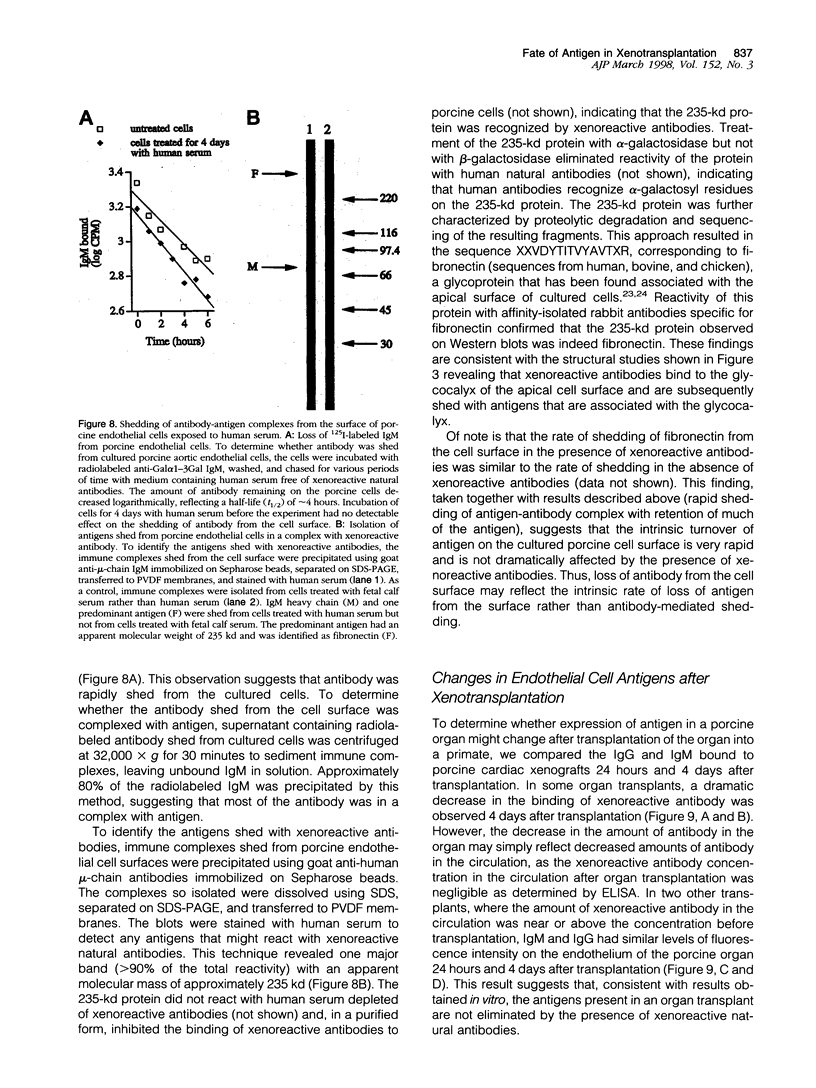
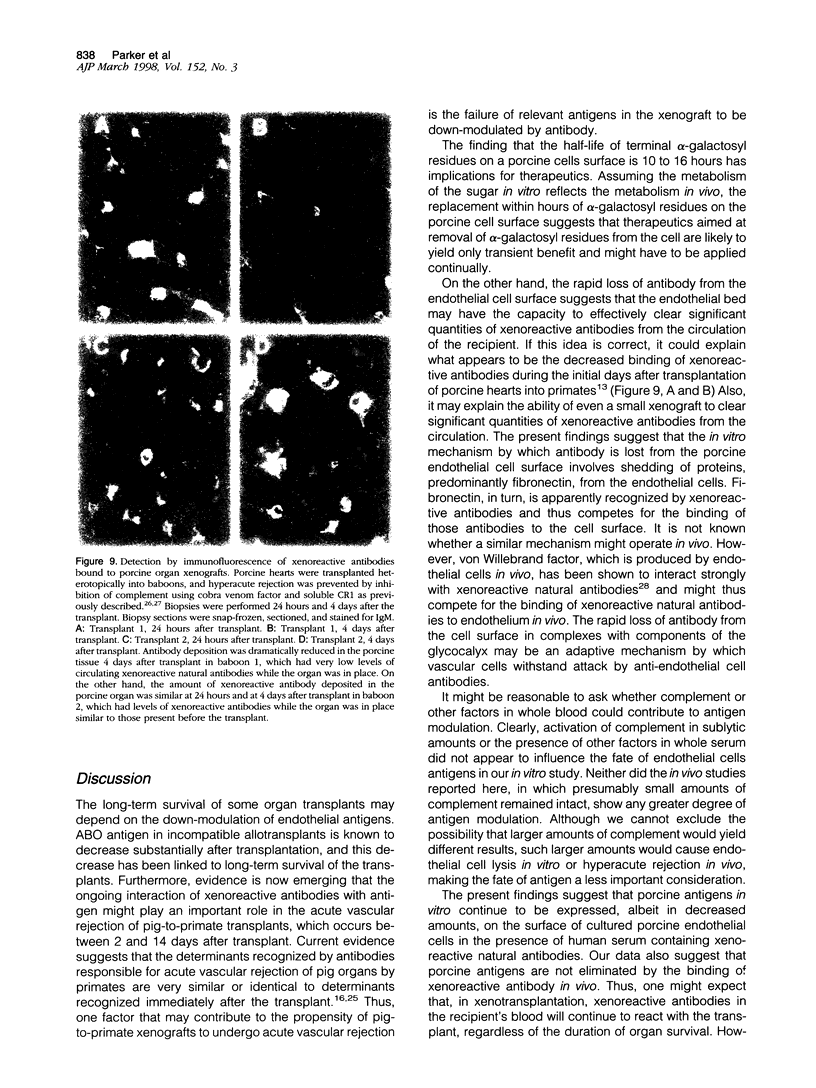
Abstract
Antigen down-modulation plays a critical role in xenotransplants involving humoral responses against the Forssman antigen and may play a role in the long-term survival of ABO-incompatible allografts. The present study investigates the fate of porcine antigens in pig-to-primate xenotransplantation. Human antibodies bound to the glycocalyx of cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells as judged by electron microscopy and were shed from the cell surface in a complex with fibronectin, a glycoprotein that is found in the apical membrane glycocalyx of cultured cells. Antibody was shed in a metabolically dependent process with a t(1/2) of 2 to 3 hours. However, the amount of antigen on the cell surface did not change appreciably within 24 hours, suggesting that antigen modulation did not occur. Over the ensuing days, antigen expression decreased, although the change was always less than 50% of baseline. Changes in antigen expression were due for the most part to changes in expression of alpha-galactosyl residues. Consistent with results obtained in vitro, antigen expression in porcine organ transplants remained at approximately the baseline level as determined by immunofluorescence analysis of IgM binding to graft endothelium. If, as these results suggest, antigen is not down-modulated in pig-to-primate xenotransplantation, then therapies aimed at prolonged xenograft survival must focus on antibody or genetic manipulation of antigen expression.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barba L. M., Caldwell P. R., Downie G. H., Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. Lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. I. In the rabbit a repeated interaction of heterologous anti-angiotensin-converting enzyme antibodies with alveolar endothelium results in resistance to immune injury through antigenic modulation. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2141–2158. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton C. J., Combe C., Walls J., Harris K. P. Fibronectin production by human tubular cells: the effect of apical protein. Kidney Int. 1996 Sep;50(3):760–767. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Caldwell P. R., Andres G., Brentjens J. R. Lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. II. Study of the effect of repeated antigen-antibody interactions in rabbits tolerant to heterologous antibody. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):216–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterell A. H., Collins B. H., Parker W., Harland R. C., Platt J. L. The humoral immune response in humans following cross-perfusion of porcine organs. Transplantation. 