Abstract
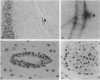
Myelin basic protein (MBP)-specific T cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and are targets of selective immunotherapies. However, autoantigen-specific T cells can also be isolated from healthy individuals. Their functional potential is unknown and obviously cannot be tested in humans. We approached this question in a closely related primate species, the rhesus monkey. CD4+ T cell lines specific for MBP were isolated from normal rhesus monkeys using the same primary limiting dilution technique that is now widely used to generate human autoreactive T cell clones in vitro. Three different epitopes were recognized by three rhesus T cell lines isolated from three different monkeys. Upon activation, all lines produced interferon-gamma, interleukin-2, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor but neither interleukin-4 nor transforming growth factor-beta. The MBP-specific T cells were injected intravenously without adjuvant into the nonirradiated autologous monkey. One of the three rhesus monkeys developed an encephalomyelitis with a pleocytosis in the spinal fluid and perivascular infiltrates in the leptomeninges, spinal nerve roots and cerebral cortex. The data demonstrate that the normal immune repertoire of a primate species contains MBP-specific CD4+ T cells that are able to induce an autoimmune encephalomyelitis upon transfer into the nonirradiated autologous recipient.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Mitchell D. J., Timmermann L., Wraith D. C., Tausch G. S., Waldor M. K., Zamvil S. S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Limited heterogeneity of T cell receptors from lymphocytes mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis allows specific immune intervention. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetta R., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Abrams J., de Vries J. E., Spits H., Roncarolo M. G. Host-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones isolated from a human chimera produce IL-5, IL-2, IFN-gamma and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor but not IL-4. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):902–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Nun A., Wekerle H., Cohen I. R. The rapid isolation of clonable antigen-specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):195–199. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beraud E., Balzano C., Zamora A. J., Varriale S., Bernard D., Ben-Nun A. Pathogenic and non-pathogenic T lymphocytes specific for the encephalitogenic epitope of myelin basic protein: functional characteristics and vaccination properties. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Aug;47(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdette D. N., Whitham R. H., Chou Y. K., Morrison W. J., Atherton J., Kenny C., Liefeld D., Hashim G. A., Offner H., Vandenbark A. A. Immunity to TCR peptides in multiple sclerosis. I. Successful immunization of patients with synthetic V beta 5.2 and V beta 6.1 CDR2 peptides. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2510–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genain C. P., Lee-Parritz D., Nguyen M. H., Massacesi L., Joshi N., Ferrante R., Hoffman K., Moseley M., Letvin N. L., Hauser S. L. In healthy primates, circulating autoreactive T cells mediate autoimmune disease. J Clin Invest. 1994 Sep;94(3):1339–1345. doi: 10.1172/JCI117454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R. Neurological autoimmune disease and the trimolecular complex of T-lymphocytes. Ann Neurol. 1989 Jun;25(6):531–538. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Winters S. T., Olee T., Powell H. C., Carlo D. J., Brostoff S. W. Vaccination against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with T cell receptor peptides. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):668–670. doi: 10.1126/science.2814489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jingwu Z., Medaer R., Hashim G. A., Chin Y., van den Berg-Loonen E., Raus J. C. Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis and controls: precursor frequency, fine specificity, and cytotoxicity. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):330–338. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi N., Usuku K., Hauser S. L. The T-cell response to myelin basic protein in familial multiple sclerosis: diversity of fine specificity, restricting elements, and T-cell receptor usage. Ann Neurol. 1993 Sep;34(3):385–393. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitz K., Lassmann H., Wisniewski H. M. Isolated leptomeninges of the spinal cord: an ideal tool to study inflammatory reaction in EAE. Acta Neuropathol Suppl. 1981;7:179–181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81553-9_54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchroo V. K., Martin C. A., Greer J. M., Ju S. T., Sobel R. A., Dorf M. E. Cytokines and adhesion molecules contribute to the ability of myelin proteolipid protein-specific T cell clones to mediate experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4371–4382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H., Brunner C., Bradl M., Linington C. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: the balance between encephalitogenic T lymphocytes and demyelinating antibodies determines size and structure of demyelinated lesions. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;75(6):566–576. doi: 10.1007/BF00686201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H., Budka H., Schnaberth G. Inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculitis in a patient with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1981 Feb;38(2):99–102. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510020057008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H., Zimprich F., Rössler K., Vass K. Inflammation in the nervous system. Basic mechanisms and immunological concepts. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1991;147(12):763–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Bradl M., Lassmann H., Brunner C., Vass K. Augmentation of demyelination in rat acute allergic encephalomyelitis by circulating mouse monoclonal antibodies directed against a myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):443–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Munoz J. J., Blaskett A. Acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. I. Adjuvant action of Bordetella pertussis is due to vasoactive amine sensitization and increased vascular permeability of the central nervous system. Cell Immunol. 