Abstract
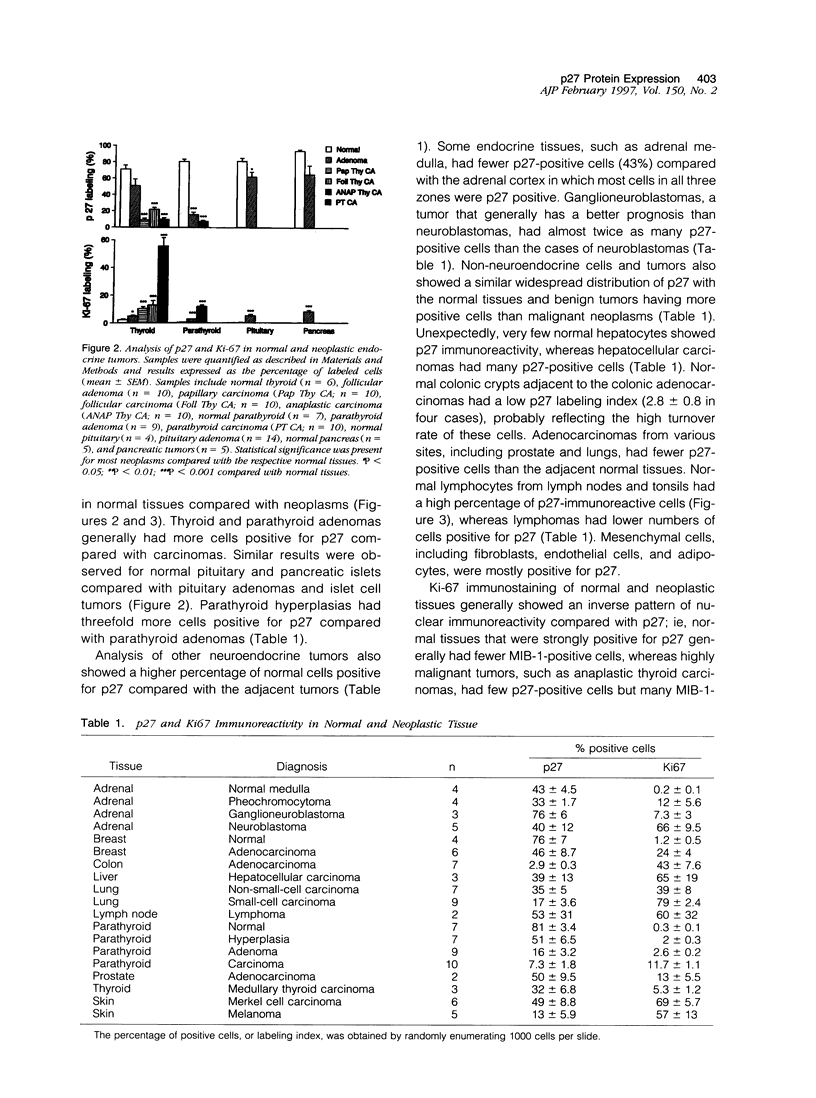
The p27kip1 (p27) gene encodes an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase activity. The expression of p27 protein in normal and neoplastic tissues was investigated by immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. Immunoblotting studies detected a 27-kd protein band that was decreased in neoplastic pituitary tissues compared with normal pituitary. Immunostaining of 177 tissues showed abundant expression of p27 protein in normal tissues with decreased numbers of immunoreactive cells in adenomas and carcinomas in both endocrine and nonendocrine tissues. p27 expression was inversely related to the proliferation marker Ki-67 antigen detected with monoclonal antibody MIB-1. Parathyroid adenomas and hyperplasias had similar Ki-67 labeling indices; however, hyperplasias had threefold more p27-positive cells than parathyroid adenomas, suggesting that p27 immunostaining may be useful in distinguishing between these two conditions. These results indicate that there is widespread aberrant p27 expression in hyperplastic tissues and in benign and malignant neoplasms compared with normal tissues. Immunohistochemical analysis of p27 along with Ki-67 may be used to assess the biological behavior of various neoplasms, to classify hyperplastic and neoplastic tissues, and to study cell cycle regulation during tumor progression.
