Abstract
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI) is most often an X-linked disorder in which urine is not concentrated due to renal resistance to arginine vasopressin. We recently identified four vasopressin type 2 receptor gene mutations in unrelated X-linked NDI families, including R143P, delta V278, R202C, and 804insG. All these mutations reduced ligand binding activity to < 10% of the normal without affecting mRNA accumulation. To elucidate whether the receptors are expressed on the cell surface, we analyzed biosynthesis and localization of tagged or untagged receptors stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, using two antibodies directed against distinct termini. Whole-cell and surface labeling studies revealed that the R202C clone had both surface-localized (50-55 kD) and intracellular proteins (40 and 75 kD), similar to the wild-type AVPR2 clone, whereas the R143P and delta V278 clones lacked the surface receptors, despite relatively increased intracellular components. The 804insG mutant cell produced no proteins despite an adequate mRNA level. Immunofluorescence staining confirmed that the R202C mutant reaches the cell surface, whereas the R143P and delta V278 mutants are retained within the cytoplasmic compartment. Thus, R202C, R143P/delta V278, and 804insG result in three distinct phenotypes, that is, a simple binding impairment at the cell surface, blocked intracellular transport, and ineffective biosynthesis or/and accelerated degradation of the receptor, respectively, and therefore are responsible for NDI. This phenotypic classification will help understanding of molecular pathophysiology of this disorder.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bichet D. G., Arthus M. F., Lonergan M., Hendy G. N., Paradis A. J., Fujiwara T. M., Morgan K., Gregory M. C., Rosenthal W., Didwania A. X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus mutations in North America and the Hopewell hypothesis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1262–1268. doi: 10.1172/JCI116698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Birnbaumer M., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Rosenthal W., Goodyer P., Nivet H., Benoit S., Giampietro P., Simonetti S. Nature and recurrence of AVPR2 mutations in X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):278–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Hendy G. N., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Ligier S., Pausova Z., Kluge R., Zingg H., Saenger P., Oppenheimer E. X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: from the ship Hopewell to RFLP studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;51(5):1089–1102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Razi M., Arthus M. F., Lonergan M., Tittley P., Smiley R. K., Rock G., Hirsch D. J. Epinephrine and dDAVP administration in patients with congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Evidence for a pre-cyclic AMP V2 receptor defective mechanism. Kidney Int. 1989 Nov;36(5):859–866. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Razi M., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Papukna V., Kortas C., Barjon J. N. Hemodynamic and coagulation responses to 1-desamino[8-D-arginine] vasopressin in patients with congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 7;318(14):881–887. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804073181403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer M., Gilbert S., Rosenthal W. An extracellular congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus mutation of the vasopressin receptor reduces cell surface expression, affinity for ligand, and coupling to the Gs/adenylyl cyclase system. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Jul;8(7):886–894. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.7.7984150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer M., Seibold A., Gilbert S., Ishido M., Barberis C., Antaramian A., Brabet P., Rosenthal W. Molecular cloning of the receptor for human antidiuretic hormone. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):333–335. doi: 10.1038/357333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Caron M. G., DeBlasi A., Frielle T., Lefkowitz R. J. Role of extracellular disulfide-bonded cysteines in the ligand binding function of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2335–2342. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Molday R. S., Khorana H. G. Role of the intradiscal domain in rhodopsin assembly and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4991–4995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faà V., Ventruto M. L., Loche S., Bozzola M., Podda R., Cao A., Rosatelli M. C. Mutations in the vasopressin V2-receptor gene in three families of Italian descent with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Sep;3(9):1685–1686. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.9.1685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. B., Caorsi C. E., Reyes C. E., Troncoso S., Barra V. Identification and purification of the vasopressin receptor from rat liver membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jul 22;689:526–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb55584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. J., Harris H. W., Jr, Kolakowski L. F., Jr, Guay-Woodford L. M., Botelho B., Ausiello D. A. Brief report: a molecular defect in the vasopressin V2-receptor gene causing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 27;328(21):1534–1537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305273282105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jans D. A., van Oost B. A., Ropers H. H., Fahrenholz F. Derivatives of somatic cell hybrids which carry the human gene locus for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI) express functional vasopressin renal V2-type receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15379–15382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Selection and coamplification of heterologous genes in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:537–566. