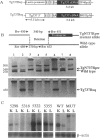
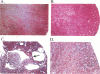
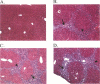
Abstract
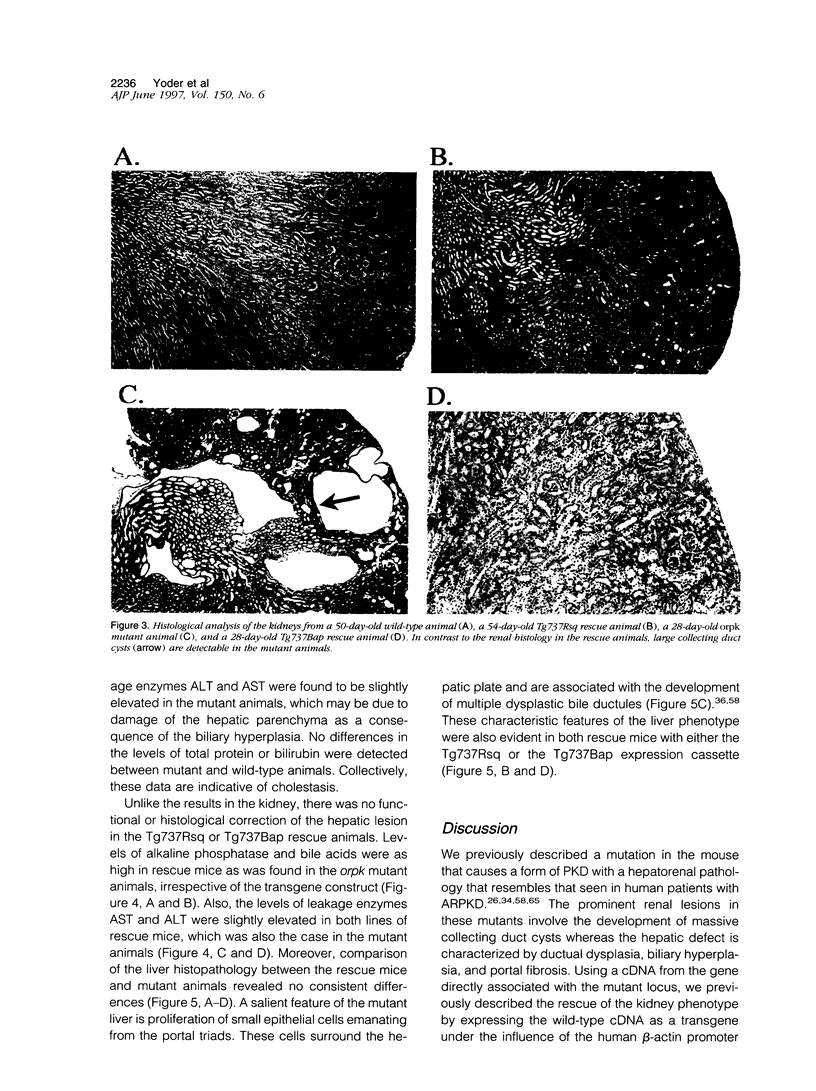
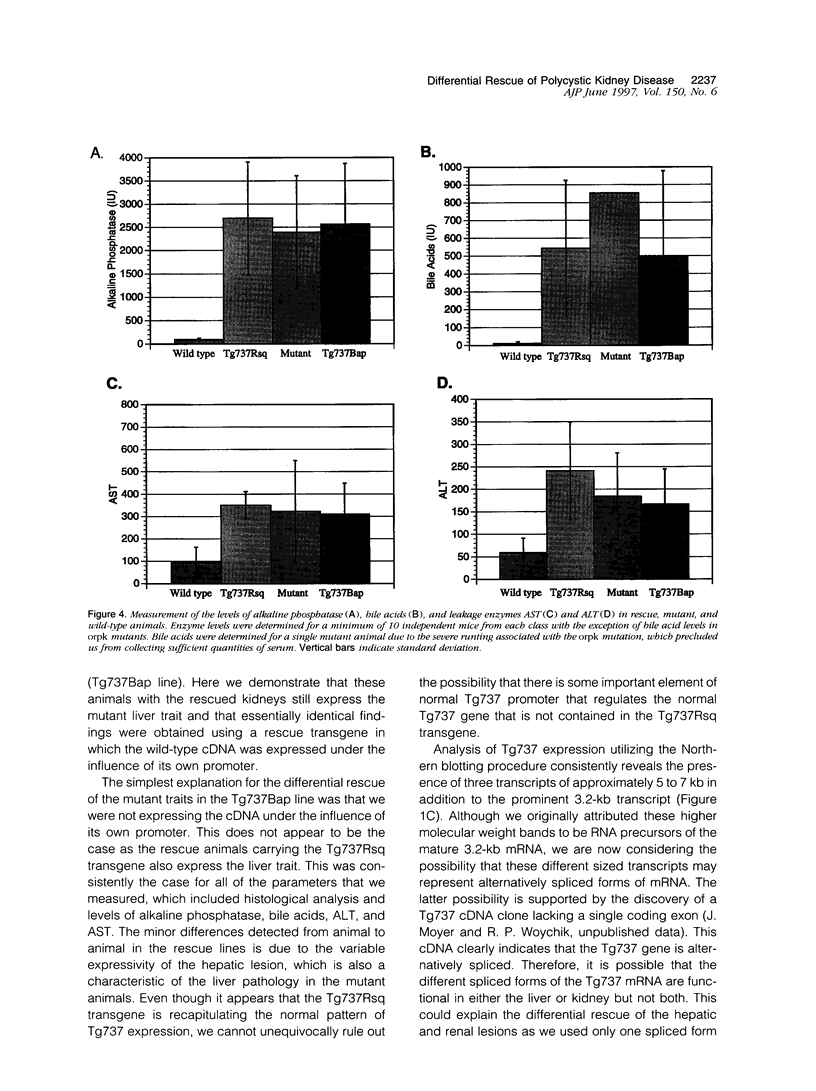
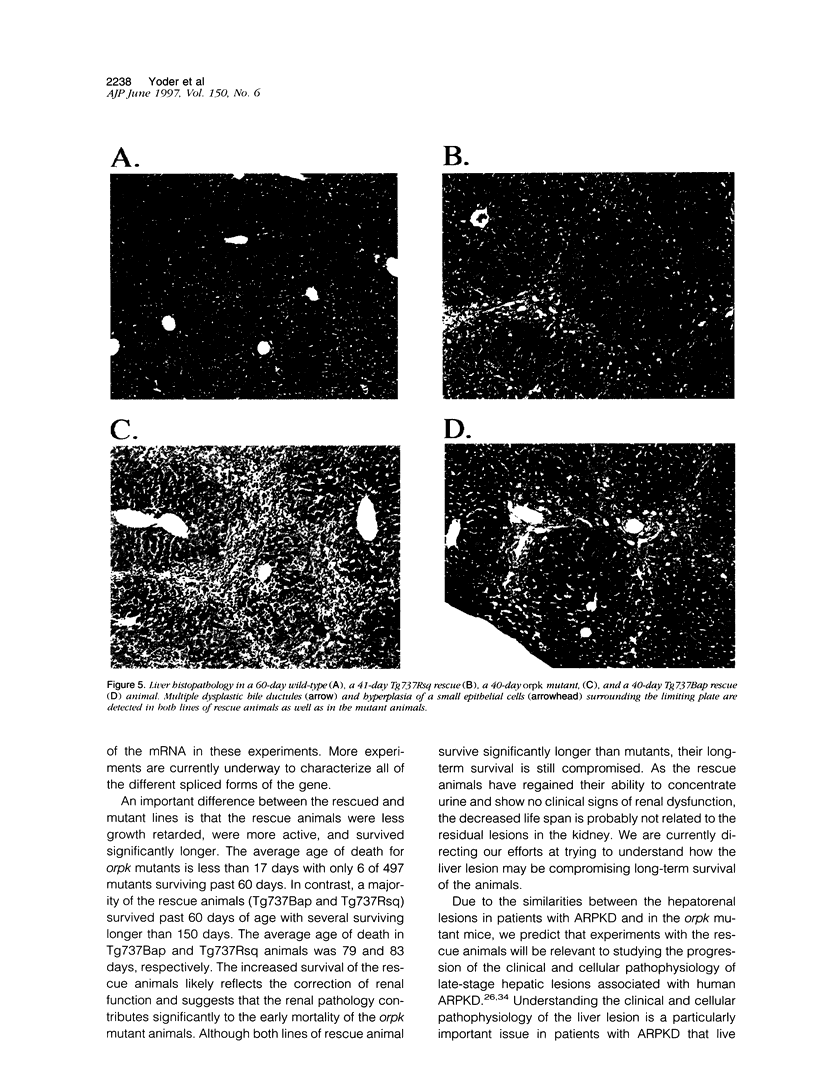
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is characterized by biliary and renal lesions that produce significant morbidity and mortality. The biliary ductual ectasia and hepatic portal fibrosis associated with ARPKD have not been well studied even though such lesions markedly affect the clinical course of patients after renal replacement therapy such as dialysis or transplantation. Here we describe the generation of a new mouse model to study the hepatic lesions associated with polycystic kidney disease. This model was generated by differentially rescuing the renal pathology in the orpk mutant mouse that displays a hepatorenal pathology that is similar to that seen in human patients with ARPKD. This was accomplished by expressing, as a transgene in the mutant animals, the cloned wild-type version of the gene associated with the mutant locus in this line of mice. Although renal function in the rescue animals is normal, the liver still exhibits biliary and ductular hyperplasia along with varying degrees of hepatic portal fibrosis that is indistinguishable from that in the mutant animals. Most important, the rescue animals survive significantly longer than mutants and will permit a more detailed analysis of the clinical and cellular pathophysiology of the hepatic defect associated with this disease.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand S. K., Chan J. C., Lieberman E. Polycystic disease and hepatic fibrosis in children. Renal function studies. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jul;129(7):810–813. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120440036008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atala A., Freeman M. R., Mandell J., Beier D. R. Juvenile cystic kidneys (jck): a new mouse mutation which causes polycystic kidneys. Kidney Int. 1993 May;43(5):1081–1085. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner E. D. Epithelial polarity and differentiation in polycystic kidney disease. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:217–222. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner E. D., Sweeney W. E., Jr, Nelson W. J. Abnormal sodium pump distribution during renal tubulogenesis in congenital murine polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner E. D., Sweeney W. E., Jr, Young M. C., Ellis D. Congenital murine polycystic kidney disease. II. Pathogenesis of tubular cyst formation. Pediatr Nephrol. 1988 Apr;2(2):210–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00862593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N. Animal models of polycystic kidney disease. Bioessays. 1995 Aug;17(8):703–712. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth H., Ockenden B. G. Polycystic disease of kidney and liver presenting in childhood. J Med Genet. 