1995 Oct 27;60(8):861–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good A. H., Cooper D. K., Malcolm A. J., Ippolito R. M., Koren E., Neethling F. A., Ye Y., Zuhdi N., Lamontagne L. R. Identification of carbohydrate structures that bind human antiporcine antibodies: implications for discordant xenografting in humans. Transplant Proc. 1992 Apr;24(2):559–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gores P. F., Platt J. L., Rabe F., Stock P., Sutherland D. E. Permanent acceptance of islet allografts in mice is not associated with immunologic tolerance. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):499–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzknecht Z. E., Platt J. L. Identification of porcine endothelial cell membrane antigens recognized by human xenoreactive natural antibodies. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4565–4575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-induced redistribution of measles virus antigens on the cell surface. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Immunologic injury in measles virus infection. II. Suppression of immune injury through antigenic modulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):864–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh K., Masuda M., Kano Y., Jinguji Y., Fujiwara K. Focal adhesion proteins associated with apical stress fibers of human fibroblasts. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;31(3):177–195. doi: 10.1002/cm.970310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm M. E., Boyse E. A., Old L. J., Lisowska-Bernstein B., Stockert E. Modulation of TL (thymus-leukemia) antigens by Fab-fragments of TL antibody. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal J. R., Dalmasso A. P., Cromwell J. W., Platt J. L., Manivel C. J., Bolman R. M., 3rd, Matas A. J. Prolongation of cardiac xenograft survival by depletion of complement. Transplantation. 1993 Apr;55(4):857–866. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199304000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal J. R., Matas A. J., Sun L. H., Reif S., Bolman R. M., 3rd, Dalmasso A. P., Platt J. L. The immunopathology of cardiac xenograft rejection in the guinea pig-to-rat model. Transplantation. 1993 Jul;56(1):1–8. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199307000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. S., Kooyman D. L., Daniels L. J., Daggett C. W., Parker W., Lawson J. H., Hoopes C. W., Gullotto C., Li L., Birch P. The role of natural anti-Gal alpha 1-3Gal antibodies in hyperacute rejection of pig-to-baboon cardiac xenotransplants. Transpl Immunol. 1997 Sep;5(3):212–218. doi: 10.1016/s0966-3274(97)80040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee J. C., Collins B. H., Harland R. C., Lindman B. J., Bollinger R. R., Frank M. M., Platt J. L. Immunoglobulin prevents complement-mediated hyperacute rejection in swine-to-primate xenotransplantation. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2404–2412. doi: 10.1172/JCI118297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Stockert E., Boyse E. A., Kim J. H. Antigenic modulation. Loss of TL antigen from cells exposed to TL antibody. Study of the phenomenon in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):523–539. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W., Bruno D., Holzknecht Z. E., Platt J. L. Characterization and affinity isolation of xenoreactive human natural antibodies. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 15;153(8):3791–3803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Fischel R. J., Matas A. J., Reif S. A., Bolman R. M., Bach F. H. Immunopathology of hyperacute xenograft rejection in a swine-to-primate model. Transplantation. 1991 Aug;52(2):214–220. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199108000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Turman M. A., Noreen H. J., Fischel R. J., Bolman R. M., 3rd, Bach F. H. An ELISA assay for xenoreactive natural antibodies. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):1000–1001. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Vercellotti G. M., Dalmasso A. P., Matas A. J., Bolman R. M., Najarian J. S., Bach F. H. Transplantation of discordant xenografts: a review of progress. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. K., Kirk A. D., Bollinger R. R., Marsh H. C., Jr, Collins B. H., Levin J. L., Mault J. R., Heinle J. S., Ibrahim S., Rudolph A. R. The effect of soluble complement receptor type 1 on hyperacute rejection of porcine xenografts. Transplantation. 1994 Feb;57(3):363–370. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199402150-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saadi S., Platt J. L. Transient perturbation of endothelial integrity induced by natural antibodies and complement. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):21–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandrin M. S., Vaughan H. A., Dabkowski P. L., McKenzie I. F. Anti-pig IgM antibodies in human serum react predominantly with Gal(alpha 1-3)Gal epitopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11391–11395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfvin A., Bäcker A. E., Clausen H., Hakomori S., Rydberg L., Samuelsson B. E., Breimer M. E. Expression of glycolipid blood group antigens in single human kidneys: change in antigen expression of rejected ABO incompatible kidney grafts. Kidney Int. 1993 Dec;44(6):1289–1297. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuzawa Y., Brett J., Fukatsu A., Matsuo S., Caldwell P. R., Niesen N., Milgrom F., Godman G., Stern D., Andres G. Interaction of antibody with Forssman antigen in guinea pigs. A mechanism of adaptation to antibody- and complement-mediated injury. Am J Pathol. 1995 May;146(5):1260–1272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]