Abstract
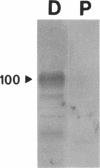
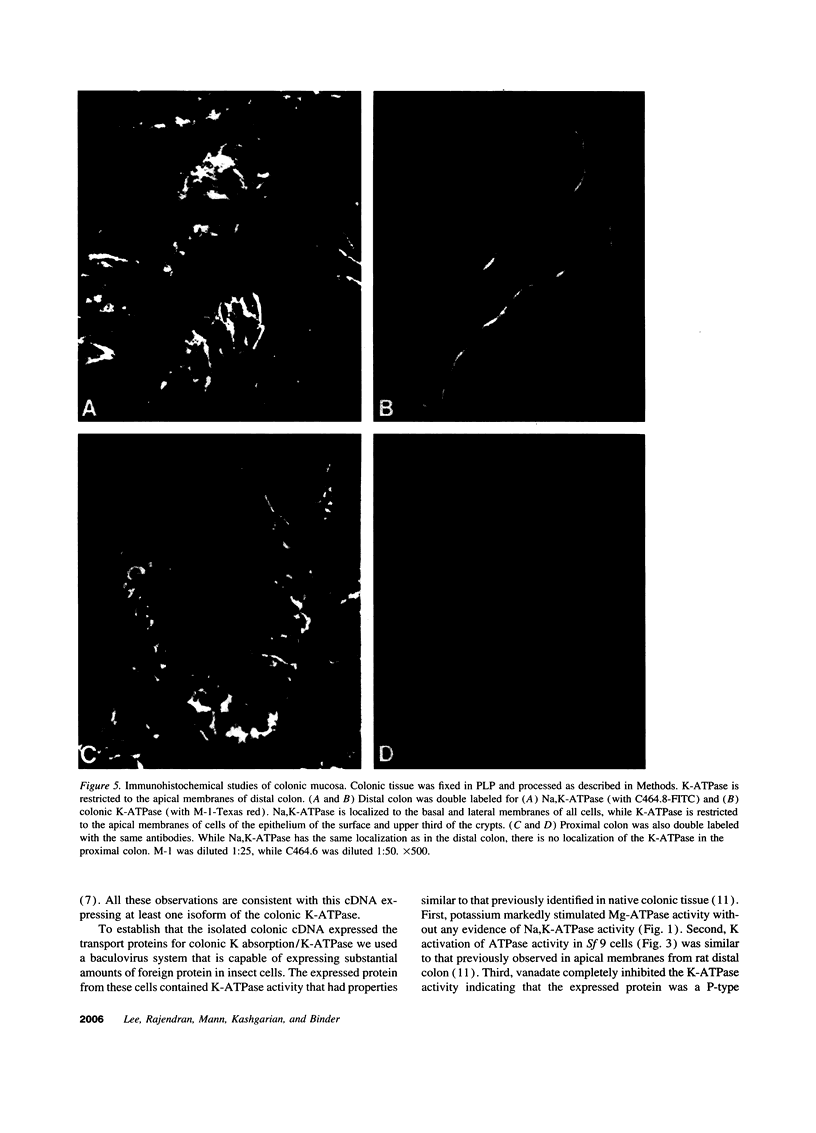
A putative cDNA for the colonic K-ATPase has recently been cloned (Crowson, M.S., and G. E. Shull. 1992. J. Biol. Chem. 267:13740-13748). Considerable evidence exists that there are two K-ATPases and active K absorptive processes in the rat distal colon: one that is ouabain sensitive and the other ouabain insensitive. The present study used the baculovirus expression system to express K-ATPase activity in insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf 9) cells and a polyclonal antibody (M-1), developed against a fusion protein produced from the 327 nucleotide fragment from 5' coding region of the putative K-ATPase cDNA, to identify the specific localization of the K-ATPase protein. K-ATPase activity (28.7 +/- 1.2 nmol inorganic phosphate/mg protein min) was expressed in plasma membranes isolated from Sf 9 cells infected with baculovirus containing recombinant DNA with the putative K-ATPase cDNA. Km for K for the K-ATPase was 1.2 mM. The expressed K-ATPase activity was not inhibited by ouabain (1 mM); while the Ki for vanadate inhibition was 8.3 microM. Western blot analysis with the M-1 antibody identified a 100-kD protein in apical membranes prepared from distal, but not proximal, rat colon. Immunohistochemical studies with M-1 antibody localized K-ATPase only in the apical membrane of surface cells, while an mAb (c464.6) against Na,K-ATPase localized basolateral membranes of both surface and crypt cells of rat distal colon. In conclusion, the putative K-ATPase cDNA encodes an ouabain-insensitive K-ATPase that is present only in the apical membrane of surface cells of rat distal colon.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanco G., Xie Z. J., Mercer R. W. Functional expression of the alpha 2 and alpha 3 isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1824–1828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowson M. S., Shull G. E. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the putative distal colon H+,K(+)-ATPase. Similarity of deduced amino acid sequence to gastric H+,K(+)-ATPase and Na+,K(+)-ATPase and mRNA expression in distal colon, kidney, and uterus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13740–13748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J. R., Rajendran V. M., Binder H. J. Apical membrane localization of ouabain-sensitive K(+)-activated ATPase activities in rat distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):G1005–G1011. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.6.G1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Mechanism of active potassium absorption and secretion in the rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):G611–G617. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.5.G611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger J. D., Jaunin P., Reuben M. A., Lasater L. S., Chow D. C., Forte J. G., Sachs G., Rossier B. C., Geering K. The H,K-ATPase beta-subunit can act as a surrogate for the beta-subunit of Na,K-pumps. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19131–19134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger J. D., Lemas V., Kraehenbühl J. P., Rossier B. C. Structure-function relationship of Na,K-ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:565–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaisser F., Coutry N., Farman N., Binder H. J., Rossier B. C. A putative H(+)-K(+)-ATPase is selectively expressed in surface epithelial cells of rat distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 1):C1080–C1089. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.4.C1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaisser F., Horisberger J. D., Geering K., Rossier B. C. Mechanisms of urinary K+ and H+ excretion: primary structure and functional expression of a novel H,K-ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 1):1421–1429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel J. B., Orlowski J., Shull M. M., Price E. M. Molecular genetics of Na,K-ATPase. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:37–89. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marxer A., Stieger B., Quaroni A., Kashgarian M., Hauri H. P. (Na+ + K+)-ATPase and plasma membrane polarity of intestinal epithelial cells: presence of a brush border antigen in the distal large intestine that is immunologically related to beta subunit. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1057–1069. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiyan V., Rajendran V. M., Binder H. J. Mucosal ouabain and Na+ inhibit active Rb+(K+) absorption in normal and sodium-depleted rat distal colon. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jun;102(6):1846–1853. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90304-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran V. M., Kashgarian M., Binder H. J. Aldosterone induction of electrogenic sodium transport in the apical membrane vesicles of rat distal colon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18638–18644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of the rat stomach (H+ + K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16788–16791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Kaneko K. Ouabain-sensitive H+-K+ exchange mechanism in the apical membrane of guinea pig colon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):G979–G988. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.6.G979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweiry J. H., Binder H. J. Active potassium absorption in rat distal colon. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:155–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Why S. K., Hildebrandt F., Ardito T., Mann A. S., Siegel N. J., Kashgarian M. Induction and intracellular localization of HSP-72 after renal ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):F769–F775. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.5.F769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Why S. K., Mann A. S., Ardito T., Siegel N. J., Kashgarian M. Expression and molecular regulation of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase after renal ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jul;267(1 Pt 2):F75–F85. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.1.F75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. K., Biagi B. Active potassium transport by rabbit descending colon epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(3):195–203. doi: 10.1007/BF01870886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S., Cain B. D. The renal H-K-ATPase: physiological significance and role in potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:323–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]