Abstract
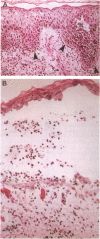
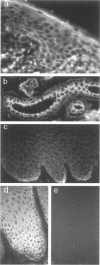
Intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis, a rare skin disease entity manifested with blisters and pustules clinically and lower epidermal blister, acantholysis, and neutrophilic infiltration pathologically, was first reported in 1985. Although the disease is characterized by IgA autoantibodies targeting the epithelial cell surface component, the target antigen has not been determined. We investigated a patient with this disease by histopathology, direct and indirect immunofluorescence, immunoblotting, and immunoadsorption studies. The pustular lesion was characterized by blister at the lower epidermis, acantholysis, and neutrophilic infiltration. Nonsecretory IgA1 subclass autoantibodies targeting the lower epithelial cell surfaces were detected in the patient's skin and serum. The patient's IgA autoantibodies labeled a recombinant desmosomal protein desmoglein 3 on immunoblotting and the immunolabeling of epithelial cell surfaces was eliminated by preadsorption with desmoglein 3. Thus, desmoglein 3 is identified as a target antigen in intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis. The ability of IgA1 autoantibodies to bind neutrophils may be responsible for the prominent neutrophilic infiltration observed histopathologically and for the pustular lesions observed clinically.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amagai M., Hashimoto T., Green K. J., Shimizu N., Nishikawa T. Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Jun;104(6):895–901. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12606168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amagai M., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90360-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amagai M., Koch P. J., Nishikawa T., Stanley J. R. Pemphigus vulgaris antigen (desmoglein 3) is localized in the lower epidermis, the site of blister formation in patients. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Feb;106(2):351–355. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12343081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anhalt G. J., Kim S. C., Stanley J. R., Korman N. J., Jabs D. A., Kory M., Izumi H., Ratrie H., 3rd, Mutasim D., Ariss-Abdo L. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 20;323(25):1729–1735. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012203232503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutner E. H., Chorzelski T. P., Wilson R. M., Kumar V., Michel B., Helm F., Jablonska S. IgA pemphigus foliaceus. Report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Jan;20(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carayannopoulos L., Hexham J. M., Capra J. D. Localization of the binding site for the monocyte immunoglobulin (Ig) A-Fc receptor (CD89) to the domain boundary between Calpha2 and Calpha3 in human IgA1. J Exp Med. 1996 Apr 1;183(4):1579–1586. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.4.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. S., Fine J. D., Briggaman R. A., Woodley D. T., Hammerberg C., Drugge R. J., Cooper K. D. Identification and partial characterization of a novel 105-kDalton lower lamina lucida autoantigen associated with a novel immune-mediated subepidermal blistering disease. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Sep;101(3):262–267. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12365189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. S., Traczyk T., Taylor T. B., Eramo L. R., Woodley D. T., Zone J. J. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis. Characterization of a subset of patients with concurrent IgA and IgG anti-basement membrane autoantibodies. Arch Dermatol. 1995 Dec;131(12):1432–1437. doi: 10.1001/archderm.131.12.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Seymour B. W., Lebman D. A., Hiraki D. D., Christiansen J. A., Shrader B., Cherwinski H. M., Savelkoul H. F., Finkelman F. D., Bond M. W. The role of helper T cell products in mouse B cell differentiation and isotype regulation. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Shrader B., Carty J., Mosmann T. R., Bond M. W. A mouse T cell product that preferentially enhances IgA production. I. Biologic characterization. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3685–3690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara T., Hashimoto T., Iwatsuki K., Takigawa M., Ando M., Ohkawara A., Nishikawa T. Autoantigens for IgA anti-intercellular antibodies of intercellular IgA vesiculopustular dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):742–745. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick R. E., Newcomer V. D. The correlation of disease activity and antibody titers in pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. 1980 Mar;116(3):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihashi K., McGhee J. R., Kweon M. N., Cooper M. D., Tonegawa S., Takahashi I., Hiroi T., Mestecky J., Kiyono H. gamma/delta T cell-deficient mice have impaired mucosal immunoglobulin A responses. J Exp Med. 1996 Apr 1;183(4):1929–1935. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P., Lawley T. J. Characterization of circulating and cutaneous IgA immune complexes in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1760–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Shafran K. M., Webber P. S., Lazarus G. S., Singer K. H. Anti-cell surface pemphigus autoantibody stimulates plasminogen activator activity of human epidermal cells. A mechanism for the loss of epidermal cohesion and blister formation. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):259–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Inamoto N., Nakamura K., Nishikawa T. Intercellular IgA dermatosis with clinical features of subcorneal pustular dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Aug;123(8):1062–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. C., Golitz L. E., Kunke K. S. Intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 26;313(26):1643–1645. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512263132606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana S., Geoghegan W. D., Jordon R. E., Nishiyama S. Deposition of the membrane attack complex of complement in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Apr;92(4):588–592. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12709624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King I. A., Sullivan K. H., Bennett R., Jr, Buxton R. S. The desmocollins of human foreskin epidermis: identification and chromosomal assignment of a third gene and expression patterns of the three isoforms. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Sep;105(3):314–321. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12319935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk A. P., Anderson J. E., Borgwardt J. E., Hashimoto T., Stanley J. R., Green K. J. Pemphigus sera recognize conformationally sensitive epitopes in the amino-terminal region of desmoglein-1. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Aug;105(2):147–152. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12316680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka S., Lazarus G. S., Jensen P. J. Involvement of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in acantholysis induced by pemphigus IgG. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Nov;89(5):474–477. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12460937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Foldès C., Cottenot F. Pustulose sous-cornée, acantholyse superficielle et IgA monoclonale. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1982;109(11):959–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Kacena A., Schuh A., Golde D. W. GM-CSF induces human neutrophil IgA-mediated phagocytosis by an IgA Fc receptor activation mechanism. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):647–648. doi: 10.1038/332647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]