Abstract
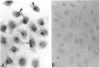
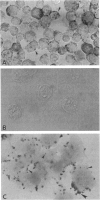
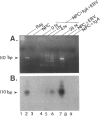
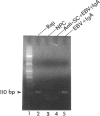
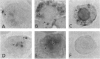
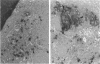
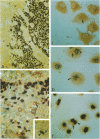
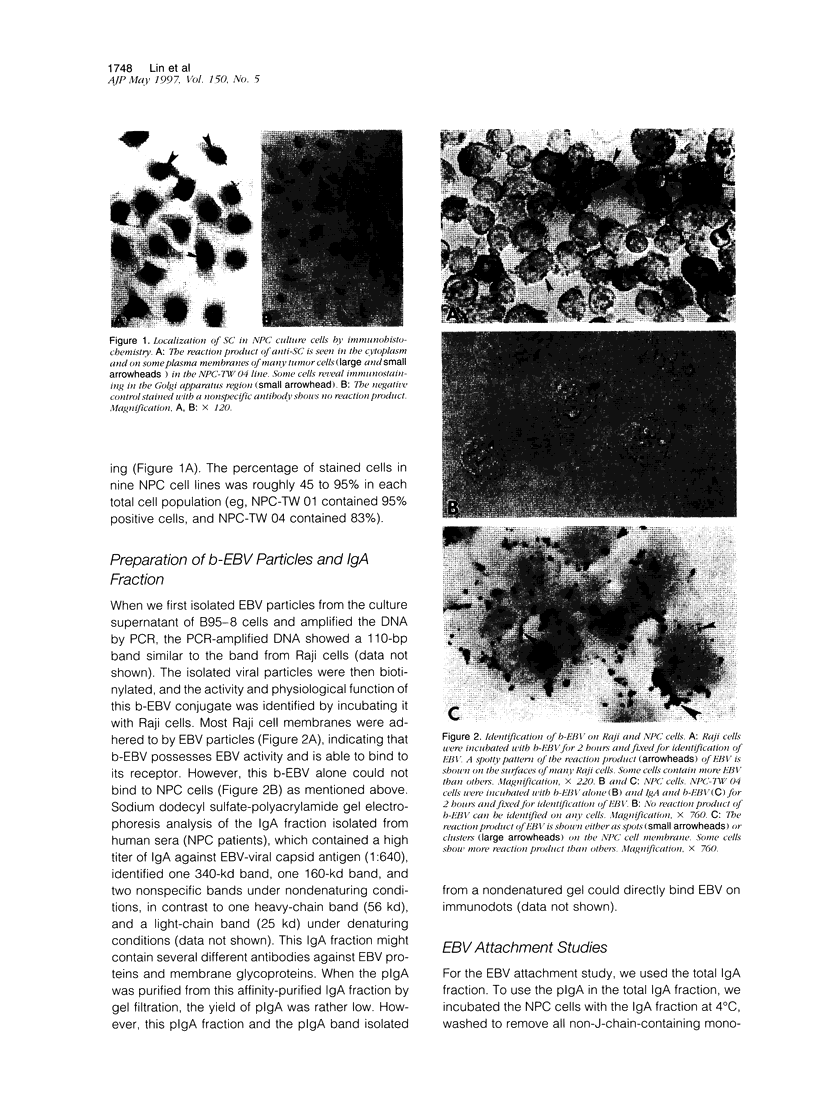
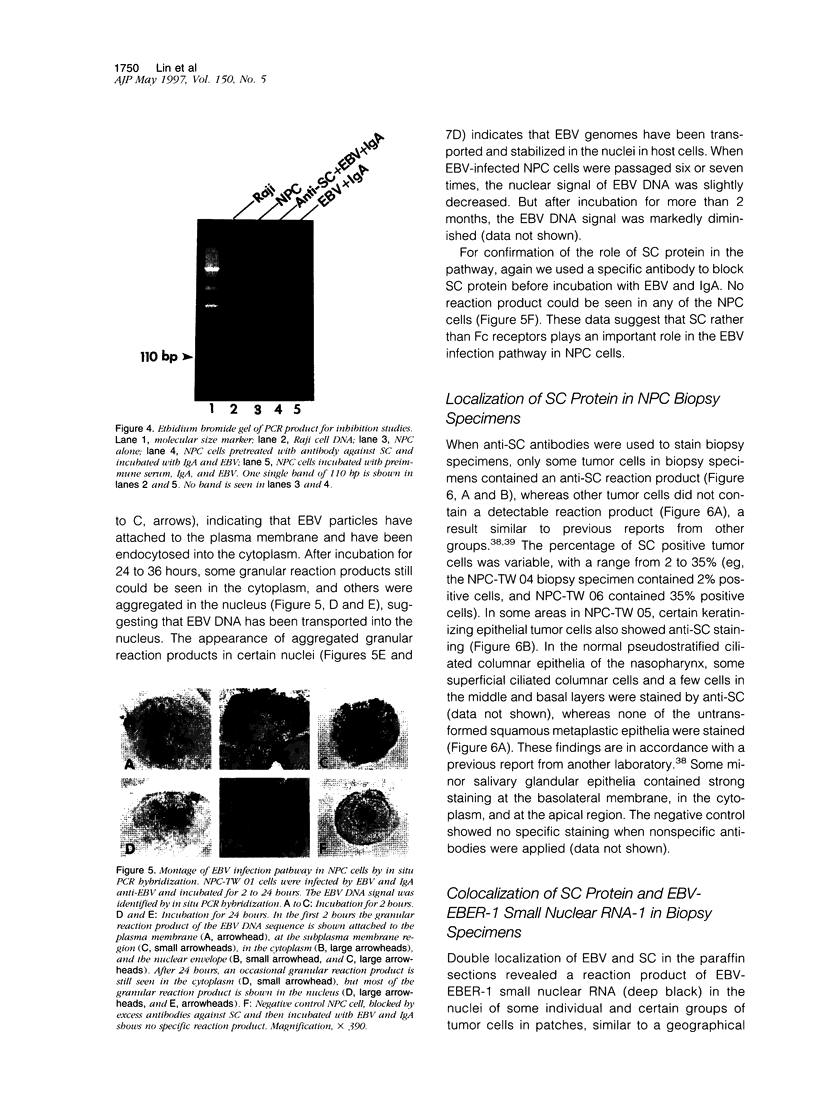
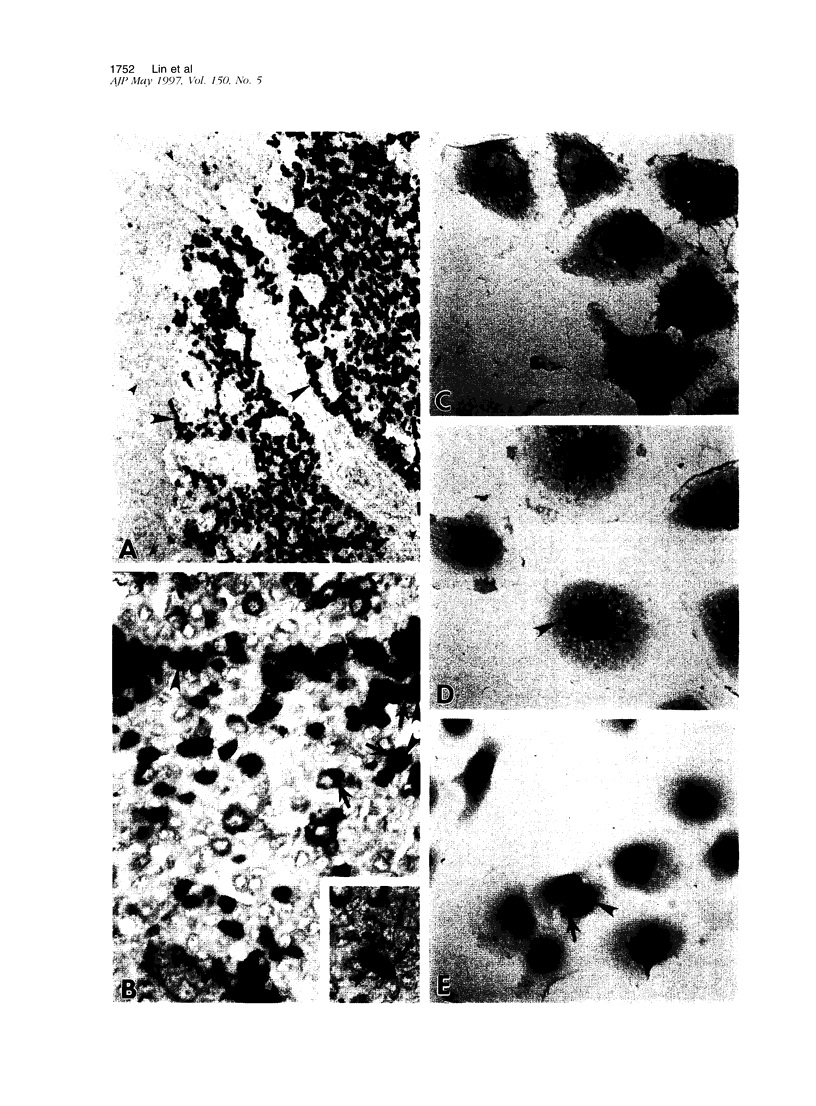
To investigate the relationship between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells, we examined the pathway of EBV infection in NPC cell lines. We used immunolocalization to investigate the EBV receptor (C3d-R) and polymeric immunoglobulin receptor [secretory component (SC) protein]. We incubated IgA anti-EBV and EBV particles with NPC cells and observed the EBV DNA signal by in situ polymerase chain reaction hybridization and polymerase chain reaction plus Southern blotting. We also colocalized SC protein and EBV RNA in NPC biopsy specimens. Results showed that: 1) NPC cells did not express the EBV receptor but did express SC protein in each line; 2) SC protein was also expressed in some tumor cells but not in untransformed squamous metaplastic epithelia in NPC biopsy specimens; 3) EBV could infect NPC cells through an EBV-IgA and SC complex and retained an EBV viral genome in their nuclei; SC expression could be down-regulated by EBV proteins; and 4) in biopsy specimens, a fraction of tumor cells showed SC protein expression; only a portion of tumor cells contained EBV, and of these cells only a few expressed SC protein. These findings indicate that EBV cannot infect untransformed nasopharyngeal squamous metaplastic epithelia but can enter NPC cells through IgA-mediated endocytosis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson-Anvret M., Forsby N., Klein G., Henle W. Relationship between the Epstein-Barr virus and undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlated nucleic acid hybridization and histopathological examination. Int J Cancer. 1977 Oct 15;20(4):486–494. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apodaca G., Bomsel M., Arden J., Breitfeld P. P., Tang K., Mostov K. E. The polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. A model protein to study transcytosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1877–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI115211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks L., Yao Q. Y., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2689–2697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2689-2697.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Isobe Y., Nakane P. K. Studies on translocation of immunoglobulins across intestinal epithelium. II. Immunoelectron-microscopic localization of immunoglobulins and secretory component in human intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):985–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. S., Tyan Y. S., Liu S. T., Tsai M. S., Pao C. C. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA sequences in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by enzymatic DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2398–2402. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2398-2402.