Abstract
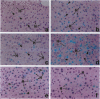
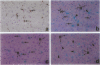
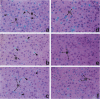
We previously demonstrated that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) gene expression primarily in endothelial cells in most organs of the mouse, with maximal induction by 3 hours. Here we show that induction in the liver occurs in a distinctly different pattern. For example, the increase in PAI-1 mRNA in liver was biphasic with an initial peak at 1 to 2 hours and a second peak at 6 to 8 hours. Moreover, in situ hybridization experiments revealed that PAI-1 mRNA was induced in both endothelial cells and hepatocytes. The endothelial cell response was monophasic and maximal between 1 and 4 hours, whereas the hepatocyte response was biphasic, peaking at 2 hours and again at 6 to 8 hours. To determine possible mechanisms involved in the induction of PAI-1 by LPS, we analyzed the tissues for changes in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha LPS caused a rapid induction of TNF-alpha mRNA in Kupffer cells, detectable within 15 minutes. Pretreatment of mice with anti-TNF antiserum before challenge with LPS reduced the subsequent increase in plasma levels of PAI-1 by 50 to 70% and significantly reduced the level of induction of PAI-1 mRNA in the liver at both early and late times. Pretreatment appeared to inhibit induction primarily within hepatocytes. These results suggest that LPS may induce PAI-1 in endothelial cells and hepatocytes by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aillaud M. F., Juhan-Vague I., Alessi M. C., Marecal M., Vinson M. F., Arnaud C., Vague P., Collen D. Increased PA-inhibitor levels in the postoperative period--no cause-effect relation with increased cortisol. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Aug 30;54(2):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander H. R., Doherty G. M., Buresh C. M., Venzon D. J., Norton J. A. A recombinant human receptor antagonist to interleukin 1 improves survival after lethal endotoxemia in mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt A., Murphy P., Hart D. A. Human HuH-7 hepatoma cells express urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: identification, characterization and regulation by inflammatory mediators. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 14;1138(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(92)90055-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauss F., Dröge W., Männel D. N. Tumor necrosis factor mediates endotoxic effects in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1622–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1622-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Nicodeme E., Chesne C., Guillouzo A., Belin D., Hyafil F. Urokinase and type I plasminogen activator inhibitor production by normal human hepatocytes: modulation by inflammatory agents. Hepatology. 1994 Jul;20(1 Pt 1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Terebuh P. D., Remick D. G., Scales W. E., Kunkel S. L. In vivo biologic and immunohistochemical analysis of interleukin-1 alpha, beta and tumor necrosis factor during experimental endotoxemia. Kinetics, Kupffer cell expression, and glucocorticoid effects. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):395–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):818–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI111777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K. Biologically active products of stimulated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):245–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. The proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor and treatment of the septic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1177–1184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diéval J., Nguyen G., Gross S., Delobel J., Kruithof E. K. A lifelong bleeding disorder associated with a deficiency of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):528–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Hoekzema R., de Vos A. F. Inhibiting interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha does not reduce induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 by endotoxin in rats in vivo. Blood. 1995 Jan 1;85(1):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay W. P., Shapiro A. D., Shih J. L., Schleef R. R., Ginsburg D. Brief report: complete deficiency of plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 due to a frame-shift mutation. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 10;327(24):1729–1733. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212103272406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Sawa H., Saffitz J. E., Lucore C. L., Sobel B. E. Induction of endothelial cell expression of the plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 gene by thrombosis in vivo. Circulation. 1992 Dec;86(6):2000–2010. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.6.2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., de Faire U., Walldius G., Dahlén G., Szamosi A., Landou C., Blombäck M., Wiman B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma: risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1987 Jul 4;2(8549):3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Gelehrter T. D. Induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in HepG2 human hepatoma cells by mediators of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19095–19100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Gordon S. Mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Identification of resident macrophages in renal medullary and cortical interstitium and the juxtaglomerular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1704–1709. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. M., Boermeester M. A., Fischer E., de Jong I. W., van der Poll T., Moldawer L. L., Hack C. E., Lowry S. F. Contribution of interleukin-1 to activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis, neutrophil degranulation, and the release of secretory-type phospholipase A2 in sepsis: studies in nonhuman primates after interleukin-1 alpha administration and during lethal bacteremia. Blood. 1995 Aug 1;86(3):1027–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton M., Eguchi Y., Sawdey M., Ahn C., Loskutoff D. J. Cellular localization of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor messenger RNA and protein in murine renal tissue. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):59–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluft C., Verheijen J. H., Jie A. F., Rijken D. C., Preston F. E., Sue-Ling H. M., Jespersen J., Aasen A. O. The postoperative fibrinolytic shutdown: a rapidly reverting acute phase pattern for the fast-acting inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator after trauma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Nov;45(7):605–610. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkle B. A., Schuster S. J., Kelly M. D., Harjes K., Hassett D. E., Bohrer M., Tavassoli M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 messenger RNA expression is induced in rat hepatocytes in vivo by dexamethasone. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2636–2642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooistra T., Bosma P. J., Töns H. A., van den Berg A. P., Meyer P., Princen H. M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: biosynthesis and mRNA level are increased by insulin in cultured human hepatocytes. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):723–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Gudinchet A., Bachmann F. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 in various disease states. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Vosburgh E., Anderson K., McDonagh J. Deficiency of plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 results in hyperfibrinolytic bleeding. Blood. 1993 May 1;81(9):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Nathan C. F., Steinman R. M., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Murine Kupffer cells. Mononuclear phagocytes deficient in the generation of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi M., Biemond B. J., van Zonneveld A. J., ten Cate J. W., Pannekoek H. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity results in promotion of endogenous thrombolysis and inhibition of thrombus extension in models of experimental thrombosis. Circulation. 1992 Jan;85(1):305–312. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.1.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster M. I., Germolec D. R., Yoshida T., Kayama F., Thompson M. Endotoxin-induced cytokine gene expression and excretion in the liver. Hepatology. 1994 Feb;19(2):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Ljungnér H., Tengborn L. Two different mechanisms in patients with venous thrombosis and defective fibrinolysis: low concentration of plasminogen activator or increased concentration of plasminogen activator inhibitor. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 May 18;290(6480):1453–1456. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6480.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podor T. J., Hirsh J., Gelehrter T. D., Zeheb R., Torry D., Guigoz Y., Sierra F., Gauldie J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor is not an acute phase reactant in rats. Lack of IL-6- and hepatocyte-dependent synthesis. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):225–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van den Hoogen C. M., Verheijen J. H., Padro T., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., van Berkel T. J., Kuiper J., Emeis J. J. Endotoxin induction of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 mRNA in rat tissues in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15560–15563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Eskandari M. K., Nguyen D. T., Genord M. A., Raiford C. L., Kunkel S. L. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in lipopolysaccharide-induced pathologic alterations. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):49–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad F., Yamamoto K., Loskutoff D. J. Distribution and regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in murine adipose tissue in vivo. Induction by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 1;97(1):37–46. doi: 10.1172/JCI118404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M. S., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of murine type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in vivo. Tissue specificity and induction by lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1346–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Higgins D. L., Pillemer E., Levitt L. J. Bleeding diathesis due to decreased functional activity of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1747–1752. doi: 10.1172/JCI114076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Sinha M., Loskutoff D. J. Immunoradiometric assay to measure the binding of a specific inhibitor to tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Oct;106(4):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman J., Sawdey M., Craig H., Thinnes T., Bordin G., Loskutoff D. J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression following partial hepatectomy. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):753–762. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Bradshaw J. D. Regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor mRNA levels in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Correlation with production of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7089–7094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahama M., Ishibashi H., Tsuchiya Y., Kurokawa S., Hayashida K., Okumura Y., Niho Y. Kupffer cells may autoregulate interleukin 1 production by producing interleukin 1 inhibitor and prostaglandin E2. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Dec;28(6):719–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Harpel P. C., Parrillo J. E. Promotion and subsequent inhibition of plasminogen activation after administration of intravenous endotoxin to normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1165–1172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton A. J., Bruzdzinski C. J., Raper S. E., Gelehrter T. D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is an immediate early response gene in regenerating rat liver. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1337–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. E., Declerck P. J., Van Houtte E., De Mol M., Collen D. Reactivated recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (rPAI-1) effectively prevents thrombolysis in vivo. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):60–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Aarden L. A., Hack C. E., Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Kooistra T., van den Berg E. A., Princen H. M., Fiers W., Emeis J. J. Tumor necrosis factor increases the production of plasminogen activator inhibitor in human endothelial cells in vitro and in rats in vivo. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1467–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Levi M., Büller H. R., van Deventer S. J., de Boer J. P., Hack C. E., ten Cate J. W. Fibrinolytic response to tumor necrosis factor in healthy subjects. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):729–732. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]