Abstract
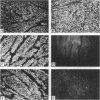
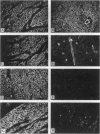
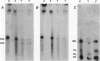
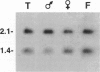
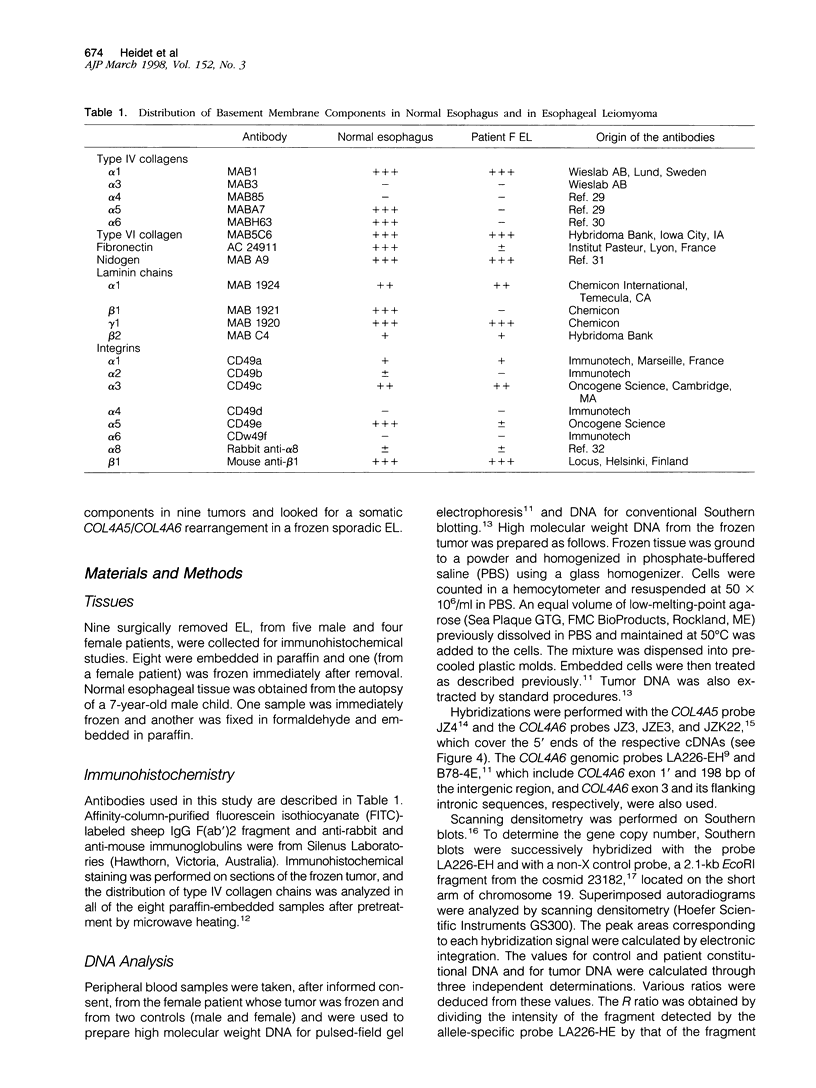
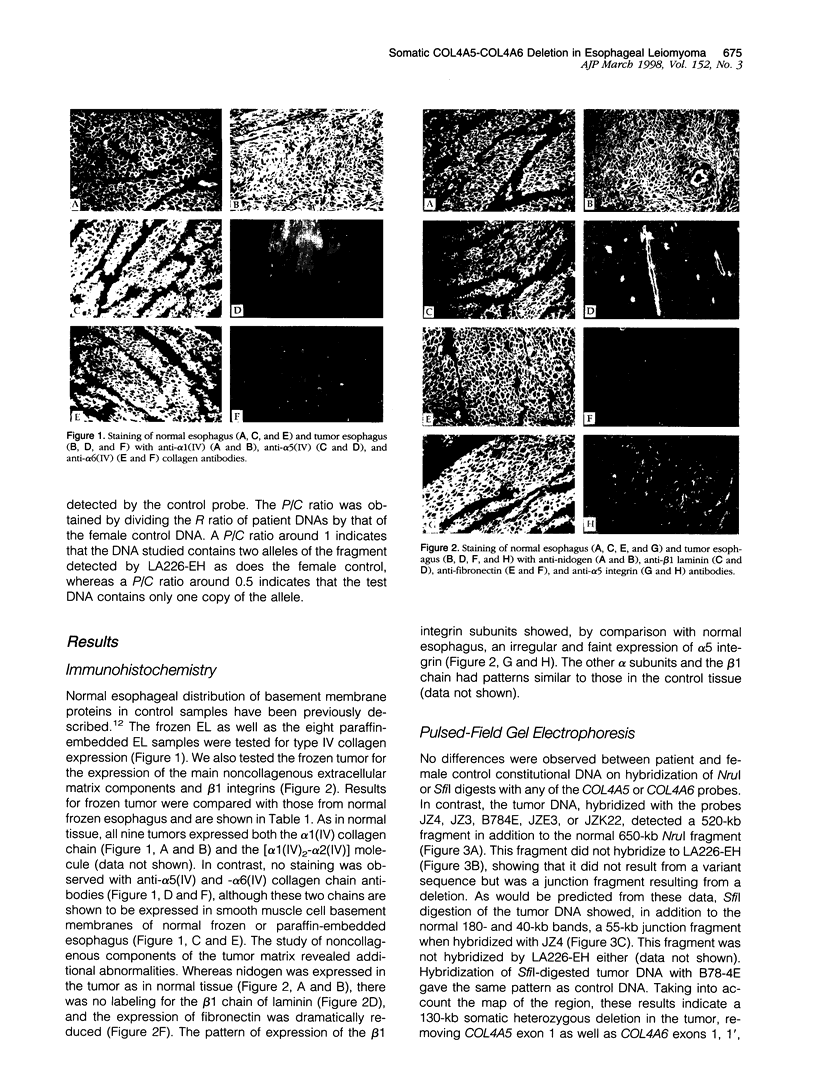
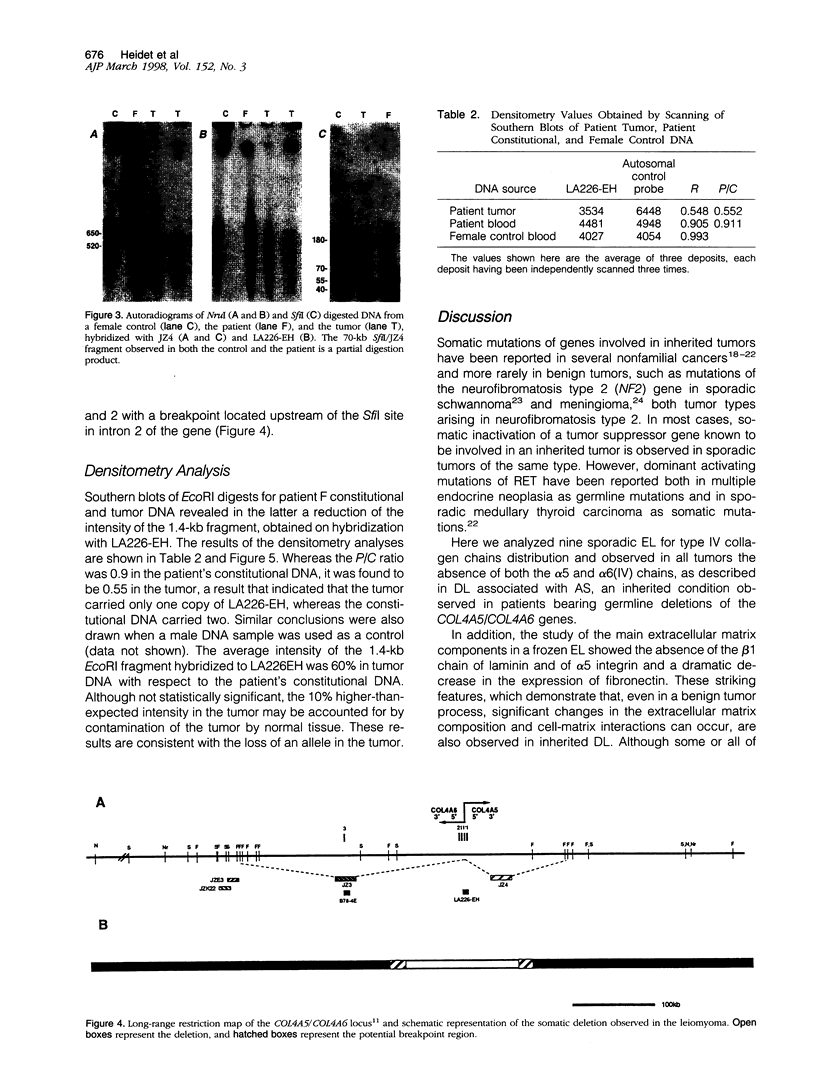
Leiomyomata of the esophagus are sporadic benign tumors of unknown etiology. We studied a collection of nine tumors for the expression of extracellular matrix components and found the same aberrant expression pattern as previously observed in inherited diffuse leiomyomatosis. We demonstrate here the occurrence of a somatic deletion at the COL4A5/COL4A6 locus at Xq22 in a frozen leiomyoma sample. These data confirm the hypothesis that the same underlying etiology is responsible for circumscribed smooth muscle proliferation in sporadic leiomyomata as for diffuse smooth muscle cell proliferation in inherited diffuse leiomyomatosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antignac C., Zhou J., Sanak M., Cochat P., Roussel B., Deschênes G., Gros F., Knebelmann B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Tryggvason K. Alport syndrome and diffuse leiomyomatosis: deletions in the 5' end of the COL4A5 collagen gene. Kidney Int. 1992 Nov;42(5):1178–1183. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth L. K., Batzer M. A., Brandriff B., Branscomb E., de Jong P., Garcia E., Garnes J. A., Gordon L. A., Lamerdin J. E., Lennon G. An integrated metric physical map of human chromosome 19. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):422–427. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardi G., Johansson B., Pandis N., Heim S., Mandahl N., Bak-Jensen E., Frederiksen H., Andrén-Sandberg A., Mitelman F. Recurrent chromosome aberrations in abdominal smooth muscle tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 Aug;62(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque M. D., Spigland N., Bensoussan A. L., Collin P. P., Saguem M. H., Brochu P., Blanchard H., Reinberg O. Esophageal leiomyoma in children: two case reports and review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg. 1989 Oct;24(10):1103–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(89)80229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppes M. J., Liefers G. J., Paul P., Yeger H., Williams B. R. Homozygous somatic Wt1 point mutations in sporadic unilateral Wilms tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1416–1419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahan K., Heidet L., Zhou J., Mettler G., Leppig K. A., Proesmans W., David A., Roussel B., Mongeau J. G., Gould J. M. Smooth muscle tumors associated with X-linked Alport syndrome: carrier detection in females. Kidney Int. 1995 Dec;48(6):1900–1906. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K., Prowse A., van den Berg A., Fleming S., Hulsbeek M. M., Crossey P. A., Richards F. M., Cairns P., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Somatic mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene in non-familial clear cell renal carcinoma. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Dec;3(12):2169–2173. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.12.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountain S. W. Leiomyoma of the esophagus. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1986 Jun;34(3):194–195. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Torres R., Orozco L. Alport-leiomyomatosis syndrome: an update. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993 Nov;22(5):641–648. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidet L., Cai Y., Sado Y., Ninomiya Y., Thorner P., Guicharnaud L., Boye E., Chauvet V., Solal L. C., Beziau A. Diffuse leiomyomatosis associated with X-linked Alport syndrome: extracellular matrix study using immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Lab Invest. 1997 Feb;76(2):233–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidet L., Dahan K., Zhou J., Xu Z., Cochat P., Gould J. D., Leppig K. A., Proesmans W., Guyot C., Guillot M. Deletions of both alpha 5(IV) and alpha 6(IV) collagen genes in Alport syndrome and in Alport syndrome associated with smooth muscle tumours. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jan;4(1):99–108. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra R. M., Landsvater R. M., Ceccherini I., Stulp R. P., Stelwagen T., Luo Y., Pasini B., Höppener J. W., van Amstel H. K., Romeo G. A mutation in the RET proto-oncogene associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B and sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma. Nature. 1994 Jan 27;367(6461):375–376. doi: 10.1038/367375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving R. M., Moffat D. A., Hardy D. G., Barton D. E., Xuereb J. H., Maher E. R. Somatic NF2 gene mutations in familial and non-familial vestibular schwannoma. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):347–350. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Fish A. J., Kleppel M. M., Hagen S. G., Michael A. F., Butkowski R. J. Renal entactin (nidogen): isolation, characterization and tissue distribution. Kidney Int. 1991 Oct;40(4):643–652. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleppel M. M., Fan W. W., Cheong H. I., Kashtan C. E., Michael A. F. Immunochemical studies of the Alport antigen. Kidney Int. 1992 Jun;41(6):1629–1637. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano H., Sadanaga N., Watanabe M., Yasuda M., Nozoe T., Sugimachi K. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma occurring in the surface epithelium over a benign tumor. J Surg Oncol. 1995 Aug;59(4):268–272. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930590414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Bollag G., Clark R., Stevens J., Conroy L., Fults D., Ward K., Friedman E., Samowitz W., Robertson M. Somatic mutations in the neurofibromatosis 1 gene in human tumors. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. B., Diaz-Arias A. A., Bochna G. S., Vogele K. A. Achalasia due to diffuse esophageal leiomyomatosis and inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder. Report of a family study. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1358–1365. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashal R. D., Fejzo M. L., Friedman A. J., Mitchner N., Nowak R. A., Rein M. S., Morton C. C., Sklar J. Analysis of androgen receptor DNA reveals the independent clonal origins of uterine leiomyomata and the secondary nature of cytogenetic aberrations in the development of leiomyomata. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1994 Sep;11(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870110102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Kagawa M., Iyama K., Naito I., Kishiro Y., Seyer J. M., Sugimoto M., Oohashi T., Sado Y. Differential expression of two basement membrane collagen genes, COL4A6 and COL4A5, demonstrated by immunofluorescence staining using peptide-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(5):1219–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.5.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oohashi T., Ueki Y., Sugimoto M., Ninomiya Y. Isolation and structure of the COL4A6 gene encoding the human alpha 6(IV) collagen chain and comparison with other type IV collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 10;270(45):26863–26867. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.45.26863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen R. M. Familial multiple upper gastrointestinal leiomyoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Mar;85(3):303–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Merel P., Lutchman M., Sanson M., Zucman J., Marineau C., Hoang-Xuan K., Demczuk S., Desmaze C., Plougastel B. Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):515–521. doi: 10.1038/363515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp L. M., Breuss J. M., Ramos D. M., Sheppard D., Pytela R. Sequence and tissue distribution of the human integrin alpha 8 subunit: a beta 1-associated alpha subunit expressed in smooth muscle cells. J Cell Sci. 1995 Feb;108(Pt 2):537–544. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.2.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A. K., Featherstone T., Wein K., Schlessinger D. YAC contigs mapping the human COL4A5 and COL4A6 genes and DXS118 within Xq21.3-q22. Genomics. 1995 Apr 10;26(3):502–509. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80168-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., Marczinek K., Neumann R., Witkowski R., Marchuk D. A., Nurnberg P. Somatic mutations in the neurofibromatosis 1 gene in gliomas and primitive neuroectodermal tumours. Anticancer Res. 1995 Nov-Dec;15(6B):2495–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryggvason K., Zhou J., Hostikka S. L., Shows T. B. Molecular genetics of Alport syndrome. Kidney Int. 1993 Jan;43(1):38–44. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikane H., Tsukamoto Y., Niwa Y., Goto H., Hase S., Maruta S., Shimodaira M., Miyata A. The coexistence of esophageal submucosal tumor and carcinoma. Endoscopy. 1995 Jan;27(1):119–123. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Ding M., Zhao Z., Reeders S. T. Complete primary structure of the sixth chain of human basement membrane collagen, alpha 6(IV). Isolation of the cDNAs for alpha 6(IV) and comparison with five other type IV collagen chains. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13193–13199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Hertz J. M., Leinonen A., Tryggvason K. Complete amino acid sequence of the human alpha 5 (IV) collagen chain and identification of a single-base mutation in exon 23 converting glycine 521 in the collagenous domain to cysteine in an Alport syndrome patient. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12475–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Mochizuki T., Smeets H., Antignac C., Laurila P., de Paepe A., Tryggvason K., Reeders S. T. Deletion of the paired alpha 5(IV) and alpha 6(IV) collagen genes in inherited smooth muscle tumors. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1167–1169. doi: 10.1126/science.8356449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]