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chintalacharuvu K. R., Piskurich J. F., Lamm M. E., Kaetzel C. S. Cell polarity regulates the release of secretory component, the epithelial receptor for polymeric immunoglobulins, from the surface of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):35–47. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crago S. S., Kulhavy R., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Secretory component of epithelial cells is a surface receptor for polymeric immunoglobulins. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1832–1837. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desgranges C., Li J. Y., De-Thé EBV specific secretory IgA in saliva of NPC patients. Presence of secretory piece in epithelial malignant cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Dec 15;20(6):881–886. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Fu H. L., Ernberg I., Finke J., Rowe M., Klein G., Falk K., Nilsson E., Yadav M., Busson P. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Sep 15;42(3):329–338. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., de Thé G., Lenoir G., Ho J. H. Superinfection epithelial nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):960–963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Therkildsen M. H., Neilsen N. H., Jensen H., Hansen J. P., Pallesen G. Undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland in Greenlandic Eskimos: demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus DNA by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Hum Pathol. 1991 Aug;22(8):811–815. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90210-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Ho H. C., Henle G., Kwan H. C. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Comparison of active cases with long-term survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Aug;51(2):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Ho J. H., Henle G., Chau J. C., Kwan H. C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: significance of changes in Epstein-Barr virus-related antibody patterns following therapy. Int J Cancer. 1977 Nov 15;20(5):663–672. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitt M. M., Allday M. J., Hara T., Karran L., Jones M. D., Busson P., Tursz T., Ernberg I., Griffin B. E. EBV gene expression in an NPC-related tumour. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2639–2651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. F., Zabarovsky E. R., Chen F., Cao S. L., Ernberg I., Klein G., Winberg G. Isolation and sequencing of the Epstein-Barr virus BNLF-1 gene (LMP1) from a Chinese nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol. 1991 Oct;72(Pt 10):2399–2409. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-10-2399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Lindahl T., Fialkow P. J., Singh S., Stehlin J. S. Direct evidence for the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and nuclear antigen in malignant epithelial cells from patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers R. J., O'Leary J. J., Crowley M., Healy I., Annis P., Burke L., O'Brien D., Hogan J., Kealy W. F., Lewis F. A. Epstein-Barr virus in normal, pre-malignant, and malignant lesions of the uterine cervix. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Oct;46(10):931–935. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.10.