Abstract
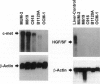
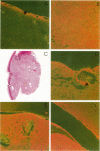
Human uveal melanoma disseminates initially and preferentially to the liver. This study describes the relationship between the expression of the c-met proto-oncogene (receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF)) in interconverted uveal melanoma cells (co-expressing vimentin and keratin intermediate filaments) and the regulation of their motogenic response to HGF/SF, a key step in local invasion and targeted dissemination to the liver. Expression of c-met in uveal melanoma cell lines correlates with both the appearance of an interconverted phenotype and invasive ability (measured in vitro). Using chemotactic checkerboard analysis, the greatest motogenic response to HGF/SF was achieved by invasive, interconverted, c-met-positive uveal melanoma cells. C-met was observed histologically in a uveal melanoma containing interconverted cells but was absent in a tumor composed of non-interconverted cells (vimentin positive/keratin negative). The c-met ligand, HGF/SF, although not expressed by uveal melanoma cell lines, was localized in tissue sections of primary uveal melanomas and metastatic melanoma to the liver. In the primary tumor, staining for HGF/SF was most intense at the level of the choriocapillaris, a finding that is significant because 1) highly remodeled neovascular loops and networks, which appear in tumors likely to disseminate, can be traced to the choriocapillaris and the draining vortex veins and 2) HGF/SF plays a role in tumor angiogenesis. Foci of metastatic melanoma to the liver stain diffusely for HGF/SF. Regulation of the uveal melanoma interconverted phenotype by HGF/SF may play an important role in the dissemination of this tumor.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert D. M., Niffenegger A. S., Willson J. K. Treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma: review and recommendations. Surv Ophthalmol. 1992 May-Jun;36(6):429–438. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(05)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedikian A. Y., Kantarjian H., Young S. E., Bodey G. P. Prognosis in metastatic choroidal melanoma. South Med J. 1981 May;74(5):574–577. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198105000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedikian A. Y., Legha S. S., Mavligit G., Carrasco C. H., Khorana S., Plager C., Papadopoulos N., Benjamin R. S. Treatment of uveal melanoma metastatic to the liver: a review of the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center experience and prognostic factors. Cancer. 1995 Nov 1;76(9):1665–1670. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19951101)76:9<1665::aid-cncr2820760925>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., Gaudino G., Tamagnone L., Coffer A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):629–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Char D. H. Metastatic choroidal melanoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978 Jul;86(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels K. J., Boldt H. C., Martin J. A., Gardner L. M., Meyer M., Folberg R. Expression of type VI collagen in uveal melanoma: its role in pattern formation and tumor progression. Lab Invest. 1996 Jul;75(1):55–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso L. A., Shields J. A., Augsburger J. J., Orth D. H., Johnson P. Metastatic uveal melanoma: diffuse hepatic metastasis in a patient with concurrent normal serum liver enzyme levels and liver scan. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985 Jun;103(6):758–758. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050060016002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn L. H., Burgess M. A., Gottlieb J. A. Metastatic patterns of choroidal melanoma. Cancer. 1974 Oct;34(4):1001–1004. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197410)34:4<1001::aid-cncr2820340406>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folberg R., Mehaffey M., Gardner L. M., Meyer M., Rummelt V., Pe'er J. The microcirculation of choroidal and ciliary body melanomas. Eye (Lond) 1997;11(Pt 2):227–238. doi: 10.1038/eye.1997.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folberg R., Rummelt V., Parys-Van Ginderdeuren R., Hwang T., Woolson R. F., Pe'er J., Gruman L. M. The prognostic value of tumor blood vessel morphology in primary uveal melanoma. Ophthalmology. 1993 Sep;100(9):1389–1398. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs U., Kivelä T., Summanen P., Immonen I., Tarkkanen A. An immunohistochemical and prognostic analysis of cytokeratin expression in malignant uveal melanoma. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):169–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong R. A. The biology of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Bioessays. 1992 Sep;14(9):613–617. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galimi F., Brizzi M. F., Comoglio P. M. The hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor. Stem Cells. 1993 Jul;11 (Suppl 2):22–30. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530110805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. S., Kleinman H. K., Goldberg I. D., Bhargava M. M., Nickoloff B. J., Kinsella J. L., Polverini P., Rosen E. M. Scatter factor induces blood vessel formation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1937–1941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., dalla Zonca P., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor stimulates the Ras-guanine nucleotide exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9165–9168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. J., Seftor E. A., Chu Y. W., Trevor K. T., Seftor R. E. Role of intermediate filaments in migration, invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1996 Dec;15(4):507–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00054016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. J., Seftor E. A., Seftor R. E., Fidler I. J. A simple quantitative assay for studying the invasive potential of high and low human metastatic variants. Cancer Lett. 1987 Dec;38(1-2):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(87)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. J., Seftor E. A., Seftor R. E., Gardner L. M., Boldt H. C., Meyer M., Pe'er J., Folberg R. Biologic determinants of uveal melanoma metastatic phenotype: role of intermediate filaments as predictive markers. Lab Invest. 