Abstract
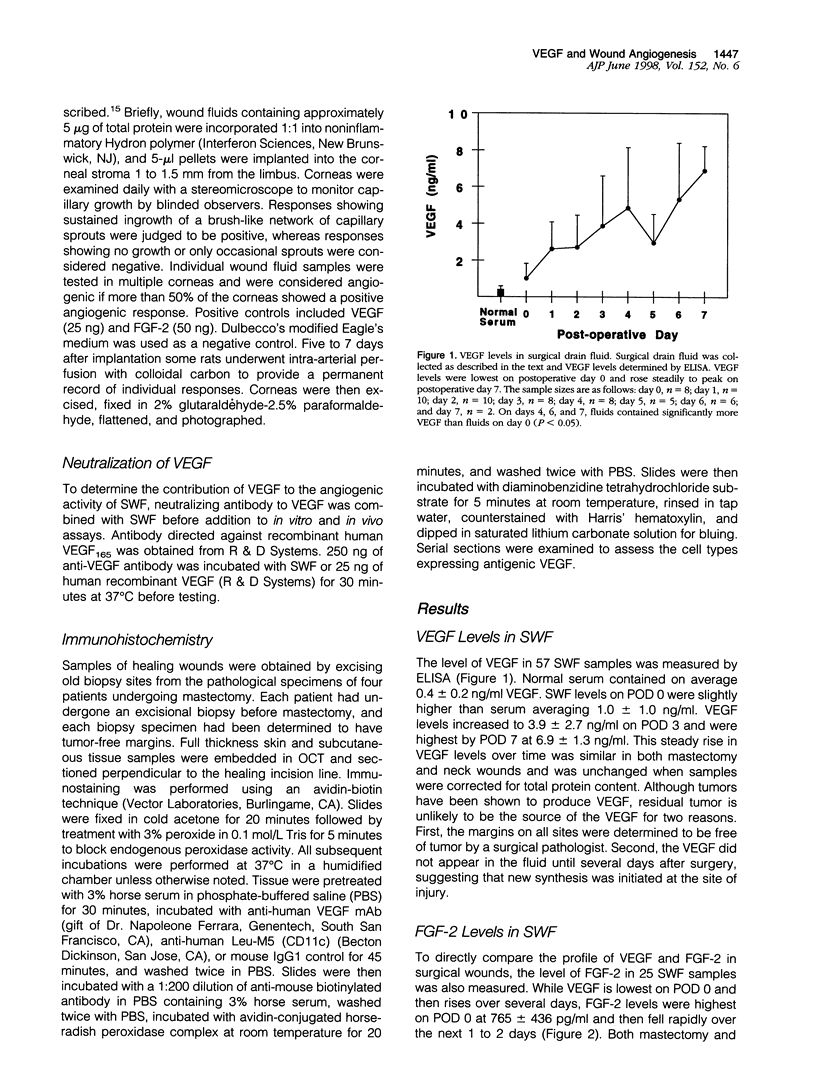
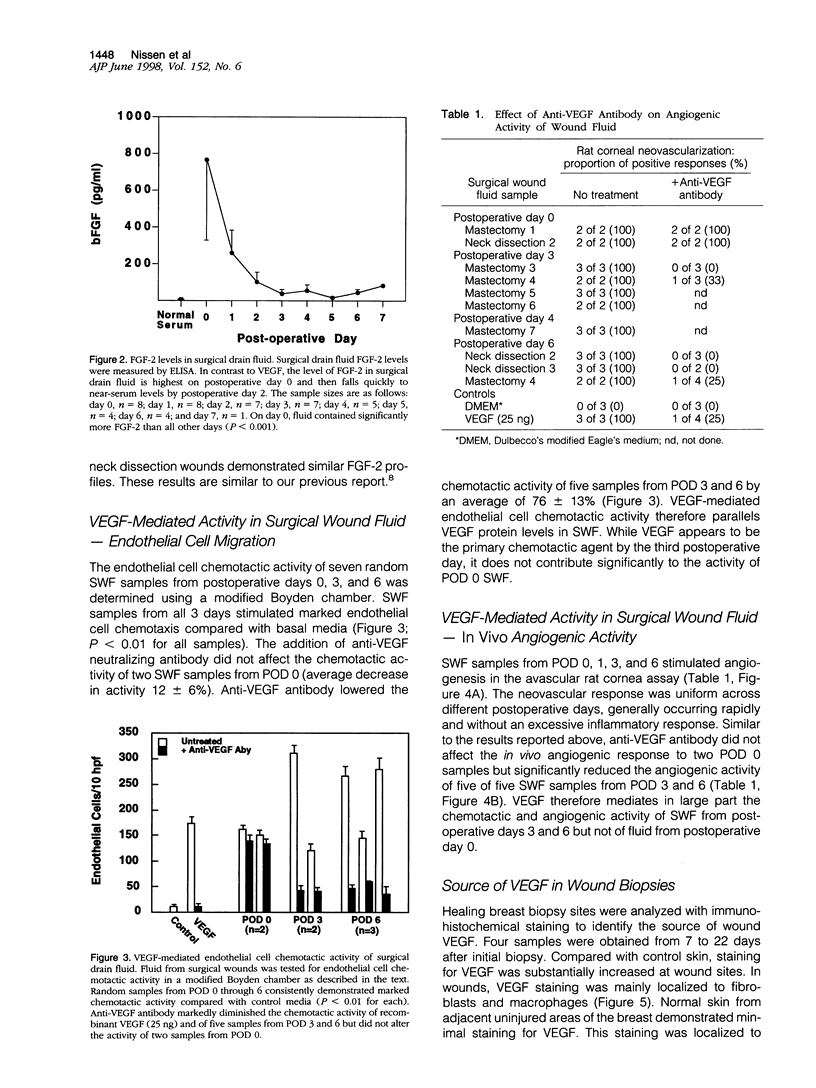
Angiogenesis is an essential component of normal wound repair, yet the primary mediators of wound angiogenesis have not been well described. The current study characterizes the contribution of vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) to the angiogenic environment of human surgical wounds. Surgical wound fluid samples (n = 70) were collected daily for up to 7 postoperative days (POD) from 14 patients undergoing mastectomy or neck dissection. VEGF levels in surgical wound fluid were lowest on POD 0, approximating values of serum, but increased steadily through POD 7. An opposite pattern was noted for basic fibroblast growth factor-2. Fibroblast growth factor-2, which has been previously described as a wound angiogenic factor, exhibited highest levels at POD 0, declining to near serum levels by POD 3. Surgical wound fluid form all time points stimulated marked endothelial cell chemotaxis and induced a brisk neovascular response in the rat corneal micropocket angiogenesis assay. Antibody neutralization of VEGF did not affect the in vitro chemotactic or the in vivo angiogenic activity early wound samples (POD 0). In contrast, VEGF neutralization significantly attenuated both chemotactic activity (mean decrease 76 +/- 13%, P < 0.01) and angiogenic activity (5 of 5 samples affected) of later wound samples (POD 3 and 6). The results suggest a model of wound angiogenesis in which an initial angiogenic stimulus is supplied by fibroblast growth factor-2, followed by a subsequent and more prolonged angiogenic stimulus mediated by VEGF.
