Abstract
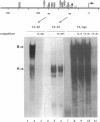
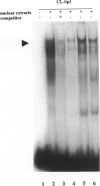
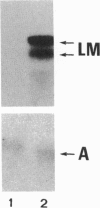
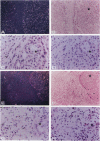
The laminin-gamma1 chain is present in most basement membranes and is involved in various physiological and pathological processes, including carcinogenesis in the liver. We have investigated the role of the transcription factor Sp1 in the activation of the LamC1 gene, which encodes laminin-gamma1, both in hepatocytes and in human hepatocellular carcinomas. DNAse I hypersensitive sites were mapped in the murine LamC1 promoter using early hepatocyte primary cultures in which LamC1 becomes activated. Three hypersensitive sites were found in enhancer-like elements that contain GC-rich regions. Gel-shift analyses showed that specific complexes were resolved using GC-containing oligonucleotides and Faza 567 hepatoma cells, which constitutively express laminin-gamma1 at a high level. Increased GC-binding activity was observed using nuclear extracts from early hepatocyte cultures versus normal liver. Sp1 overexpression in normal hepatocytes transfected with an Sp1 expression vector induced a marked increased of laminin-gamma1 mRNA content and co-transfection of promoter fragments in Drosophila melanogaster SL2 cells demonstrated that Sp1 transactivates LamC1. In human hepatocellular carcinomas, Sp1 and laminin-gamma1 mRNA were simultaneously expressed at high levels, and gel-shift experiments demonstrated a higher GC-binding activity to Sp1 compared with control livers. In situ hybridization indicated that cells exhibiting a high content of laminin-gamma1 mRNA were also strongly positive for Sp1 mRNA, including both cancer cells at the invasion front and stromal cells. These results show that Sp1 is involved in the activation of LamC1 that occurs in human hepatocellular carcinomas.
Full text
PDF


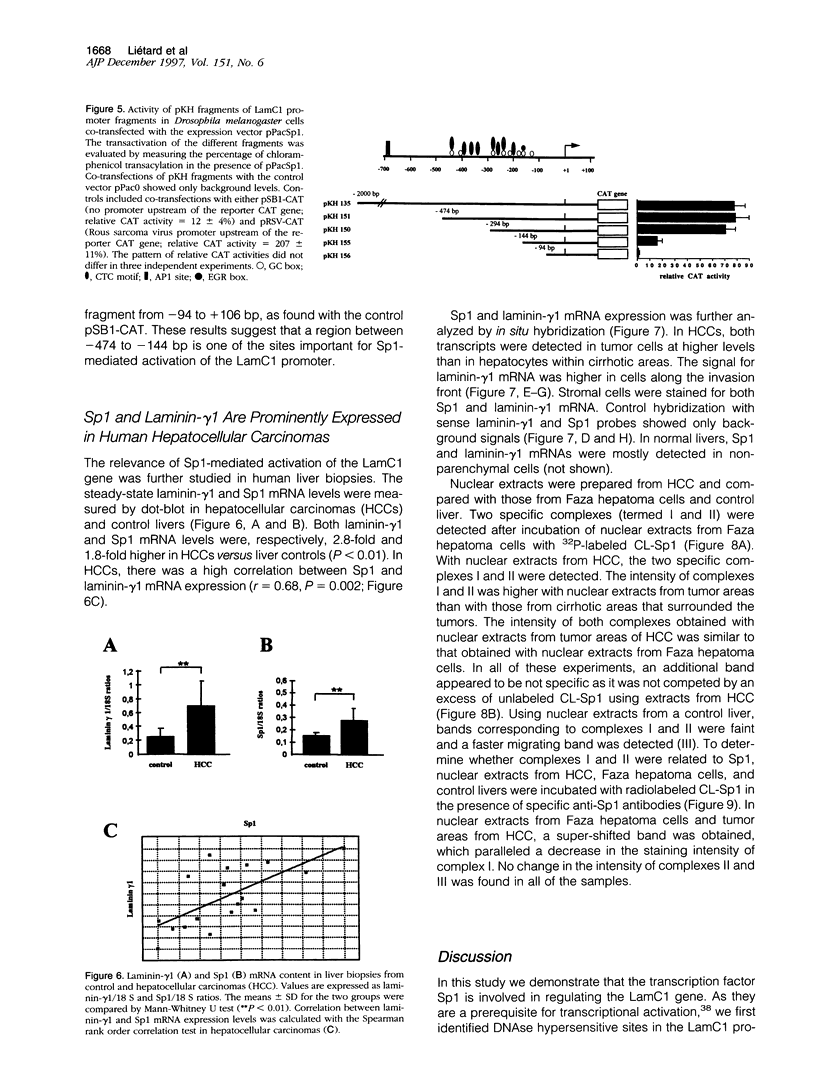
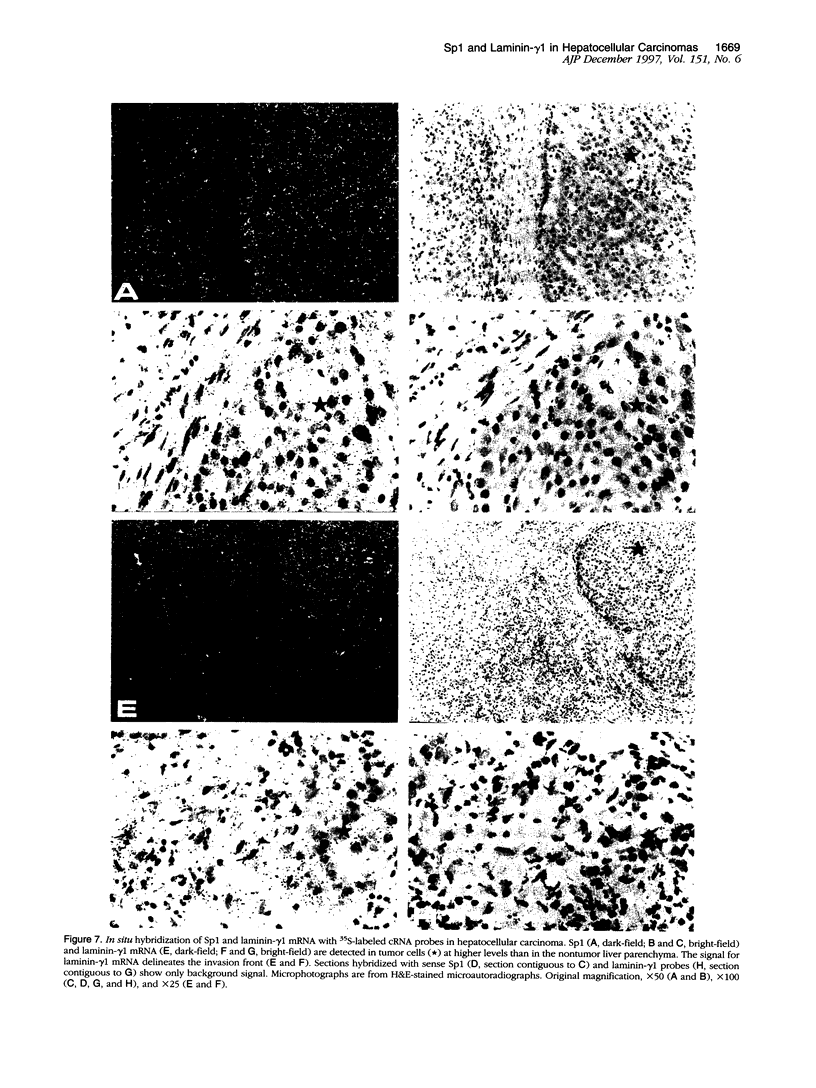
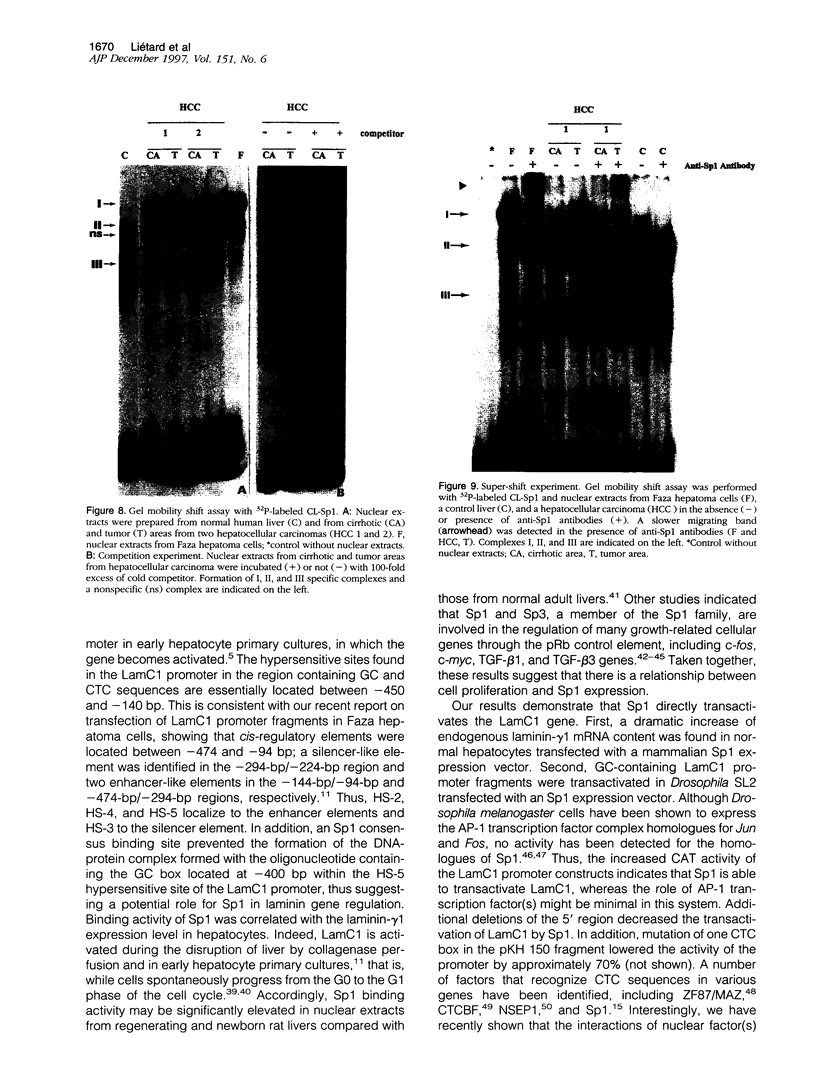


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bossard P., Parsa R., Decaux J. F., Iynedjian P., Girard J. Glucose administration induces the premature expression of liver glucokinase gene in newborn rats. Relation with DNase-I-hypersensitive sites. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):883–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbelo P. D., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Alpha 1(IV) and alpha 2(IV) collagen genes are regulated by a bidirectional promoter and a shared enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9679–9682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Chiquet M., Deutzmann R., Ekblom P., Engel J., Kleinman H., Martin G. R., Meneguzzi G., Paulsson M., Sanes J. A new nomenclature for the laminins. Matrix Biol. 1994 Apr;14(3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0945-053x(94)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron J. M. Induction of albumin gene transcription in hepatocytes by extracellular matrix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1239–1243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Gutell R., Noller H. F., Wool I. G. The nucleotide sequence of a rat 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene and a proposal for the secondary structure of 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Azizkhan J. C., Lee D. C. The binding of transcription factor Sp1 to multiple sites is required for maximal expression from the rat transforming growth factor alpha promoter. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1805–1815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément B., Rescan P. Y., Baffet G., Loréal O., Lehry D., Campion J. P., Guillouzo A. Hepatocytes may produce laminin in fibrotic liver and in primary culture. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):794–803. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Grässel S., Murdoch A. D., Iozzo R. V. Structural characterization of the complete human perlecan gene and its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10404–10408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesJardins E., Hay N. Repeated CT elements bound by zinc finger proteins control the absolute and relative activities of the two principal human c-myc promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5710–5724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusing M. R., Wiginton D. A. Sp1 is essential for both enhancer-mediated and basal activation of the TATA-less human adenosine deaminase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):669–677. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Earwicker D., Haaparanta T., Ruoslahti E., Sanes J. R. Distribution and isolation of four laminin variants; tissue restricted distribution of heterotrimers assembled from five different subunits. Cell Regul. 1990 Sep;1(10):731–740. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.10.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne P. L., Baffet G., Desvergne B., Boisnard-Rissel M., Glaise D., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Transient expression of c-fos and constant expression of c-myc in freshly isolated and cultured normal adult rat hepatocytes. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(3):255–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio M. J., O'Leary J., Kähäri V. M., Chen Y. Q., Saitta B., Uitto J. Human nidogen gene: structural and functional characterization of the 5'-flanking region. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Aug;97(2):281–285. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser A. G., Busam K. J., Kim S. J., Lafyatis R., O'Reilly M. A., Webbink R., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Regulation of the transforming growth factor-beta 1 and -beta 3 promoters by transcription factor Sp1. Gene. 1993 Jul 30;129(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genersch E., Eckerskorn C., Lottspeich F., Herzog C., Kühn K., Pöschl E. Purification of the sequence-specific transcription factor CTCBF, involved in the control of human collagen IV genes: subunits with homology to Ku antigen. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):791–800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkilä P., Soininen R., Tryggvason K. Directional regulatory activity of cis-acting elements in the bidirectional alpha 1(IV) and alpha 2(IV) collagen gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24677–24682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Onwuta U. S., Lee Y. I., Li R., Botchan M. R., Robbins P. D. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates Sp1-mediated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2455–2463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Torrey T. A., Kinniburgh A. J. A CT promoter element binding protein: definition of a double-strand and a novel single-strand DNA binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):111–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A. P., Mar P. K., Zhao B., Montgomery R. L., Kang D. C., Butler A. P. Regulation of rat ornithine decarboxylase promoter activity by binding of transcription factor Sp1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4341–4348. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett R. W., Armstrong S. A., Barry D., Mueller C. R. Sp1 is phosphorylated and its DNA binding activity down-regulated upon terminal differentiation of the liver. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25879–25884. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