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85044-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoers N. V., van den Ouweland A. M., Verdijk M., Monnens L. A., van Oost B. A. Inheritance of mutations in the V2 receptor gene in thirteen families with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Kidney Int. 1994 Jul;46(1):170–176. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki R., Yamamoto A., Tashiro Y. Microsomal aldehyde dehydrogenase is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum via its carboxyl-terminal 35 amino acids. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1407–1420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Yamamoto J., Hirata Y., Mori Y., Oikawa S., Inada M. Changes of atrial natriuretic peptide and its messenger RNA with development and regression of cardiac hypertrophy in renovascular hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1990 Jan;66(1):176–184. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merendino J. J., Jr, Speigel A. M., Crawford J. D., O'Carroll A. M., Brownstein M. J., Lolait S. J. Brief report: a mutation in the vasopressin V2-receptor gene in a kindred with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 27;328(21):1538–1541. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305273282106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J. Rhodopsin: structure, function, and genetics. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):4923–4931. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y., Metzenberg A., Das S., Jing B., Gitschier J. Mutations in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene are associated with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):103–106. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y., Wilson P., Gitschier J. The effect of eight V2 vasopressin receptor mutations on stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and binding to vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31933–31937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak R. K., Merkle R. K., Cummings R. D., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G. Immunocytochemical localization of mutant low density lipoprotein receptors that fail to reach the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Antaramian A., Gilbert S., Birnbaumer M. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. A V2 vasopressin receptor unable to stimulate adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13030–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Seibold A., Antaramian A., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Hendy G. N., Birnbaumer M., Bichet D. G. Molecular identification of the gene responsible for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):233–235. doi: 10.1038/359233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibold A., Brabet P., Rosenthal W., Birnbaumer M. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human antidiuretic hormone receptor gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;51(5):1078–1083. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. H., Schneider B. G., Agarwal N., Papermaster D. S., Nathans J. Functional heterogeneity of mutant rhodopsins responsible for autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8840–8844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukaguchi H., Matsubara H., Aritaki S., Kimura T., Abe S., Inada M. Two novel mutations in the vasopressin V2 receptor gene in unrelated Japanese kindreds with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):1000–1010. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
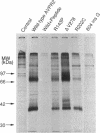
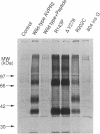
- Tsukaguchi H., Matsubara H., Inada M. Expression studies of two vasopressin V2 receptor gene mutations, R202C and 804insG, in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Kidney Int. 1995 Aug;48(2):554–562. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukaguchi H., Matsubara H., Mori Y., Yoshimasa Y., Yoshimasa T., Nakao K., Inada M. Two vasopressin type 2 receptor gene mutations R143P and delta V278 in patients with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus impair ligand binding of the receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jun 26;211(3):967–977. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenkert D., Merendino J. J., Jr, Shenker A., Thambi N., Robertson G. L., Moses A. M., Spiegel A. M. Novel mutations in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene of patients with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1429–1430. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildin R. S., Antush M. J., Bennett R. L., Schoof J. M., Scott C. R. Heterogeneous AVPR2 gene mutations in congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):266–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa Y., Paul J. I., Whittaker J., Steiner D. F. Effects of amino acid replacements within the tetrabasic cleavage site on the processing of the human insulin receptor precursor expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17230–17237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Dreesen J. C., Verdijk M., Knoers N. V., Monnens L. A., Rocchi M., van Oost B. A. Mutations in the vasopressin type 2 receptor gene (AVPR2) associated with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):99–102. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Knoop M. T., Knoers V. V., Markslag P. W., Rocchi M., Warren S. T., Ropers H. H., Fahrenholz F., Monnens L. A., van Oost B. A. Colocalization of the gene for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (DIR) and the vasopressin type 2 receptor gene (AVPR2) in the Xq28 region. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1350–1352. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zastrow M., Link R., Daunt D., Barsh G., Kobilka B. Subtype-specific differences in the intracellular sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):763–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]