Full text
PDF

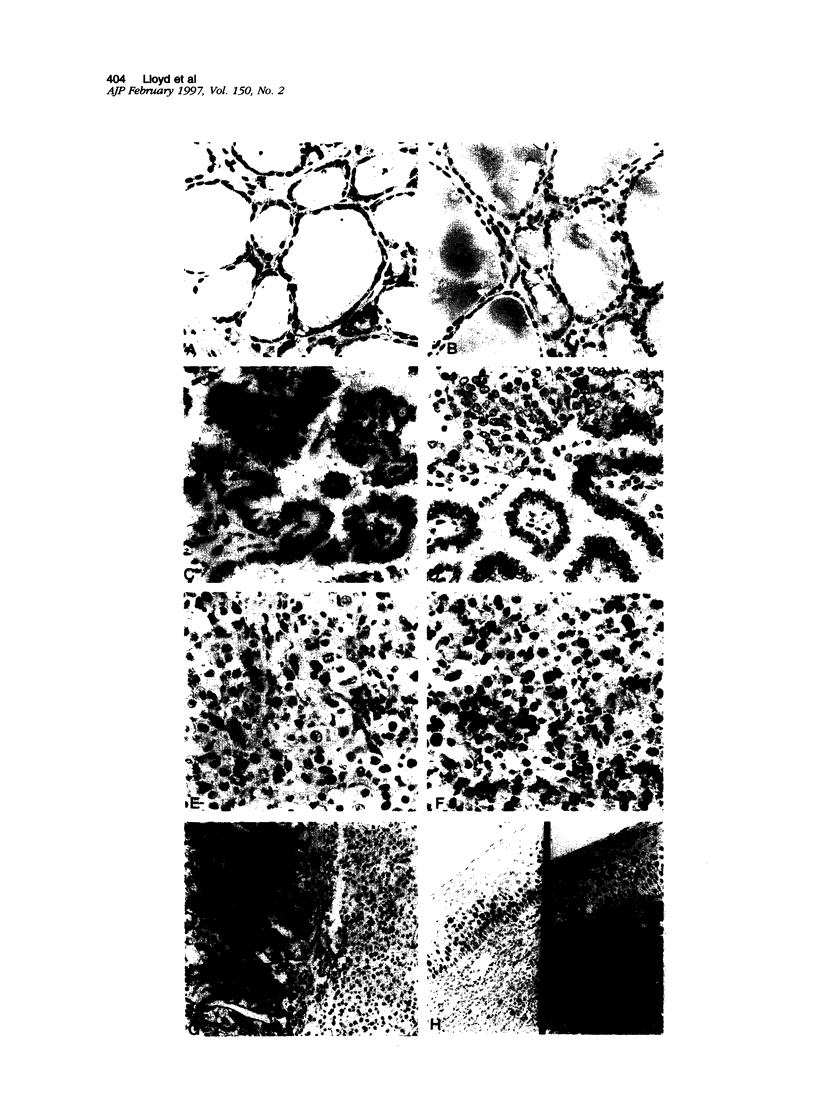



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. C., Gatter K. C. Monoclonal antibody Ki-67: its use in histopathology. Histopathology. 1990 Dec;17(6):489–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Willingham T., Shuford M., Nisen P. D. Tumor suppression and inhibition of aneuploid cell accumulation in human brain tumor cells by ectopic overexpression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27KIP1. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 15;97(8):1983–1988. doi: 10.1172/JCI118631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coats S., Flanagan W. M., Nourse J., Roberts J. M. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science. 1996 May 10;272(5263):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5263.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fero M. L., Rivkin M., Tasch M., Porter P., Carow C. E., Firpo E., Polyak K., Tsai L. H., Broudy V., Perlmutter R. M. A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):733–744. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geradts J., Wilson P. A. High frequency of aberrant p16(INK4A) expression in human breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jul;149(1):15–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Becker M. H., Key G., Cattoretti G. Immunohistological detection of tumour growth fraction (Ki-67 antigen) in formalin-fixed and routinely processed tissues. J Pathol. 1992 Sep;168(1):85–86. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Jenkins C. W., Li Y., Nichols M. A., Wu X., O'Keefe C. L., Matera A. G., Xiong Y. Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2939–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengst L., Reed S. I. Translational control of p27Kip1 accumulation during the cell cycle. Science. 1996 Mar 29;271(5257):1861–1864. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5257.1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Roussel M. F., Kato J. Y., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Novel INK4 proteins, p19 and p18, are specific inhibitors of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2672–2681. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirama T., Koeffler H. P. Role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in the development of cancer. Blood. 1995 Aug 1;86(3):841–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin X., Nguyen D., Zhang W. W., Kyritsis A. P., Roth J. A. Cell cycle arrest and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation by the p16INK4 gene mediated by an adenovirus vector. Cancer Res. 1995 Aug 1;55(15):3250–3253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A. Cell-cycle regulators and cancer. Trends Genet. 1995 Apr;11(4):136–140. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamata N., Morosetti R., Miller C. W., Park D., Spirin K. S., Nakamaki T., Takeuchi S., Hatta Y., Simpson J., Wilcyznski S. Molecular analysis of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor gene p27/Kip1 in human malignancies. Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 1;55(11):2266–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa H., Kineman R. D., Manova-Todorova K. O., Soares V. C., Hoffman E. S., Ono M., Khanam D., Hayday A. C., Frohman L. A., Koff A. Enhanced growth of mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor function of p27(Kip1). Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Nikolic M., Baptista C. A., Lai E., Tsai L. H., Massagué J. The brain-specific activator p35 allows Cdk5 to escape inhibition by p27Kip1 in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Reynisdóttir I., Massagué J. Cloning of p57KIP2, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 15;9(6):639–649. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Schmidt K., Coleman K., Wilson B. S. Prolactin and growth hormone synthesis and thymidine incorporation in dissociated rat pituitary tumor cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Jan;181(1):18–23. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka S., Edwards M. C., Bai C., Parker S., Zhang P., Baldini A., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J. p57KIP2, a structurally distinct member of the p21CIP1 Cdk inhibitor family, is a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 15;9(6):650–662. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Ishida N., Shirane M., Inomata A., Inoue T., Shishido N., Horii I., Loh D. Y., Nakayama K. Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):707–720. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Bohlander S. K., Sato Y., Papadopoulos N., Liu B., Friedman C., Trask B. J., Roberts J. M., Kinzler K. W., Rowley J. D. Assignment of the human p27Kip1 gene to 12p13 and its analysis in leukemias. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1206–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Kato J. Y., Solomon M. J., Sherr C. J., Massague J., Roberts J. M., Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Castañeda M. V., Lee M. H., Latres E., Polyak K., Lacombe L., Montgomery K., Mathew S., Krauter K., Sheinfeld J., Massague J. p27Kip1: chromosomal mapping to 12p12-12p13.1 and absence of mutations in human tumors. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1211–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Toyoshima H., Hunter T. Redistribution of the CDK inhibitor p27 between different cyclin.CDK complexes in the mouse fibroblast cell cycle and in cells arrested with lovastatin or ultraviolet irradiation. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Sep;6(9):1197–1213. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.9.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., Jin L., Grande J. P., Lloyd R. V. Transforming growth factor-beta and p27 expression in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1996 Jul;137(7):3051–3060. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.7.8770931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravitz M. J., Yan S., Herr K. D., Wenner C. E. Transforming growth factor beta-induced activation of cyclin E-cdk2 kinase and down-regulation of p27Kip1 in C3H 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1995 Apr 1;55(7):1413–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. A., Loganzo F., Jr, Shea C. R., Walker G. J., Flores J. F., Glendening J. M., Bogdany J. K., Shiel M. J., Haluska F. G., Fountain J. W. Loss of expression of the p16/cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2 tumor suppressor gene in melanocytic lesions correlates with invasive stage of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1995 Jul 1;55(13):2713–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonk D. M., Kuijpers H. J., van Drunen E., van Dalen C. H., Geurts van Kessel A. H., Verheijen R., Ramaekers F. C. Assignment of the gene(s) involved in the expression of the proliferation-related Ki-67 antigen to human chromosome 10. Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;83(3):297–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00285178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Roberts J. M. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995 May 15;9(10):1149–1163. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.10.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin K. S., Simpson J. F., Takeuchi S., Kawamata N., Miller C. W., Koeffler H. P. p27/Kip1 mutation found in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996 May 15;56(10):2400–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., Kuijpers H. J., van Driel R., Beck J. L., van Dierendonck J. H., Brakenhoff G. J., Ramaekers F. C. Ki-67 detects a nuclear matrix-associated proliferation-related antigen. II. Localization in mitotic cells and association with chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1989 Apr;92(Pt 4):531–540. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloschak M., Yu A., Xiao J., Post K. D. Frequent loss of the P16INK4a gene product in human pituitary tumors. Cancer Res. 1996 Jun 1;56(11):2493–2496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]