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. X., Young L. S., Niedobitek G., Dawson C. W., Birkenbach M., Wang F., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus infection and replication in a human epithelial cell system. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):347–350. doi: 10.1038/356347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Chan W. Y., Chen W., Huang H. M., Wu H. C., Hsu M. M., Chuang S. M., Wang C. C. Characterization of seven newly established nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Lab Invest. 1993 Jun;68(6):716–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Chan W. Y., Chen W., Shew J. Y. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and retinoblastoma gene expression. Lab Invest. 1992 Jul;67(1):56–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Dee A. N., Chen W., Chan W. Y. Association of Epstein-Barr virus, human papilloma virus, and cytomegalovirus with nine nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Lab Invest. 1994 Nov;71(5):731–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Liu J. W., Wu J. Y., Dang H., Li C. Y., Lam K. W. Alteration of acid phosphatase isoenzyme in a human prostatic cancer cell line. Lab Invest. 1986 Dec;55(6):666–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Wong C. I., Chan W. Y., Tzung K. W., Ho J. K., Hsu M. M., Chuang S. M. Establishment and characterization of two nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Lab Invest. 1990 Jun;62(6):713–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Wu H. C., Cheng H. F., Chang J. T., Chang K. J. Identification of beta-subunit of GTP-binding regulatory protein in mitotic spindle. Lab Invest. 1992 Dec;67(6):770–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Chang G. C. Detection of distinct Epstein-Barr virus genotypes in NPC biopsies from southern Chinese and Caucasians. Int J Cancer. 1992 Aug 19;52(1):34–37. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec M. B., Kaetzel C. S., Lamm M. E., Fletcher D., Nedrud J. G. Intracellular neutralization of virus by immunoglobulin A antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6901–6905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Cooper N. R. Isolation of Epstein Barr-virus and studies of its neutralization by human IgG and complement. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):272–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Hansmann M. L., Herbst H., Young L. S., Dienemann D., Hartmann C. A., Finn T., Pitteroff S., Welt A., Anagnostopoulos I. Epstein-Barr virus and carcinomas: undifferentiated carcinomas but not squamous cell carcinomas of the nasopharynx are regularly associated with the virus. J Pathol. 1991 Sep;165(1):17–24. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomori H., Kameya T., Shimosato Y., Saito H., Ebihara S., Ono I. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: immunohistochemical study for keratin, secretory component and leukocyte common antigen. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1985 Mar;15(1):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Huang C. H., Pagano J. S., Klein G., Singh S. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus detected in tissue of Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathmanathan R., Prasad U., Sadler R., Flynn K., Raab-Traub N. Clonal proliferations of cells infected with Epstein-Barr virus in preinvasive lesions related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1995 Sep 14;333(11):693–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199509143331103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Flynn K., Pearson G., Huang A., Levine P., Lanier A., Pagano J. The differentiated form of nasopharyngeal carcinoma contains Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Int J Cancer. 