1971 Sep;8(3):257–284. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet J. P. Injury and development in polycystic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1994 May;3(3):340–348. doi: 10.1097/00041552-199405000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet J. P. Polycystic kidney disease: primary extracellular matrix abnormality or defective cellular differentiation? Kidney Int. 1993 Jan;43(1):101–108. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carone F. A., Butkowski R. J., Nakamura S., Polenakovic M., Kanwar Y. S. Tubular basement membrane changes during induction and regression of drug-induced polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 1994 Nov;46(5):1368–1374. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley B. D., Jr, Chadwick L. J., Grantham J. J., Calvet J. P. Elevated proto-oncogene expression in polycystic kidneys of the C57BL/6J (cpk) mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Feb;1(8):1048–1053. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V181048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley B. D., Jr, Smardo F. L., Jr, Grantham J. J., Calvet J. P. Elevated c-myc protooncogene expression in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8394–8398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agata I. D., Jonas M. M., Perez-Atayde A. R., Guay-Woodford L. M. Combined cystic disease of the liver and kidney. Semin Liver Dis. 1994 Aug;14(3):215–228. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davisson M. T., Guay-Woodford L. M., Harris H. W., D'Eustachio P. The mouse polycystic kidney disease mutation (cpk) is located on proximal chromosome 12. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):778–781. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90376-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du J., Wilson P. D. Abnormal polarization of EGF receptors and autocrine stimulation of cyst epithelial growth in human ADPKD. Am J Physiol. 1995 Aug;269(2 Pt 1):C487–C495. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.2.C487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara I., Killen P. D., Laurie G. W., Huang T., Yamada Y., Martin G. R., Brown K. S. Altered mRNA expression of basement membrane components in a murine model of polycystic kidney disease. Lab Invest. 1988 Mar;58(3):262–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick G. M., Gabow P. A. Hereditary and acquired cystic disease of the kidney. Kidney Int. 1994 Oct;46(4):951–964. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty L., Bryda E. C., Collins D., Rudofsky U., Montogomery J. C. New mouse model for polycystic kidney disease with both recessive and dominant gene effects. Kidney Int. 1995 Feb;47(2):552–558. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich G., Soriano P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1513–1523. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. L., Jr, Koch W. E., Jennette J. C., McFarland E., Fried F. A., Mandell J. A genetically determined murine model of infantile polycystic kidney disease. J Urol. 1985 Oct;134(4):828–833. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)47448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gang D. L., Herrin J. T. Infantile polycystic disease of the liver and kidneys. Clin Nephrol. 1986 Jan;25(1):28–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattone V. H., 2nd, Calvet J. P., Cowley B. D., Jr, Evan A. P., Shaver T. S., Helmstadter K., Grantham J. J. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in a murine model. A gross and microscopic description. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):231–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni-Baruch R., Nachlieli T., Leibo R., Degani S., Weissman I. Cystic kidney dysplasia and polydactyly in 3 sibs with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Oct 1;44(3):269–273. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M., Yanagida M. The TPR snap helix: a novel protein repeat motif from mitosis to transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90070-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J. Pathogenesis of renal cyst expansion: opportunities for therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994 Feb;23(2):210–218. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80974-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J. Polycystic kidney disease: I. Etiology and pathogenesis. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1992 Mar 15;27(3):51–59. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1992.11705379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J. Polycystic kidney disease: a predominance of giant nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F3–10. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. A., Gattone V. H., 2nd, Grantham J. J., Calvet J. P. Localization of overexpressed c-myc mRNA in polycystic kidneys of the cpk mouse. Kidney Int. 1992 Feb;41(2):317–325. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverty T. P., Neilson E. G. Basement membrane gene expression in polycystic kidney disease. Lab Invest. 1988 Mar;58(3):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iakoubova O. A., Dushkin H., Beier D. R. Localization of a murine recessive polycystic kidney disease mutation and modifying loci that affect disease severity. Genomics. 1995 Mar 1;26(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Fay J., Shah V., Dillon M. J., Barratt T. M. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 1989 Jan;3(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00859625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspareit-Rittinghausen J., Deerberg F., Wcislo A. Hereditary polycystic kidney disease. Adult polycystic kidney disease associated with renal hypertension, renal osteodystrophy, and uremic enteritis in SPRD rats. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):693–696. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen H., Koskimies O., Norio R. Dominant and recessive polycystic kidney disease in children: evaluation of clinical features and laboratory data. Pediatr Nephrol. 1988 Jul;2(3):296–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00858681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Tugendreich S., Hieter P. Tetratrico peptide repeat interactions: to TPR or not to TPR? Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jul;20(7):257–259. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald R. A., Avner E. D. Inherited polycystic kidney disease in children. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Nov;11(6):632–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer J. H., Lee-Tischler M. J., Kwon H. Y., Schrick J. J., Avner E. D., Sweeney W. E., Godfrey V. L., Cacheiro N. L., Wilkinson J. E., Woychik R. P. Candidate gene associated with a mutation causing recessive polycystic kidney disease in mice. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1329–1333. doi: 10.1126/science.8191288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogborn M. R., Sareen S., Tomobe K., Takahashi H., Crocker J. F. Renal tubule Na,K-ATPase polarity in different animal models of polycystic kidney disease. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995 Aug;43(8):785–790. doi: 10.1177/43.8.7622841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., Sweeney W. E., Neff C. D., Avner E. D. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is abnormal in murine polycystic kidney. Kidney Int. 1995 Feb;47(2):490–499. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa Y., Nauta J., Sweeney W. E., Avner E. D. A new murine model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1993 Apr;35(4):349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C. A., Grantham J. J., Calvet J. P. C-fos expression is hypersensitive to serum-stimulation in cultured cystic kidney cells from the C57BL/6J-cpk mouse. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Sep;152(3):578–586. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. G., Yoder B. K., Isfort R. J., Detilleux P. G., Foster C., Neilsen N., Woychik R. P., Wilkinson J. E. Isolation and characterization of liver epithelial cell lines from wild-type and mutant TgN737Rpw mice. Am J Pathol. 1997 Apr;150(4):1189–1197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. G., Yoder B. K., Isfort R. J., Detilleux P. G., Foster C., Neilsen N., Woychik R. P., Wilkinson J. E. Oval cell proliferation associated with the murine insertional mutation TgN737Rpw. Am J Pathol. 1996 Dec;149(6):1919–1930. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrick J. J., Onuchic L. F., Reeders S. T., Korenberg J., Chen X. N., Moyer J. H., Wilkinson J. E., Woychik R. P. Characterization of the human homologue of the mouse Tg737 candidate polycystic kidney disease gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):559–567. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer K., Bader M., Gretz N., Oberbäumer I., Bachmann S. Focal overexpression of collagen IV characterizes the initiation of epithelial changes in polycystic kidney disease. Exp Nephrol. 