1982 Nov 1;73(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Howell M. D., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Brostoff S., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. A myelin basic protein peptide is recognized by cytotoxic T cells in the context of four HLA-DR types associated with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):19–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:153–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massacesi L., Genain C. P., Lee-Parritz D., Letvin N. L., Canfield D., Hauser S. L. Active and passively induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in common marmosets: a new model for multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1995 Apr;37(4):519–530. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medaer R., Stinissen P., Truyen L., Raus J., Zhang J. Depletion of myelin-basic-protein autoreactive T cells by T-cell vaccination: pilot trial in multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1995 Sep 23;346(8978):807–808. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91622-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinl E., Aloisi F., Ertl B., Weber F., de Waal Malefyt R., Wekerle H., Hohlfeld R. Multiple sclerosis. Immunomodulatory effects of human astrocytes on T cells. Brain. 1994 Dec;117(Pt 6):1323–1332. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.6.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinl E., Weber F., Drexler K., Morelle C., Ott M., Saruhan-Direskeneli G., Goebels N., Ertl B., Jechart G., Giegerich G. Myelin basic protein-specific T lymphocyte repertoire in multiple sclerosis. Complexity of the response and dominance of nested epitopes due to recruitment of multiple T cell clones. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2633–2643. doi: 10.1172/JCI116879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinl E., t Hart B. A., Bontrop R. E., Hoch R. M., Iglesias A., de Waal Malefyt R., Fickenscher H., Müller-Fleckenstein I., Fleckenstein B., Wekerle H. Activation of a myelin basic protein-specific human T cell clone by antigen-presenting cells from rhesus monkeys. Int Immunol. 1995 Sep;7(9):1489–1495. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.9.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nooij F. J., Jonker M., Balner H. Differentiation antigens on rhesus monkey lymphocytes. II. Characterization of RhT3, a CD3-like antigen on T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):981–984. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota K., Matsui M., Milford E. L., Mackin G. A., Weiner H. L., Hafler D. A. T-cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):183–187. doi: 10.1038/346183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., Hirsch R. L., Schindler J., Johnson K. P. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with gamma interferon: exacerbations associated with activation of the immune system. Neurology. 1987 Jul;37(7):1097–1102. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.7.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette M., Fujita K., Wilkinson D., Altmann D. M., Trowsdale J., Giegerich G., Hinkkanen A., Epplen J. T., Kappos L., Wekerle H. Myelin autoreactivity in multiple sclerosis: recognition of myelin basic protein in the context of HLA-DR2 products by T lymphocytes of multiple-sclerosis patients and healthy donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7968–7972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. B., Mitchell D., Lederman J., Buckmeier J., Zamvil S. S., Graham M., Ruddle N. H., Steinman L. Lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by myelin basic protein-specific T cell clones correlates with encephalitogenicity. Int Immunol. 1990;2(6):539–544. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S. Biology of disease. Analysis of autoimmune demyelination: its impact upon multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;50(6):608–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann K. A., Waite B. C., Lee-Parritz D. E., Lin W., Uchanska-Ziegler B., O'Connell M. J., Letvin N. L. Use of human leukocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies for clinically immunophenotyping lymphocytes of rhesus monkeys. Cytometry. 1994 Sep 1;17(1):102–108. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990170113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluesener H. J., Wekerle H. Autoaggressive T lymphocyte lines recognizing the encephalitogenic region of myelin basic protein: in vitro selection from unprimed rat T lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3128–3133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Hentges R. Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease progression in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 15;325(7):467–472. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slierendregt B. L., van Noort J. T., Bakas R. M., Otting N., Jonker M., Bontrop R. E. Evolutionary stability of transspecies major histocompatibility complex class II DRB lineages in humans and rhesus monkeys. Hum Immunol. 1992 Sep;35(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(92)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Qin Y., Chluba J., Epplen J. T., Wekerle H. Suppression of experimentally induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis by cytolytic T-T cell interactions. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):843–845. doi: 10.1038/332843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbark A. A., Chou Y. K., Bourdette D., Whitham R., Chilgren J., Chou C. H., Konat G., Hashim G., Vainiene M., Offner H. Human T lymphocyte response to myelin basic protein: selection of T lymphocyte lines from MBP-responsive donors. J Neurosci Res. 1989 May;23(1):21–30. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490230104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbark A. A., Hashim G., Offner H. Immunization with a synthetic T-cell receptor V-region peptide protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):541–544. doi: 10.1038/341541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis as a model of immune-mediated CNS disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Oct;3(5):779–784. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90153-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Weiner H. L., Hafler D. A. T-cell recognition of myelin basic protein. Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90126-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Steinman L. The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:579–621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Besouw N. M., van der Meide P. H., Bakker N. P. The mitogen-induced generation of interferon-gamma producing cells in cultures of rhesus monkey peripheral blood mononuclear cells is age-dependent. J Med Primatol. 1994 Jan;23(1):42–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.1994.tb00094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]