Abstract
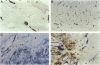
Cutaneous melanoma has an initial preference for lymphatic spread. Remarkably, melanoma progression toward this metastasizing phenotype is accompanied by intense blood vessel angiogenesis (hemangiogenesis), but lymphangiogenesis, the formation of new lymph vessels in the tumor, has never been reported. To investigate how primary melanoma cells interact with the existing lymphatic microvasculature, and whether lymphangiogenesis occurs, an immunostaining was developed that differentially decorates blood and lymph vessels in frozen tissue sections. The density and distribution of both these vessel types in and around thin (< or = 1.5 mm) and thick (> or = 1.5 mm) primary melanoma lesions and in normal and uninvolved skin were determined. Although especially in thick melanoma lesions a significant increase in blood vessel density was observed, lymphatic density remained unaltered, showing that lymphangiogenesis did not occur. Morphological analysis indicated, however, that melanoma progression is accompanied by a sequence of events that involves hemangiogenesis supporting tumor expansion, especially in the vertical growth phase. Often, stromal sepia are formed around the blood capillaries in the tumor neovasculature protecting them from invasion. Lymph vessels inside the tumor were infrequently observed. However, subepidermal lymph vessels often seemed to be entrapped and penetrated by the expanding tumor mass. In this way, hemangiogenesis, as the driving force behind tumor expansion, might indirectly increase the chance of lymphatic invasion in the absence of lymphangiogenesis. This model explains the paradox that, although melanoma metastasis seems to require angiogenesis, a consistent relation of prognosis with blood capillary density in primary cutaneous melanoma is lacking.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnhill R. L., Fandrey K., Levy M. A., Mihm M. C., Jr, Hyman B. Angiogenesis and tumor progression of melanoma. Quantification of vascularity in melanocytic nevi and cutaneous malignant melanoma. Lab Invest. 1992 Sep;67(3):331–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busam K. J., Berwick M., Blessing K., Fandrey K., Kang S., Karaoli T., Fine J., Cochran A. J., White W. L., Rivers J. Tumor vascularity is not a prognostic factor for malignant melanoma of the skin. Am J Pathol. 1995 Oct;147(4):1049–1056. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnochan P., Briggs J. C., Westbury G., Davies A. J. The vascularity of cutaneous melanoma: a quantitative histological study of lesions 0.85-1.25 mm in thickness. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jul;64(1):102–107. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch A., Lubach D., Nissen S., Neukam D. Ultrastructural studies on the invasion of melanomas in initial lymphatics of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jan;98(1):64–67. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12495259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erhard H., Rietveld F. J., Bröcker E. B., de Waal R. M., Ruiter D. J. Phenotype of normal cutaneous microvasculature. Immunoelectron microscopic observations with emphasis on the differences between blood vessels and lymphatics. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Jan;106(1):135–140. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12329708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallowfield M. E., Cook M. G. Lymphatics in primary cutaneous melanoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 Apr;14(4):370–374. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199004000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jan 3;82(1):4–6. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham C. H., Rivers J., Kerbel R. S., Stankiewicz K. S., White W. L. Extent of vascularization as a prognostic indicator in thin (< 0.76 mm) malignant melanomas. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):510–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leedy D. A., Trune D. R., Kronz J. D., Weidner N., Cohen J. I. Tumor angiogenesis, the p53 antigen, and cervical metastasis in squamous carcinoma of the tongue. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994 Oct;111(4):417–422. doi: 10.1177/019459989411100405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. A., Ratti C. M., McDonnell S. L., Cohn Z. A. A human endothelial cell-restricted, externally disposed plasmalemmal protein enriched in intercellular junctions. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. J., Berndt M. C., Gorski J., White G. C., 2nd, Lyman S., Paddock C., Muller W. A. PECAM-1 (CD31) cloning and relation to adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1219–1222. doi: 10.1126/science.1690453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rongioletti F., Miracco C., Gambini C., Pastorino A., Tosi P., Rebora A. Tumor vascularity as a prognostic indicator in intermediate-thickness (0.76-4 mm) cutaneous melanoma. A quantitative assay. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996 Oct;18(5):474–477. doi: 10.1097/00000372-199610000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiter D. J., Schlingemann R. O., Rietveld F. J., de Waal R. M. Monoclonal antibody-defined human endothelial antigens as vascular markers. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Aug;93(2 Suppl):25S–32S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12580902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlingemann R. O., Dingjan G. M., Emeis J. J., Blok J., Warnaar S. O., Ruiter D. J. Monoclonal antibody PAL-E specific for endothelium. Lab Invest. 1985 Jan;52(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Laidler P., Davies R. P., Horgan K., Hughes L. E. The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76-4.0 mm thick) skin melanoma. A quantitative histologic study. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):419–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N. Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jul;147(1):9–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]