1994 May-Jun;2(3):190–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer K., Gretz N., Bader M., Oberbäumer I., Eckardt K. U., Kriz W., Bachmann S. Characterization of the Han:SPRD rat model for hereditary polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 1994 Jul;46(1):134–152. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walpole I. R., Goldblatt J., Hockey A., Knowles S. Dandy-Walker malformation (variant), cystic dysplastic kidneys, and hepatic fibrosis: a distinct entity or Meckel syndrome? Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jun 1;39(3):294–298. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320390310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. D., Du J., Norman J. T. Autocrine, endocrine and paracrine regulation of growth abnormalities in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;61(1):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. D., Falkenstein D. The pathology of human renal cystic disease. Curr Top Pathol. 1995;88:1–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79517-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. D., Sherwood A. C., Palla K., Du J., Watson R., Norman J. T. Reversed polarity of Na(+) -K(+) -ATPase: mislocation to apical plasma membranes in polycystic kidney disease epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):F420–F430. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.3.F420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C., Healicon R., English C., Burn J. Meckel syndrome: what are the minimum diagnostic criteria? J Med Genet. 1994 Jun;31(6):482–485. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.6.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. K., Richards W. G., Sommardahl C., Sweeney W. E., Michaud E. J., Wilkinson J. E., Avner E. D., Woychik R. P. Functional correction of renal defects in a mouse model for ARPKD through expression of the cloned wild-type Tg737 cDNA. Kidney Int. 1996 Oct;50(4):1240–1248. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. K., Richards W. G., Sweeney W. E., Wilkinson J. E., Avener E. D., Woychik R. P. Insertional mutagenesis and molecular analysis of a new gene associated with polycystic kidney disease. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1995 Oct;107(3):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeier M., Pohlmeyer G., Deerberg F., Schönherr R., Ritz E. Progression of renal failure in the Han: SPRD polycystic kidney rat. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994;9(12):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida S., de Almeida E., Peters D., Pinto J. R., Távora I., Lavinha J., Breuning M., Prata M. M. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: evidence for the existence of a third locus in a Portuguese family. Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;96(1):83–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00214191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]