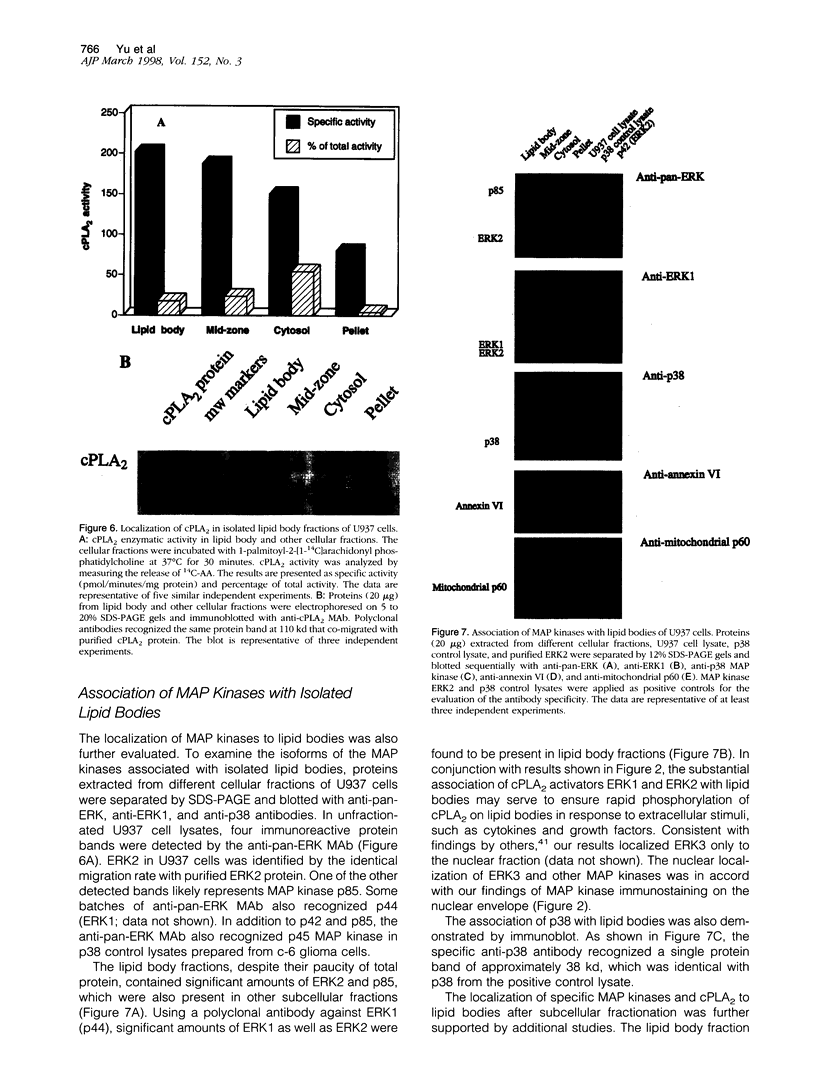
Abstract
Lipid bodies are inducible lipid domains abundantly present in leukocytes engaged in inflammation. They are rich in esterified arachidonate and are also potential sites for eicosanoid-forming enzyme localization. It is therefore of interest to know whether arachidonate-releasing cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) localizes at lipid bodies. Here, we present evidence that cPLA2 and its activating protein kinases, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases, co-localize at lipid bodies. U937 cells express high levels of cPLA2 and contain numerous cytoplasmic lipid bodies. Using double-labeling immunocytochemistry we demonstrated punctate cytoplasmic localizations of both cPLA2 and MAP kinases in U937 cells that were perfectly concordant with fluorescent fatty-acid-labeled lipid bodies. The co-localization of cPLA2 and MAP kinases at lipid bodies was confirmed by subcellular fractionation and immunoblot. Lipid body fractions free of cytosol and other organelles contained significant amounts of [14C]arachidonate-labeled phosphatidylcholine and cPLA2 enzymatic activities. Immunoblotting with specific antibodies identified cPLA2 as well as MAP kinases, including ERK1, ERK2, p85, and p38, in lipid bodies. The co-compartmentalization within arachidonate-rich lipid bodies of cPLA2 and its potentially activating protein kinases suggests that lipid bodies may be structurally distinct intracellular sites active in extracellular ligand-induced arachidonate release and eicosanoid formation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. D., Parker P. J. TPA-induced activation of MAP kinase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil W. J., Weller P. F., Peppercorn M. A., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural immunogold localization of subcellular sites of TNF-alpha in colonic Crohn's disease. J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Sep;58(3):284–298. doi: 10.1002/jlb.58.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Gronich J. H., Nemenoff R. A. Epidermal growth factor enhances glomerular mesangial cell soluble phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4934–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozza P. T., Payne J. L., Goulet J. L., Weller P. F. Mechanisms of platelet-activating factor-induced lipid body formation: requisite roles for 5-lipoxygenase and de novo protein synthesis in the compartmentalization of neutrophil lipids. J Exp Med. 1996 Apr 1;183(4):1515–1525. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.4.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozza P. T., Payne J. L., Morham S. G., Langenbach R., Smithies O., Weller P. F. Leukocyte lipid body formation and eicosanoid generation: cyclooxygenase-independent inhibition by aspirin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Oct 1;93(20):11091–11096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.20.11091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozza P. T., Yu W., Penrose J. F., Morgan E. S., Dvorak A. M., Weller P. F. Eosinophil lipid bodies: specific, inducible intracellular sites for enhanced eicosanoid formation. J Exp Med. 1997 Sep 15;186(6):909–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.6.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. G., McNish R. W., Peters-Golden M. Translocation and leukotriene synthetic capacity of nuclear 5-lipoxygenase in rat basophilic leukemia cells and alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21652–21658. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. G., Paine R., 3rd, Peters-Golden M. Localization of 5-lipoxygenase to the nucleus of unstimulated rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):22059–22066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Beaufay H., Nyssens-Jadin M. Analytical fractionation of mouse peritoneal macrophages: physical and biochemical properties of subcellular organelles from resident (unstimulated) and cultivated cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Aug;24(2):115–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channon J. Y., Leslie C. C. A calcium-dependent mechanism for associating a soluble arachidonoyl-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 with membrane in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5409–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng M., Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. ERK3 is a constitutively nuclear protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 12;271(15):8951–8958. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.15.8951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Milona N., Knopf J. L. Purification of a 110-kilodalton cytosolic phospholipase A2 from the human monocytic cell line U937. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt D. L., Rollins T. E., Day J. S., Gauger J. A., Smith W. L. Orientation of the active site and antigenic determinants of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10375–10382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler M. E., Weiss J., Clark J. D., Elsbach P. