Abstract
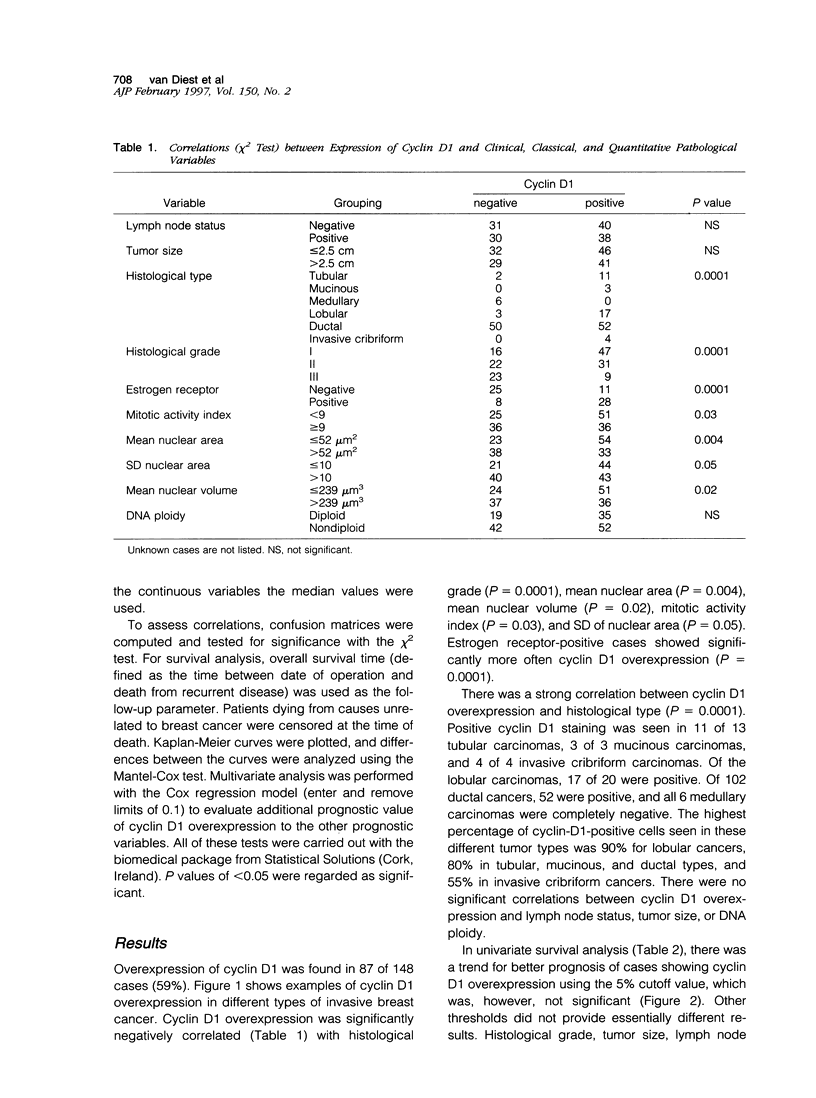
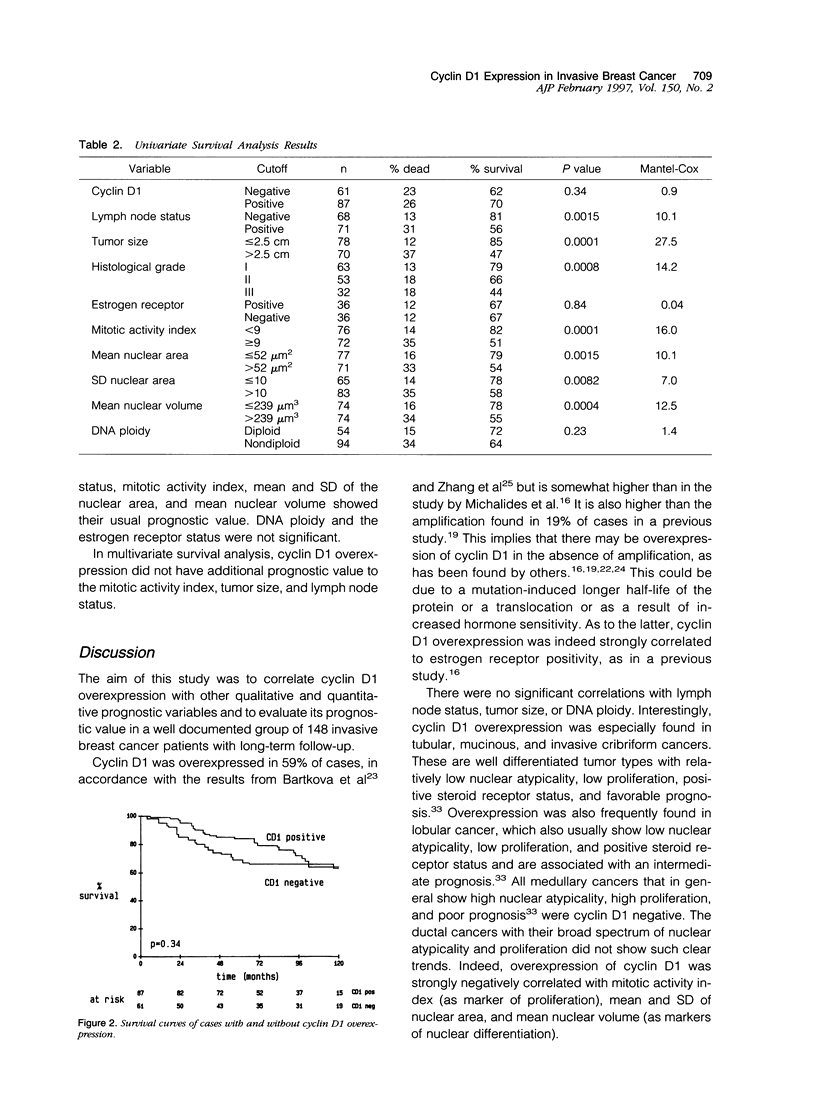
Cyclin D1 overexpression, detected by standard immunohistochemistry, was correlated with other prognostic variables and its prognostic value was evaluated in a group of 148 invasive breast cancers with long-term follow-up. Overexpression of cyclin D1 (59% of cases) was negatively correlated (chi 2 test) with histological grade (P = 0.0001), mean nuclear area (P = 0.004), mean nuclear volume (P = 0.02), and mitotic activity (P = 0.03) and positively correlated with estrogen receptor (P = 0.0001). There was a strong correlation between cyclin D1 overexpression and histological type (P = 0.0001). Positive cyclin D1 staining was seen in 11 of 13 tubular carcinomas, 3 of 3 mucinous carcinomas, 4 of 4 invasive cribriform carcinomas, and 17 of 20 lobular carcinomas. Of 102 ductal cancers, 52 were positive, and all 6 medullary carcinomas were negative. There were no significant correlations with lymph node status, tumor size, or DNA ploidy. In survival analysis, cyclin D1 overexpression did not provide significant univariate or multivariate prognostic value. In conclusion, cyclin D1 is mainly overexpressed in the well differentiated and lobular types of invasive breast cancer and is strongly associated with estrogen receptor positivity. It is negatively correlated with the proliferation marker mitoses count and with the differentiation markers nuclear area and nuclear volume. However, cyclin D1 overexpression does not seem to have prognostic value in invasive breast cancer when no adjuvant treatment is given.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltomaa S., Lipponen P., Eskelinen M., Kosma V. M., Marin S., Alhava E., Syrjänen K. Prognostic factors in axillary lymph node-negative (pN-) breast carcinomas. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(12):1555–1559. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baak J. P., Ladekarl M., Sørensen F. B. Reproducibility of mean nuclear volume and correlation with mean nuclear area in breast cancer: an investigation of various sampling schemes. Hum Pathol. 1994 Jan;25(1):80–85. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baak J. P., Van Dop H., Kurver P. H., Hermans J. The value of morphometry to classic prognosticators in breast cancer. Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;56(2):374–382. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850715)56:2<374::aid-cncr2820560229>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkova J., Lukas J., Müller H., Lützhøft D., Strauss M., Bartek J. Cyclin D1 protein expression and function in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1994 May 1;57(3):353–361. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S., Parry D., Bonetta L., Vousden K., Dickson C., Peters G. Absence of cyclin D/cdk complexes in cells lacking functional retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1633–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey B., Williams R. T., Carbonaro-Hall D. A., Horvath A., Tolo V. T., Luck J. V., Jr, Taylor C. R., Hall F. L. Immunocytochemical detection of cyclin A and cyclin D in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: novel, pertinent markers of cell proliferation. Mod Pathol. 1994 Oct;7(8):846–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzubar N., Walker K. J., Griffiths K., Ellis I. O., Elston C. W., Robertson J. F., Blamey R. W., Nicholson R. I. Ki67 immunostaining in primary breast cancer: pathological and clinical associations. Br J Cancer. 1989 Jun;59(6):943–947. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton F. Pathologic correlates of survival in 378 lymph node-negative infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas. Mitotic count is the best single predictor. Cancer. 1991 Sep 15;68(6):1309–1317. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910915)68:6<1309::aid-cncr2820680621>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis I. O., Galea M., Broughton N., Locker A., Blamey R. W., Elston C. W. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1992 Jun;20(6):479–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb01032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleege J. C., van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. Computer assisted efficiency testing of different sampling methods for selective nuclear graphic tablet morphometry. Lab Invest. 1990 Aug;63(2):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillett C., Fantl V., Smith R., Fisher C., Bartek J., Dickson C., Barnes D., Peters G. Amplification and overexpression of cyclin D1 in breast cancer detected by immunohistochemical staining. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1812–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W., Rugg C. A., Musgrove E. A. Method for analysis of cellular DNA content of paraffin-embedded pathological material using flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1333–1335. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6619538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannink I., Bennen J. N., Blaauw J., van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. At convenience and systematic random sampling: effects on the prognostic value of nuclear area assessments in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36(1):55–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00690185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Kahn S. M., Zhou P., Zhang Y. J., Cacace A. M., Infante A. S., Doi S., Santella R. M., Weinstein I. B. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3447–3457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joensuu H., Toikkanen S., Klemi P. J. DNA index and S-phase fraction and their combination as prognostic factors in operable ductal breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1990 Jul 15;66(2):331–340. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900715)66:2<331::aid-cncr2820660222>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel O. W., Franklin W. A., Ringus J. C., Meyer J. S. Thymidine labeling index and Ki-67 growth fraction in lesions of the breast. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):107–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp J. E., Broder S. Molecular foundations of cancer: new targets for intervention. Nat Med. 1995 Apr;1(4):309–320. doi: 10.1038/nm0495-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammie G. A., Fantl V., Smith R., Schuuring E., Brookes S., Michalides R., Dickson C., Arnold A., Peters G. D11S287, a putative oncogene on chromosome 11q13, is amplified and expressed in squamous cell and mammary carcinomas and linked to BCL-1. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Pagano M., Staskova Z., Draetta G., Bartek J. Cyclin D1 protein oscillates and is essential for cell cycle progression in human tumour cell lines. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):707–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Friedman E., McCrate M. M., Bauer W. C. Prediction of early course of breast carcinoma by thymidine labeling. Cancer. 1983 May 15;51(10):1879–1886. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830515)51:10<1879::aid-cncr2820511021>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Hageman P., van Tinteren H., Houben L., Wientjens E., Klompmaker R., Peterse J. A clinicopathological study on overexpression of cyclin D1 and of p53 in a series of 248 patients with operable breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1996 Mar;73(6):728–734. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., van Veelen N., Hart A., Loftus B., Wientjens E., Balm A. Overexpression of cyclin D1 correlates with recurrence in a group of forty-seven operable squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 1;55(5):975–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove E. A., Lee C. S., Buckley M. F., Sutherland R. L. Cyclin D1 induction in breast cancer cells shortens G1 and is sufficient for cells arrested in G1 to complete the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8022–8026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C. L., Kim H. G., Shows T. B., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. Rearrangement and overexpression of D11S287E, a candidate oncogene on chromosome 11q13 in benign parathyroid tumors. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):449–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuuring E., Verhoeven E., Mooi W. J., Michalides R. J. Identification and cloning of two overexpressed genes, U21B31/PRAD1 and EMS1, within the amplified chromosome 11q13 region in human carcinomas. Oncogene. 1992 Feb;7(2):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuuring E., Verhoeven E., van Tinteren H., Peterse J. L., Nunnink B., Thunnissen F. B., Devilee P., Cornelisse C. J., van de Vijver M. J., Mooi W. J. Amplification of genes within the chromosome 11q13 region is indicative of poor prognosis in patients with operable breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5229–5234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson H., Baldetorp B., Borg A., Dalberg M., Fernö M., Killander D., Olsson H. Indicators of prognosis in node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 12;322(15):1045–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004123221505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyterlinde A. M., Schipper N. W., Baak J. P., Peterse H., Matze E. Limited prognostic value of cellular DNA content to classical and morphometrical parameters in invasive ductal breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988 Mar;89(3):301–307. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/89.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. Y., Caamano J., Cooper F., Guo X., Klein-Szanto A. J. Immunohistochemistry of cyclin D1 in human breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Nov;102(5):695–698. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/102.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukerberg L. R., Yang W. I., Arnold A., Harris N. L. Cyclin D1 expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Detection by immunohistochemistry. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jun;103(6):756–760. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.6.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. The morphometric prognostic index is the strongest prognosticator in premenopausal lymph node-negative and lymph node-positive breast cancer patients. Hum Pathol. 1991 Apr;22(4):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden J. C., Baak J. P., Lindeman J., Hermans J., Meyer C. J. Prospective evaluation of prognostic value of morphometry in patients with primary breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):302–306. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]