1998 Feb;78(2):153–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. J., Seftor E. A., Seftor R. E., Trevor K. T. Experimental co-expression of vimentin and keratin intermediate filaments in human breast cancer cells results in phenotypic interconversion and increased invasive behavior. Am J Pathol. 1997 Feb;150(2):483–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffers M., Rong S., Vande Woude G. F. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-Met signaling in tumorigenicity and invasion/metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl) 1996 Sep;74(9):505–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00204976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan-Mitchell J., Mitchell M. S., Rao N., Liggett P. E. Characterization of uveal melanoma cell lines that grow as xenografts in rabbit eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 May;30(5):829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivelä T., Summanen P. Retinoinvasive malignant melanoma of the uvea. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Aug;81(8):691–697. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.8.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamszus K., Jin L., Fuchs A., Shi E., Chowdhury S., Yao Y., Polverini P. J., Laterra J., Goldberg I. D., Rosen E. M. Scatter factor stimulates tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis in human breast cancers in the mammary fat pads of nude mice. Lab Invest. 1997 Mar;76(3):339–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laterra J., Nam M., Rosen E., Rao J. S., Lamszus K., Goldberg I. D., Johnston P. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor gene transfer enhances glioma growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Lab Invest. 1997 Apr;76(4):565–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorigan J. G., Wallace S., Mavligit G. M. The prevalence and location of metastases from ocular melanoma: imaging study in 110 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991 Dec;157(6):1279–1281. doi: 10.2214/ajr.157.6.1950883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Nakamura T. Emerging multipotent aspects of hepatocyte growth factor. J Biochem. 1996 Apr;119(4):591–600. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Foster W. D., Zimmerman L. E., Gamel J. W. Modifications of Callender's classification of uveal melanoma at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Oct;96(4):502–509. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77914-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Keefe K. S., Burnier M. N. Uveal melanoma. Comparison of the prognostic value of fibrovascular loops, mean of the ten largest nucleoli, cell type, and tumor size. Ophthalmology. 1997 May;104(5):777–780. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(97)30234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehaffey M. G., Folberg R., Meyer M., Bentler S. E., Hwang T., Woolson R., Moore K. C. Relative importance of quantifying area and vascular patterns in uveal melanomas. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997 Jun;123(6):798–809. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Matsumoto K., Kiritoshi A., Tano Y., Nakamura T. Induction of hepatocyte growth factor in fibroblasts by tumor-derived factors affects invasive growth of tumor cells: in vitro analysis of tumor-stromal interactions. Cancer Res. 1997 Aug 1;57(15):3305–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nawa K., Ichihara A. Partial purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1450–1459. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigel K., Hedelin G., Speeg-Schatz C., Sahel J., Brini A. Facteurs pronostiques du mélanome choroïdien: étude rétrospective anatomo-clinique et statistique de 76 cas énuclés. J Fr Ophtalmol. 1992;15(6-7):410–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusciano D., Lorenzoni P., Burger M. M. Expression of constitutively activated hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor (c-met) in B16 melanoma cells selected for enhanced liver colonization. Oncogene. 1995 Nov 16;11(10):1979–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto T., Sakamoto M., Yoshikawa H., Hata Y., Ishibashi T., Ohnishi Y., Inomata H. Histologic findings and prognosis of uveal malignant melanoma in japanese patients. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Mar;121(3):276–283. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner K. M., Sachs M., Birchmeier W. The Met receptor tyrosine kinase transduces motility, proliferation, and morphogenic signals of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):145–154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Spitzer E., Meyer D., Sachs M., Niemann C., Hartmann G., Weidner K. M., Birchmeier C., Birchmeier W. Sequential requirement of hepatocyte growth factor and neuregulin in the morphogenesis and differentiation of the mammary gland. J Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;131(1):215–226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Anand-Apte B., Zetter B. R. Differential endothelial migration and proliferation to basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. Growth Factors. 1996;13(1-2):57–64. doi: 10.3109/08977199609034566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakka K. A., Foos R. Y., Omphroy C. A., Straatsma B. R. Malignant melanoma. Analysis of an autopsy population. Ophthalmology. 1980 Jun;87(6):549–556. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(80)35197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]