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide primes human neutrophils for enhanced release of arachidonic acid and causes phosphorylation of an 85-kD cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1583–1591. doi: 10.1172/JCI117138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durstin M., Durstin S., Molski T. F., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 translocates to membrane fraction in human neutrophils activated by stimuli that phosphorylate mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3142–3146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Peters S. P., Shulman E. S., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Pyne K., Harvey V. S., Galli S. J., Lichtenstein L. M. Lipid bodies: cytoplasmic organelles important to arachidonate metabolism in macrophages and mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2965–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Morgan E., Schleimer R. P., Ryeom S. W., Lichtenstein L. M., Weller P. F. Ultrastructural immunogold localization of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) to non-membrane-bound cytoplasmic lipid bodies in human lung mast cells, alveolar macrophages, type II pneumocytes, and neutrophils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Jun;40(6):759–769. doi: 10.1177/40.6.1316915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoràk A. M., Morgan E. S., Tzizik D. M., Weller P. F. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase): ultrastructural localization to nonmembrane-bound cytoplasmic lipid bodies in human eosinophils and 3T3 fibroblasts. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1994 Nov;105(3):245–250. doi: 10.1159/000236764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover S., de Carvalho M. S., Bayburt T., Jonas M., Chi E., Leslie C. C., Gelb M. H. Translocation of the 85-kDa phospholipase A2 from cytosol to the nuclear envelope in rat basophilic leukemia cells stimulated with calcium ionophore or IgE/antigen. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 23;270(25):15359–15367. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.25.15359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Seth A., Raden D. L., Bowman D. S., Fay F. S., Davis R. J. Serum-induced translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase to the cell surface ruffling membrane and the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1089–1101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines K. A., Giedd K. N., Weissmann G. Leukotriene B4 synthesis and metabolism by neutrophils and granule-free cytoplasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj2330583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W. G., Ramesha C. S., Chang D. J., Fan N., Heller R. A. Cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 activity and gene expression are stimulated by tumor necrosis factor: dexamethasone blocks the induced synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4475–4479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäckle S., Beisiegel U., Rinninger F., Buck F., Grigoleit A., Block A., Gröger I., Greten H., Windler E. Annexin VI, a marker protein of hepatocytic endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1026–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasurinen J., Somerharju P. Metabolism of pyrenyl fatty acids in baby hamster kidney fibroblasts. Effect of the acyl chain length. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6563–6569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Hyslop P. A., Utterback B. G., Hui K. Y., Jakubowski J. A. Differential activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) by thrombin and thrombin receptor agonist peptide in human platelets. Evidence for activation of cPLA2 independent of the mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14816–14823. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J. V., Hyslop P. A., Jakubowski J. A. Thrombin-induced phosphorylation and activation of Ca(2+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26796–26804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Roberts E. F., Manetta J., Putnam J. E. The Ca2(+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a 100-kDa protein in human monoblast U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5268–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. C. Kinetic properties of a high molecular mass arachidonoyl-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 that exhibits lysophospholipase activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11366–11371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. C., Voelker D. R., Channon J. Y., Wall M. M., Zelarney P. T. Properties and purification of an arachidonoyl-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 from a macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 16;963(3):476–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., DeWitt D. L. Interleukin-1 alpha induces the accumulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and