1987 Jan 15;39(1):25–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Hood R., Yang C. S., Henry B., 2nd, Pagano J. S. Epstein-Barr virus transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):580–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.580-590.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roque-Barreira M. C., Campos-Neto A. Jacalin: an IgA-binding lectin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1740–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Se Thoe S. Y., Wong K. K., Pathmanathan R., Sam C. K., Cheng H. M., Prasad U. Elevated secretory IgA antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and presence of EBV DNA and EBV receptors in patients with cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1993 Aug;50(2):168–172. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1993.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Davis D. S., Young L. S., Hutt-Fletcher L., Tedder T. F., Rickinson A. B. Human epithelial cell expression of an Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Vesterinen E. H., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Walton L. A., Pagano J. S. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus in human epithelial cells infected in vitro. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):480–483. doi: 10.1038/306480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Yao Q. Y. Immunoglobulin A-induced shift of Epstein-Barr virus tissue tropism. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1578–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.1312750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari R., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Biosynthesis of the IgA antibody receptor: a model for the transepithelial sorting of a membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Uemura Y., Tokudome T., Ishidate T., Masuda H., Okazaki E., Kaneko K., Naoe S., Ito M., Okamura A. Epstein-Barr virus related gastric cancer in Japan: a molecular patho-epidemiological study. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1993 Oct;43(10):574–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1993.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao K. T., Zhang H. Y., Zhu H. C., Wang F. X., Li G. Y., Wen D. S., Li Y. P., Tsai C. H., Glaser R. Establishment and characterization of two epithelial tumor cell lines (HNE-1 and HONE-1) latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus and derived from nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jan 15;45(1):83–89. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung W. M., Zong Y. S., Chiu C. T., Chan K. H., Sham J. S., Choy D. T., Ng M. H. Epstein-Barr virus carriage by nasopharyngeal carcinoma in situ. Int J Cancer. 1993 Mar 12;53(5):746–750. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Clark D., Sixbey J. W., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human pharyngeal epithelia. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):240–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]