Full text
PDF


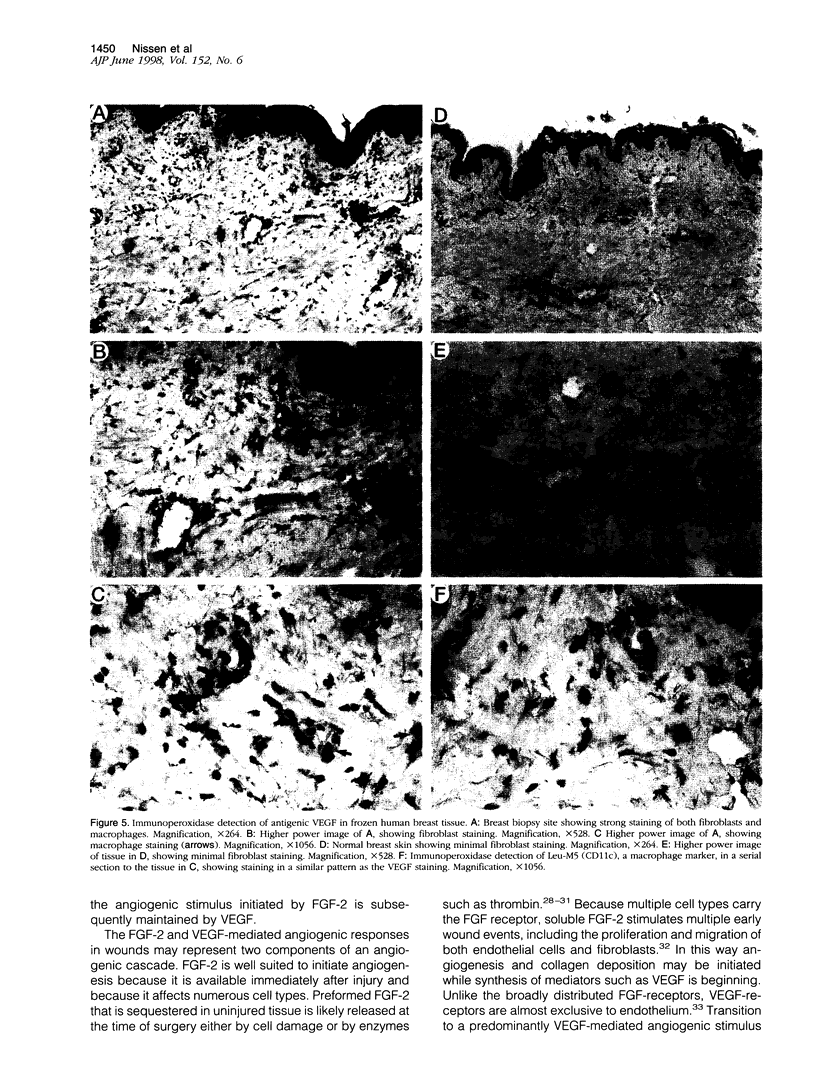
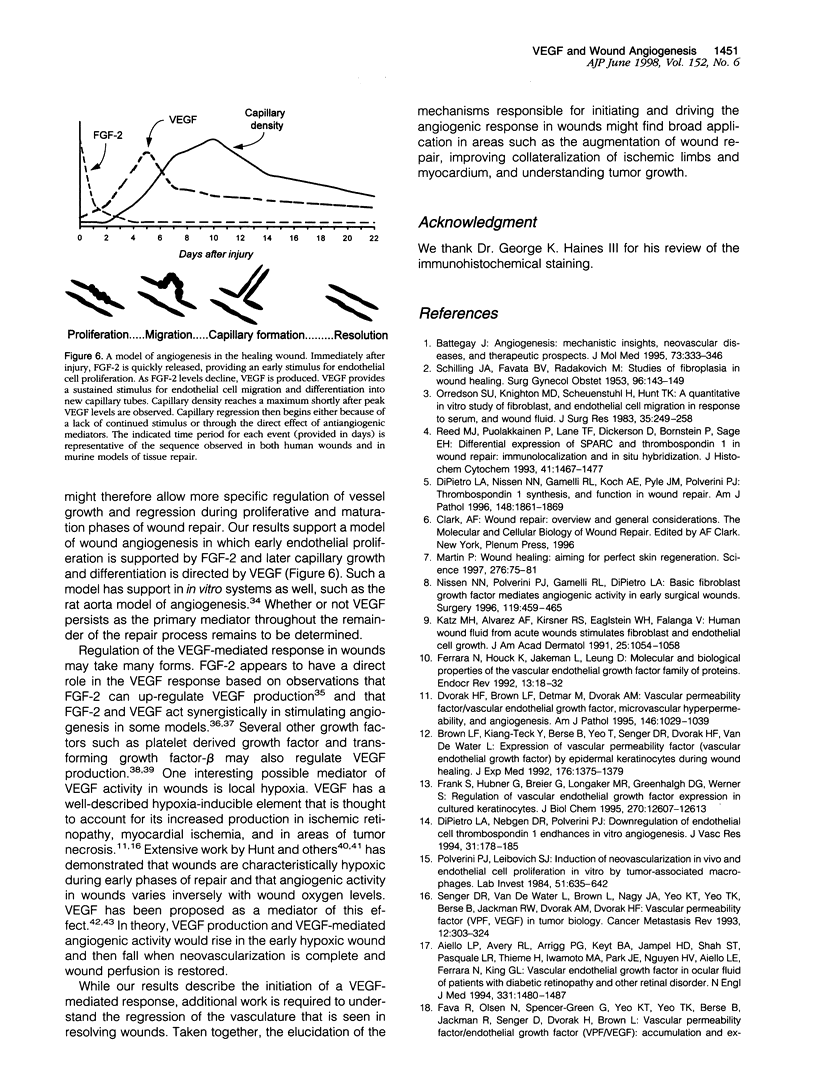

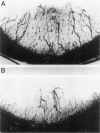
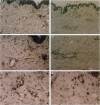
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiello L. P., Avery R. L., Arrigg P. G., Keyt B. A., Jampel H. D., Shah S. T., Pasquale L. R., Thieme H., Iwamoto M. A., Park J. E. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994 Dec 1;331(22):1480–1487. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199412013312203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battegay E. J. Angiogenesis: mechanistic insights, neovascular diseases, and therapeutic prospects. J Mol Med (Berl) 1995 Jul;73(7):333–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00192885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Av P., Crofford L. J., Wilder R. L., Hla T. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in synovial fibroblasts by prostaglandin E and interleukin-1: a potential mechanism for inflammatory angiogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1995 Sep 18;372(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00956-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra M., Vlodavsky I., Ishai-Michaeli R., Neufeld G., Bar-Shavit R. Thrombin-induced release of active basic fibroblast growth factor-heparan sulfate complexes from subendothelial extracellular matrix. Blood. 1993 Jun 15;81(12):3324–3331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berse B., Brown L. F., Van de Water L., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):211–220. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuing K., Eriksson E., Liu P., Miller D. R. Healing of partial thickness porcine skin wounds in a liquid environment. J Surg Res. 1992 Jan;52(1):50–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(92)90278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Van de Water L., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Fibrinogen influx and accumulation of cross-linked fibrin in healing wounds and in tumor stroma. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):455–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Yeo K. T., Berse B., Yeo T. K., Senger D. R., Dvorak H. F., van de Water L. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) by epidermal keratinocytes during wound healing. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1375–1379. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Vlodavsky I., Haimovitz-Friedman A., Hicklin D., Fuks Z. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1990 Dec;63(6):832–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmar M., Brown L. F., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Elicker B. M., Dvorak H. F., Claffey K. P. Hypoxia regulates the expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF) and its receptors in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Mar;108(3):263–268. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12286453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPietro L. A., Nebgen D. R., Polverini P. J. Downregulation of endothelial cell thrombospondin 1 enhances in vitro angiogenesis. J Vasc Res. 1994 May-Jun;31(3):178–185. doi: 10.1159/000319585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolecki G. J., Connolly D. T. Effects of a variety of cytokines and inducing agents on vascular permeability factor mRNA levels in U937 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):572–578. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F., Detmar M., Dvorak A. M. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1995 May;146(5):1029–1039. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Houck K., Jakeman L., Leung D. W. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):18–32. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Hübner G., Breier G., Longaker M. T., Greenhalgh D. G., Werner S. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12607–12613. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. K., Twomey P., Zederfeldt B., Dunphy J. E. Respiratory gas tensions and pH in healing wounds. Am J Surg. 1967 Aug;114(2):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. H., Alvarez A. F., Kirsner R. S., Eaglstein W. H., Falanga V. Human wound fluid from acute wounds stimulates fibroblast and endothelial cell growth. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Dec;25(6 Pt 1):1054–1058. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(91)70306-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Li B., Winer J., Armanini M., Gillett N., Phillips H. S., Ferrara N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):841–844. doi: 10.1038/362841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Silver I. A., Hunt T. K. Regulation of wound-healing angiogenesis-effect of oxygen gradients and inspired oxygen concentration. Surgery. 1981 Aug;90(2):262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koolwijk P., van Erck M. G., de Vree W. J., Vermeer M. A., Weich H. A., Hanemaaijer R., van Hinsbergh V. W. Cooperative effect of TNFalpha, bFGF, and VEGF on the formation of tubular structures of human microvascular endothelial cells in a fibrin matrix. Role of urokinase activity. J Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;132(6):1177–1188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.6.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. Wound healing--aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science. 1997 Apr 4;276(5309):75–81. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5309.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan L., Warder E., McNeil P. L. Basic fibroblast growth factor is efficiently released from a cytolsolic storage site through plasma membrane disruptions of endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia R. F., Lin Y. J., Hazelton D., Qian X. Endogenous regulation of angiogenesis in the rat aorta model. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Am J Pathol. 1997 Nov;151(5):1379–1386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen N. N., Polverini P. J., Gamelli R. L., DiPietro L. A. Basic fibroblast growth factor mediates angiogenic activity in early surgical wounds. Surgery. 1996 Apr;119(4):457–465. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(96)80148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander J. V., Connolly D. T., DeLarco J. E. Specific binding of vascular permeability factor to endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orredson S. U., Knighton D. R., Scheuenstuhl H., Hunt T. K. A quantitative in vitro study of fibroblast and endothelial cell migration in response to serum and wound fluid. J Surg Res. 1983 Sep;35(3):249–258. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(83)80011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertovaara L., Kaipainen A., Mustonen T., Orpana A., Ferrara N., Saksela O., Alitalo K. Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6271–6274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Leibovich S. J. Induction of neovascularization in vivo and endothelial proliferation in vitro by tumor-associated macrophages. Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):635–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS R., BENDITT E. P. Wound healing and collagen formation. II. Fine structure in experimental scurvy. J Cell Biol. 1962 Mar;12:533–551. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. J., Puolakkainen P., Lane T. F., Dickerson D., Bornstein P., Sage E. H. Differential expression of SPARC and thrombospondin 1 in wound repair: immunolocalization and in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Oct;41(10):1467–1477. doi: 10.1177/41.10.8245406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLING J. A., FAVATA B. V., RADAKOVICH M. Studies of fibroplasia in wound healing. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1953 Feb;96(2):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Perruzzi C. A., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Perruzzi C. A., Feder J., Dvorak H. F. A highly conserved vascular permeability factor secreted by a variety of human and rodent tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5629–5632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Van de Water L., Brown L. F., Nagy J. A., Yeo K. T., Yeo T. K., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993 Sep;12(3-4):303–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00665960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki D., Itin A., Soffer D., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):843–845. doi: 10.1038/359843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavri G. T., Zachary I. C., Baskerville P. A., Martin J. F., Erusalimsky J. D. Basic fibroblast growth factor upregulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Synergistic interaction with hypoxia. Circulation. 1995 Jul 1;92(1):11–14. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaschi S., Nicosia R. F. Angiogenic role of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor released by rat aorta after injury. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jul;143(1):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Tammi M., Guo H., Tammi R. Hyaluronan distribution in the normal epithelium of esophagus, stomach, and colon and their cancers. Am J Pathol. 1996 Jun;148(6):1861–1869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki A. B., Staiano-Coico L., Grinnell F. Wound fluid from chronic leg ulcers contains elevated levels of metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Jul;101(1):64–68. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12359590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]