the release of prostaglandin E2 in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23451–23454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Fagan D., Mudd J., Needleman P. Isolation and characterization of the complementary DNA for sheep seminal vesicle prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase). J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3550–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Winitz S., Qian N. X., Van Putten V., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1960–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto J. C., Smith W. L. The orientation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthases-1 and -2 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19868–19875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters-Golden M., McNish R. W. Redistribution of 5-lipoxygenase and cytosolic phospholipase A2 to the nuclear fraction upon macrophage activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 15;196(1):147–153. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Z. H., Leslie C. C. Protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in macrophages by stimuli that activate phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19480–19487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radom J., Salvayre R., Maret A., Nègre A., Douste-Blazy L. Metabolism of 1-pyrenedecanoic acid and accumulation of neutral fluorescent lipids in cultured fibroblasts of multisystemic lipid storage myopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 31;920(2):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90252-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sa G., Murugesan G., Jaye M., Ivashchenko Y., Fox P. L. Activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by basic fibroblast growth factor via a p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation pathway in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 3;270(5):2360–2366. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schievella A. R., Regier M. K., Smith W. L., Lin L. L. Calcium-mediated translocation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30749–30754. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Gonzalez F. A., Gupta S., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Signal transduction within the nucleus by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24796–24804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Sakata N., Hara M., Kitani A., Harigai M., Hirose W., Kawaguchi Y., Kawagoe M., Nakamura H. Flow cytometric analysis of lipid droplet formation in cells of the human monocytic cell line, U937. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;69(8):571–576. doi: 10.1139/o91-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggiani M., Oriente A., Seeds M. C., Bass D. A., Marone G., Chilton F. H. Migration of human inflammatory cells into the lung results in the remodeling of arachidonic acid into a triglyceride pool. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1181–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voetman A. A., Weening R. S., Hamers M. N., Meerhof L. J., Bot A. A., Roos D. Phagocytosing human neutrophils inactivate their own granular enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1541–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI110185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Ackerman S. J., Nicholson-Weller A., Dvorak A. M. Cytoplasmic lipid bodies of human neutrophilic leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Nov;135(5):947–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Dvorak A. M. Arachidonic acid incorporation by cytoplasmic lipid bodies of human eosinophils. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1269–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Monahan-Earley R. A., Dvorak H. F., Dvorak A. M. Cytoplasmic lipid bodies of human eosinophils. Subcellular isolation and analysis of arachidonate incorporation. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):141–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Ryeom S. W., Picard S. T., Ackerman S. J., Dvorak A. M. Cytoplasmic lipid bodies of neutrophils: formation induced by cis-unsaturated fatty acids and mediated by protein kinase C. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):137–146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. W., Coffey M. J., Brock T. G., Singer I. I., Peters-Golden M. 5-Lipoxygenase is located in the euchromatin of the nucleus in resting human alveolar macrophages and translocates to the nuclear envelope upon cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2035–2046. doi: 10.1172/JCI117889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. W., Evans J. F., Ethier D., Scott S., Vickers P. J., Hearn L., Heibein J. A., Charleson S., Singer I. I. 5-lipoxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein are localized in the nuclear envelope of activated human leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):1935–1946. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







