J Reprod Immunol. 1989 Nov;16(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(89)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarrere C. A., McIntyre J. A., Faulk W. P. Immunohistologic evidence that villitis in human normal term placentas is an immunologic lesion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Feb;162(2):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafrenie R. M., Wahl L. M., Epstein J. S., Hewlett I. K., Yamada K. M., Dhawan S. HIV-1-Tat modulates the function of monocytes and alters their interactions with microvessel endothelial cells. A mechanism of HIV pathogenesis. J Immunol. 1996 Feb 15;156(4):1638–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Stueber D., Banner D., Mackay F., Lesslauer W. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) mutants with exclusive specificity for the 55-kDa or 75-kDa TNF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26350–26357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay F., Loetscher H., Stueber D., Gehr G., Lesslauer W. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced cell adhesion to human endothelial cells is under dominant control of one TNF receptor type, TNF-R55. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1277–1286. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier J. A., Statuto M., Ragnotti G. Senescence stimulates U937-endothelial cell interactions. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Sep;208(1):270–274. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Skillman D. R., Hoover D. L., Hanson B. D., Turpin J. A., Kalter D. C., Gendelman H. E. Macrophages and the human immunodeficiency virus. Immunol Today. 1990 Jun;11(6):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90086-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrish D. W., Bhardwaj D., Dabbagh L. K., Marusyk H., Siy O. Epidermal growth factor induces differentiation and secretion of human chorionic gonadotropin and placental lactogen in normal human placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Dec;65(6):1282–1290. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-6-1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulesu L., Romagnoli R., Cintorino M., Ricci M. G., Garotta G. First trimester human trophoblast expresses both interferon-gamma and interferon-gamma-receptor. J Reprod Immunol. 1994 Aug;27(1):37–48. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Maduzia L., Springer T. A. Activation of lymphocyte function-associated molecule-1 (CD11a/CD18) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) mimicked by an antibody directed against CD18. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 15;155(2):854–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe E., Walter P. Les lésions placentaires du paludisme. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1985 Dec;42 (Suppl 2):921–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popek E. J. Granulomatous villitis due to Toxoplasma gondii. Pediatr Pathol. 1992 Mar-Apr;12(2):281–288. doi: 10.3109/15513819209023307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi F., Jacques S. M., Reyes M. P. Placental histopathology in syphilis. Hum Pathol. 1993 Jul;24(7):779–784. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90016-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redline R. W., Patterson P. Villitis of unknown etiology is associated with major infiltration of fetal tissue by maternal inflammatory cells. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):473–479. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. A., Seamark R. F., Guilbert L. J., Wegmann T. G. The role of cytokines in gestation. Crit Rev Immunol. 1994;14(3-4):239–292. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v14.i3-4.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salafia C. M., Haynes N., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R. Distribution of ICAM-1 within decidua and placenta and its gestational age-associated changes. Pediatr Pathol. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):381–388. doi: 10.3109/15513819109064774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salafia C. M., Vintzileos A. M., Silberman L., Bantham K. F., Vogel C. A. Placental pathology of idiopathic intrauterine growth retardation at term. Am J Perinatol. 1992 May;9(3):179–184. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattock R. J., Griffin G. E. Cellular adherence enhances HIV replication in monocytic cells. Res Virol. 1994 May-Aug;145(3-4):139–145. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2516(07)80015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrikant P., Chung I. Y., Ballestas M. E., Benveniste E. N. Regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interferon-gamma in astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 May;51(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinzger C., Müntefering H., Löning T., Stöss H., Plachter B., Jahn G. Cell types infected in human cytomegalovirus placentitis identified by immunohistochemical double staining. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;423(4):249–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01606887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Jacques S., Forte M., Lye S. J., Letarte M. Localization of endoglin, a transforming growth factor-beta binding protein, and of CD44 and integrins in placenta during the first trimester of pregnancy. Biol Reprod. 1994 Sep;51(3):405–413. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod51.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Wiedeman J., Sissons J. G., Borysiewicz L. K., Sinclair J. H. Monocytes are a major site of persistence of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2059–2064. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova P. F., Hunter V. J., Roby K. F., Hunt J. S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the female reproductive tract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1995 Sep;209(4):325–342. doi: 10.3181/00379727-209-43905b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian L., King N. J. Interferon gamma induces intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on murine midterm trophoblast and enhances susceptibility to specific lysis by paternally directed allo-immune cytotoxic T cells. Biol Reprod. 1994 Dec;51(6):1164–1172. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod51.6.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. F., Stark J. M., Hamedani A., Smith C. W., Gruenert D. C., Huang Y. T. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)-dependent and ICAM-1-independent adhesive interactions between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and human airway epithelial cells infected with parainfluenza virus type 2. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3345–3349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderpuye O. A., Smith C. H. Proteins of the apical and basal plasma membranes of the human placental syncytiotrophoblast: immunochemical and electrophoretic studies. Placenta. 1987 Nov-Dec;8(6):591–608. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(87)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P. R., Garin Y., Blot P. Placental pathologic changes in malaria. A histologic and ultrastructural study. Am J Pathol. 1982 Dec;109(3):330–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann T. G., Lin H., Guilbert L., Mosmann T. R. Bidirectional cytokine interactions in the maternal-fetal relationship: is successful pregnancy a TH2 phenomenon? Immunol Today. 1993 Jul;14(7):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90235-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertheimer S. J., Myers C. L., Wallace R. W., Parks T. P. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene expression in human endothelial cells. Differential regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12030–12035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelavarthi K. K., Hunt J. S. Analysis of p60 and p80 tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor messenger RNA and protein in human placentas. Am J Pathol. 1993 Oct;143(4):1131–1141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yui J., Garcia-Lloret M., Brown A. J., Berdan R. C., Morrish D. W., Wegmann T. G., Guilbert L. J. Functional, long-term cultures of human term trophoblasts purified by column-elimination of CD9 expressing cells. Placenta. 1994 Apr;15(3):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(94)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yui J., Garcia-Lloret M., Wegmann T. G., Guilbert L. J. Cytotoxicity of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and gamma-interferon against primary human placental trophoblasts. Placenta. 1994 Dec;15(8):819–835. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yui J., Hemmings D., Garcia-Lloret M., Guilbert L. J. Expression of the human p55 and p75 tumor necrosis factor receptors in primary villous trophoblasts and their role in cytotoxic signal transduction. Biol Reprod. 1996 Aug;55(2):400–409. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod55.2.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Qin X., Springer T. A. Characterization of the function of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-3 and comparison with ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in immune responses. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):619–629. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]