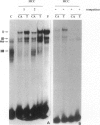
- Levavasseur F., Liétard J., Ogawa K., Théret N., Burbelo P. D., Yamada Y., Guillouzo A., Clément B. Expression of laminin gamma 1 cultured hepatocytes involves repeated CTC and GC elements in the LAMC1 promoter. Biochem J. 1996 Feb 1;313(Pt 3):745–752. doi: 10.1042/bj3130745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreal O., Levavasseur F., Rescan P. Y., Yamada Y., Guillouzo A., Clement B. Differential expression of laminin chains in hepatic lipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81213-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyer P., Cariou S., Glaise D., Bilodeau M., Baffet G., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Growth factor dependence of progression through G1 and S phases of adult rat hepatocytes in vitro. Evidence of a mitogen restriction point in mid-late G1. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 10;271(19):11484–11492. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.19.11484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Lee W., Jiang C., Keller E. B. Start site selection by Sp1 in the TATA-less human Ha-ras promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5391–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
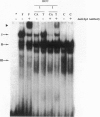
- Maher J. J., McGuire R. F. Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1641–1648. doi: 10.1172/JCI114886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., De Luca P., Suske G., Lania L. Differential transcriptional regulation of c-myc promoter through the same DNA binding sites targeted by Sp1-like proteins. Oncogene. 1995 May 4;10(9):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R. Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milani S., Herbst H., Schuppan D., Grappone C., Pellegrini G., Pinzani M., Casini A., Calabró A., Ciancio G., Stefanini F. Differential expression of matrix-metalloproteinase-1 and -2 genes in normal and fibrotic human liver. Am J Pathol. 1994 Mar;144(3):528–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso O., Théret N., Campion J. P., Turlin B., Milani S., Grappone C., Clément B. In situ detection of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) and the metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP2 transcripts in human primary hepatocellular carcinoma and in liver metastasis. J Hepatol. 1997 Mar;26(3):593–605. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nakajima T., Tsunoda S., Nakada S., Oda K., Tsurui H., Wada A. Induction of E1A-responsive negative factors for transcription of the fibronectin gene in adenovirus E1-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6436–6450. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6436-6450.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls M. C., Rippe R. A., Veloz L., Brenner D. A. Transcription factors nuclear factor I and Sp1 interact with the murine collagen alpha 1 (I) promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4065–4073. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Burbelo P. D., Sasaki M., Yamada Y. The laminin B2 chain promoter contains unique repeat sequences and is active in transient transfection. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8384–8389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. Novel Jun- and Fos-related proteins in Drosophila are functionally homologous to enhancer factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4265–4273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyrc J. J., Moberg K. H., Hall D. J. Isolation of a novel cDNA encoding a zinc-finger protein that binds to two sites within the c-myc promoter. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):4102–4110. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescan P. Y., Clement B., Yamada Y., Glaise D., Segui-Real B., Guguen-Guillouzo C., Guillouzo A. Expression of laminin and its receptor LBP-32 in human and rat hepatoma cells. Hepatology. 1991 Feb;13(2):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescan P. Y., Clément B., Yamada Y., Segui-Real B., Baffet G., Guguen-Guillouzo C., Guillouzo A. Differential expression of laminin chains and receptor (LBP-32) in fetal and neoplastic hepatocytes compared to normal adult hepatocytes in vivo and in culture. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):701–709. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe R. A., Almounajed G., Brenner D. A. Sp1 binding activity increases in activated Ito cells. Hepatology. 1995 Jul;22(1):241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Fischer G., Kadner H., Genersch E., Kühn K., Pöschl E. Differential effects of DNA-binding proteins on bidirectional transcription from the common promoter region of human collagen type IV genes COL4A1 and COL4A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 18;1174(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90085-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Hörz W. Histones, nucleosomes and transcription. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90026-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Ohnishi K., Hartl C., LeRoy E. C., Trojanowska M. Characterization of a GC-rich region containing Sp1 binding site(s) as a constitutive responsive element of the alpha 2(I) collagen gene in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4299–4304. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvadia A. J., Rogers K. T., Higgins P. D., Murata Y., Martin K. H., Humphrey P. A., Horowitz J. M. Sp-1 binds promoter elements regulated by the RB protein and Sp-1-mediated transcription is stimulated by RB coexpression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Sparkes R. S., Bertolotti R. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids: IX extinction and reexpression of liver-specific enzymes in rat hepatoma-Chinese hamster fibroblast hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Jan;1(1):27–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01538730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Albrechtsen R. Carcinoma-associated perisinusoidal laminin may signal tumour cell metastasis to the liver. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421(2):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01607040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Engvall E., Paulsson M., Yamada Y., Albrechtsen R. Laminin A, B1, B2, S and M subunits in the postnatal rat liver development and after partial hepatectomy. Lab Invest. 1992 Mar;66(3):378–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]