Abstract
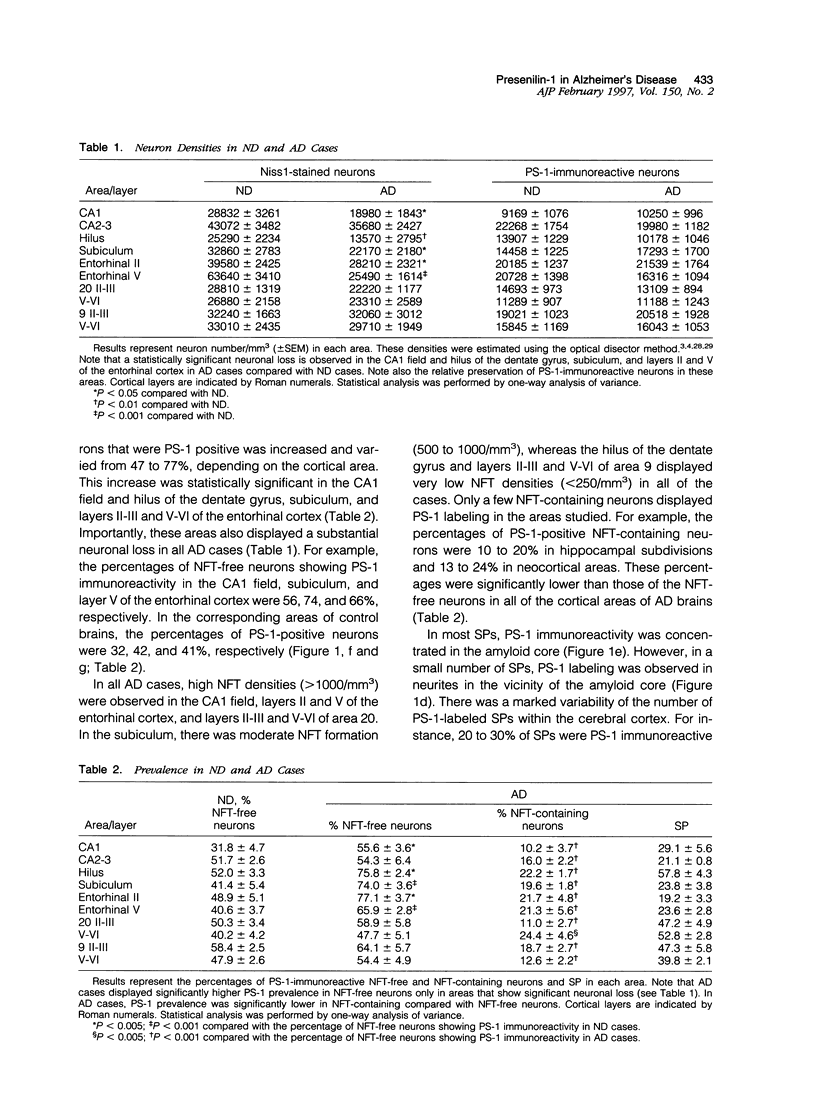
Recent studies have suggested that missense mutations in the presenilin-1 gene are causally related to the majority of familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). To examine the possible involvement of presenilin-1 in late-onset sporadic AD, a quantitative analysis of its distribution in the cerebral cortex of nondemented and AD patients was performed using immunocytochemistry. Stereological analyses revealed that AD brains showed a marked neuronal loss in the CA1 field of the hippocampus and hilus of the dentate gyrus, subiculum, and entorhinal cortex. In these areas, however, the fraction of neurofibrillary tangle (NFT)-free neurons showing presenilin-1 immunoreactivity was increased compared with nondemented controls. In contrast, cortical areas, which displayed no neuronal loss, did not show any significant increase in the fraction of presenilin-1-positive neurons. Moreover, presenilin-1 immunoreactivity was reduced in NFT-containing neurons. Thus, in AD, the fraction of NFT-free neurons that contained presenilin-1 varied from 0.48 to 0.77, whereas the fraction of NFT-containing neurons that were presenilin-1 positive varied from 0.1 to 0.24. Together, these observations indicate that presenilin-1 may have a neuroprotective role and that in AD low cellular expression of this protein may be associated with increased neuronal loss and NFT formation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alzheimer's Disease Collaborative Group The structure of the presenilin 1 (S182) gene and identification of six novel mutations in early onset AD families. Nat Genet. 1995 Oct;11(2):219–222. doi: 10.1038/ng1095-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar R., Moynihan T. P., Ardley H., Brindle N., Coletta P. L., Cairns N., Markham A. F., Robinson P. A. Molecular analysis of the presenilin 1 (S182) gene in "sporadic" cases of Alzheimer's disease: identification and characterisation of unusual splice variants. J Neurochem. 1996 Apr;66(4):1774–1777. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66041774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouras C., Giannakopoulos P., Schioi J., Tezapsidis N., Robakis N. K. Presenilin-1 polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1996 Apr 27;347(9009):1185–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouras C., Hof P. R., Giannakopoulos P., Michel J. P., Morrison J. H. Regional distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in the cerebral cortex of elderly patients: a quantitative evaluation of a one-year autopsy population from a geriatric hospital. Cereb Cortex. 1994 Mar-Apr;4(2):138–150. doi: 10.1093/cercor/4.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion D., Flaman J. M., Brice A., Hannequin D., Dubois B., Martin C., Moreau V., Charbonnier F., Didierjean O., Tardieu S. Mutations of the presenilin I gene in families with early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2373–2377. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall R. E., Lekan H. A. Methods for determining numbers of cells and synapses: a case for more uniform standards of review. J Comp Neurol. 1996 Jan 1;364(1):6–15. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960101)364:1<6::AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. G., Sung J. C., Golde T. E., Felsenstein K. M., Wojczyk B. S., Tanzi R. E., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Doms R. W. Expression and analysis of presenilin 1 in a human neuronal system: localization in cell bodies and dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 20;93(17):9223–9228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.9223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs D. H., Chen L. S., Bende S. M., LaFerla F. M. Widespread neuronal expression of the presenilin-1 early-onset Alzheimer's disease gene in the murine brain. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):1797–1806. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruts M., Backhovens H., Wang S. Y., Van Gassen G., Theuns J., De Jonghe C. D., Wehnert A., De Voecht J., De Winter G., Cras P. Molecular genetic analysis of familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease linked to chromosome 14q24.3. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2363–2371. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng G., Su J. H., Cotman C. W. Gene expression of Alzheimer-associated presenilin-2 in the frontal cortex of Alzheimer and aged control brain. FEBS Lett. 1996 Sep 23;394(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00922-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. A., Tezapsidis N., Carter J., Shioi J., Bouras C., Li H. C., Johnston J. M., Efthimiopoulos S., Friedrich V. L., Jr, Robakis N. K. Identification and neuron specific expression of the S182/presenilin I protein in human and rodent brains. J Neurosci Res. 1996 Aug 1;45(3):308–320. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19960801)45:3<308::AID-JNR13>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Isla T., Price J. L., McKeel D. W., Jr, Morris J. C., Growdon J. H., Hyman B. T. Profound loss of layer II entorhinal cortex neurons occurs in very mild Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1996 Jul 15;16(14):4491–4500. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-14-04491.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman A., Wilkinson W. E., Hurwitz B. J., Helms M. J., Haynes C. S., Utley C. M., Gwyther L. P. Early-onset Alzheimer's disease: clinical predictors of institutionalization and death. Neurology. 1987 Jun;37(6):980–984. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.6.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs D. M., Fausett H. J., Page K. J., Kim T. W., Moir R. D., Merriam D. E., Hollister R. D., Hallmark O. G., Mancini R., Felsenstein K. M. Alzheimer-associated presenilins 1 and 2: neuronal expression in brain and localization to intracellular membranes in mammalian cells. Nat Med. 1996 Feb;2(2):224–229. doi: 10.1038/nm0296-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Ellisman M., Carragher B., Mallory M., Young S., Hansen L., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D. Three-dimensional analysis of the relationship between synaptic pathology and neuropil threads in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jul;51(4):404–414. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199207000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirra S. S., Heyman A., McKeel D., Sumi S. M., Crain B. J., Brownlee L. M., Vogel F. S., Hughes J. P., van Belle G., Berg L. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1991 Apr;41(4):479–486. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moussaoui S., Czech C., Pradier L., Blanchard V., Bonici B., Gohin M., Imperato A., Revah F. Immunohistochemical analysis of presenilin-1 expression in the mouse brain. FEBS Lett. 1996 Apr 1;383(3):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Tur J., Wavrant-De Vrieze F., Lambert J. C., Chartier-Harlin M. C. Presenilin-1 polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. The Alzheimer's Study Group. Lancet. 1996 Jun 1;347(9014):1560–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. K., Growdon J. H., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Presenilin-1 polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1996 Apr 27;347(9009):1186–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Rogaev E. I., Liang Y., Rogaeva E. A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Chi H., Lin C., Li G., Holman K. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):754–760. doi: 10.1038/375754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterio D. C. The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the disector. J Microsc. 1984 May;134(Pt 2):127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1984.tb02501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Nishiyama K., Murayama S., Yamamoto A., Sato S., Kanazawa I., Sakaki Y. Regional and cellular presenilin 1 gene expression in human and rat tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Feb 27;219(3):708–713. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Chi H., Liang Y., Rogaeva E. A., Sherrington R., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Rogaev E. I., Pollen D., Freedman M. Failure to detect missense mutations in the S182 gene in a series of late-onset Alzheimer's disease cases. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Dec 8;201(2):188–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)12170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallet P. G., Guntern R., Hof P. R., Golaz J., Delacourte A., Robakis N. K., Bouras C. A comparative study of histological and immunohistochemical methods for neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;83(2):170–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00308476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vito P., Lacanà E., D'Adamio L. Interfering with apoptosis: Ca(2+)-binding protein ALG-2 and Alzheimer's disease gene ALG-3. Science. 1996 Jan 26;271(5248):521–525. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. J., Coleman P. D., Flood D. G., Troncoso J. C. Differences in the pattern of hippocampal neuronal loss in normal ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1994 Sep 17;344(8925):769–772. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. J. Regionally specific loss of neurons in the aging human hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging. 1993 Jul-Aug;14(4):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(93)90113-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Palha J. A., Ghiso J., Frangione B. S182 protein in Alzheimer's disease neuritic plaques. Lancet. 1995 Nov 18;346(8986):1366–1366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg M., Hutton M., Talbot C. Genetic association between intronic polymorphism in presenilin-1 gene and late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Disease Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1996 Feb 24;347(9000):509–512. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]