Abstract
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4, CD152) is a molecule expressed on in vitro activated T cells. CTLA-4 shares important sequence homology with CD28 and binds to the same ligands, CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). CTLA-4 probably functions as a negative regulator of T lymphocyte activation in the mouse, although this remains to be proven for human T lymphocytes. We have developed new monoclonal antibodies against human CTLA-4 and have investigated the in situ expression of CTLA-4 in a wide variety of normal and pathological human tissues expressing CD80 and CD86. As revealed in this study, CTLA-4 is expressed on thymocytes in thymic medulla, on a subset of CD4+ T lymphocytes in germinal centers of follicular hyperplasia, on T cells, mainly CD8+, infiltrating skin affected by graft-versus-host disease, and on T cells, mainly CD4+, infiltrating Hodgkin's disease lesions. In immunoelectron microscopy, CTLA-4 was found on the plasma membrane as well as in the hyaloplasm and cytoplasmic vesicles, in agreement with its pattern of expression on in vitro activated T cells. Interestingly, no or at most scarce expression of CTLA-4 was found in granulomatous lymph nodes, T-cell-mediated inflammatory diseases, or non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, regardless of their expression of CD80 or CD86. Thus, expression of CTLA-4 appears to be induced in selective pathological conditions in vivo. The pathways leading to selective induction of CTLA-4 and its role in the pathophysiology of these conditions need to be further investigated.
Full text
PDF

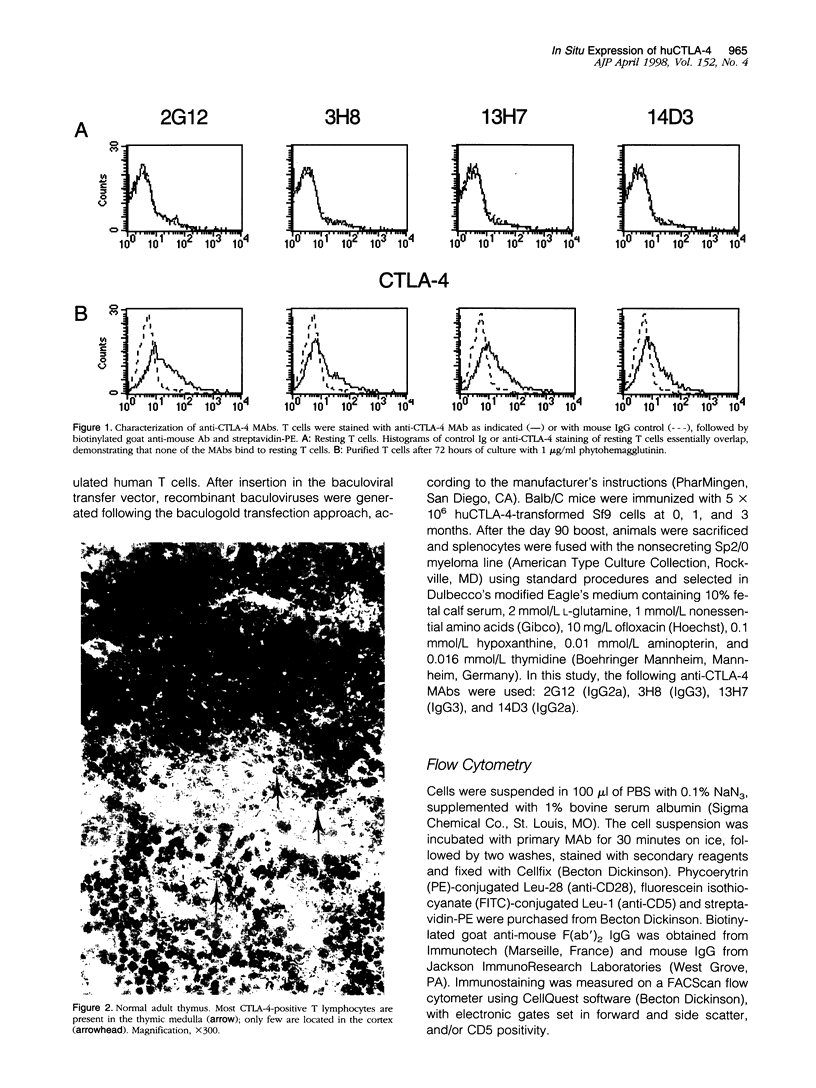








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alegre M. L., Noel P. J., Eisfelder B. J., Chuang E., Clark M. R., Reiner S. L., Thompson C. B. Regulation of surface and intracellular expression of CTLA4 on mouse T cells. J Immunol. 1996 Dec 1;157(11):4762–4770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone J. A. Is CTLA-4 a master switch for peripheral T cell tolerance? J Immunol. 1997 Mar 1;158(5):1989–1993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Denizot F., Luciani M. F., Roux-Dosseto M., Suzan M., Mattei M. G., Golstein P. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily--CTLA-4. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):267–270. doi: 10.1038/328267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyse I., Decorte R., Baens M., Cuppens H., Semana G., Emonds M. P., Marynen P., Cassiman J. J. Rapid DNA typing of class II HLA antigens using the polymerase chain reaction and reverse dot blot hybridization. Tissue Antigens. 1993 Jan;41(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1993.tb01970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castan J., Tenner-Racz K., Racz P., Fleischer B., Bröker B. M. Accumulation of CTLA-4 expressing T lymphocytes in the germinal centres of human lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1997 Feb;90(2):265–271. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1997.00162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., De Wolf-Peeters C., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. A recommended procedure for ultrastructural immunohistochemistry on small human tissue samples. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Sep;33(9):959–964. doi: 10.1177/33.9.3860562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wolf-Peeters C., Delabie J. Anatomy and histophysiology of lymphoid tissue. Semin Oncol. 1993 Dec;20(6):555–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabie J., Ceuppens J. L., Vandenberghe P., de Boer M., Coorevits L., De Wolf-Peeters C. The B7/BB1 antigen is expressed by Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease and contributes to the stimulating capacity of Hodgkin's disease-derived cell lines. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2845–2852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper K., Balzano C., Rouvier E., Mattéi M. G., Luciani M. F., Golstein P. CTLA-4 and CD28 activated lymphocyte molecules are closely related in both mouse and human as to sequence, message expression, gene structure, and chromosomal location. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):1037–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Bluestone J. A., Nadler L. M., Thompson C. B. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol Today. 1994 Jul;15(7):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Vandenberghe P., Thompson C. B. The CD28 and CTLA-4 receptor family. Chem Immunol. 1994;59:62–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karandikar N. J., Vanderlugt C. L., Walunas T. L., Miller S. D., Bluestone J. A. CTLA-4: a negative regulator of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1996 Aug 1;184(2):783–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosco-Vilbois M. H., Zentgraf H., Gerdes J., Bonnefoy J. Y. To 'B' or not to 'B' a germinal center? Immunol Today. 1997 May;18(5):225–230. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(97)01048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel M. F., Allison J. P. CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on the response of T cells to stimulation. J Exp Med. 1995 Aug 1;182(2):459–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel M. F., Allison J. P. CTLA-4 engagement inhibits IL-2 accumulation and cell cycle progression upon activation of resting T cells. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2533–2540. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper H. M., Brouwer M., Linsley P. S., van Lier R. A. Activated T cells can induce high levels of CTLA-4 expression on B cells. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 15;155(4):1776–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D. R., Krummel M. F., Allison J. P. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science. 1996 Mar 22;271(5256):1734–1736. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5256.1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung H. T., Bradshaw J., Cleaveland J. S., Linsley P. S. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated molecule-4, a high-avidity receptor for CD80 and CD86, contains an intracellular localization motif in its cytoplasmic tail. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):25107–25114. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.25107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., Lee K. P., Harris E. S., Petryniak B., Craighead N., Reynolds P. J., Lombard D. B., Freeman G. J., Nadler L. M., Gray G. S. Characterization of CTLA-4 structure and expression on human T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3489–3499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Bradshaw J., Greene J., Peach R., Bennett K. L., Mittler R. S. Intracellular trafficking of CTLA-4 and focal localization towards sites of TCR engagement. Immunity. 1996 Jun;4(6):535–543. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80480-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S. Distinct roles for CD28 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated molecule-4 receptors during T cell activation? J Exp Med. 1995 Aug 1;182(2):289–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Greene J. L., Brady W., Bajorath J., Ledbetter J. A., Peach R. Human B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) bind with similar avidities but distinct kinetics to CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors. Immunity. 1994 Dec;1(9):793–801. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(94)80021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Greene J. L., Tan P., Bradshaw J., Ledbetter J. A., Anasetti C., Damle N. K. Coexpression and functional cooperation of CTLA-4 and CD28 on activated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Chesnokova V., Forman S. J., Diamond D. J. Molecular analysis of T-cell receptor repertoire in bone marrow transplant recipients: evidence for oligoclonal T-cell expansion in graft-versus-host disease lesions. Blood. 1996 Apr 1;87(7):3032–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Johnson G. D., Gordon J., MacLennan I. C. Germinal centres in T-cell-dependent antibody responses. Immunol Today. 1992 Jan;13(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90199-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy K., Camberis M., Gros G. L. Protective immunity to nematode infection is induced by CTLA-4 blockade. J Exp Med. 1997 Jul 21;186(2):183–187. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Freedman A. S., Aster J. C., Gribben J. G., Lee N. C., Rhynhart K. K., Banchereau J., Nadler L. M. In vivo expression of the B7 costimulatory molecule by subsets of antigen-presenting cells and the malignant cells of Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1994 Feb 1;83(3):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa Y., Wachi E., Tominaga K., Abe M., Wakasa H. A novel monoclonal antibody (FUN-1) identifies an activation antigen in cells of the B-cell lineage and Reed-Sternberg cells. J Pathol. 1993 Mar;169(3):309–315. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetermans W. E., D'Haens G. R., Ceuppens J. L., Rutgeerts P., Geboes K. Mucosal expression by B7-positive cells of the 60-kilodalton heat-shock protein in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jan;108(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P. J., Maldonado J. H., Davis T. A., June C. H., Racke M. K. CTLA-4 blockade enhances clinical disease and cytokine production during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 15;157(4):1333–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przepiorka D., Weisdorf D., Martin P., Klingemann H. G., Beatty P., Hows J., Thomas E. D. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995 Jun;15(6):825–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tivol E. A., Borriello F., Schweitzer A. N., Lynch W. P., Bluestone J. A., Sharpe A. H. Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity. 1995 Nov;3(5):541–547. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tivol E. A., Boyd S. D., McKeon S., Borriello F., Nickerson P., Strom T. B., Sharpe A. H. CTLA4Ig prevents lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction in CTLA-4-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1997 Jun 1;158(11):5091–5094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gool S. W., Delabie J., Vandenberghe P., Coorevits L., De Wolf-Peeters C., Ceuppens J. L. Expression of B7-2 (CD86) molecules by Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Leukemia. 1997 Jun;11(6):846–851. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe P., Ceuppens J. L. Immobilized anti-CD5 together with prolonged activation of protein kinase C induce interleukin 2-dependent T cell growth: evidence for signal transduction through CD5. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):251–259. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe P., Delabie J., de Boer M., De Wolf-Peeters C., Ceuppens J. L. In situ expression of B7/BB1 on antigen-presenting cells and activated B cells: an immunohistochemical study. Int Immunol. 1993 Mar;5(3):317–321. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwilghen J., Lovis R., De Boer M., Linsley P. S., Haines G. K., Koch A. E., Pope R. M. Expression of functional B7 and CTLA4 on rheumatoid synovial T cells. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 1;153(3):1378–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. H., Jr, Hagman J., Linsley P. S., Hodsdon W., Freed J. H., Newell M. K. Rescue of thymocytes from glucocorticoid-induced cell death mediated by CD28/CTLA-4 costimulatory interactions with B7-1/B7-2. J Exp Med. 1996 Nov 1;184(5):1631–1638. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.5.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walunas T. L., Bakker C. Y., Bluestone J. A. CTLA-4 ligation blocks CD28-dependent T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2541–2550. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walunas T. L., Lenschow D. J., Bakker C. Y., Linsley P. S., Freeman G. J., Green J. M., Thompson C. B., Bluestone J. A. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):405–413. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse P., Penninger J. M., Timms E., Wakeham A., Shahinian A., Lee K. P., Thompson C. B., Griesser H., Mak T. W. Lymphoproliferative disorders with early lethality in mice deficient in Ctla-4. Science. 1995 Nov 10;270(5238):985–988. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5238.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]