Abstract
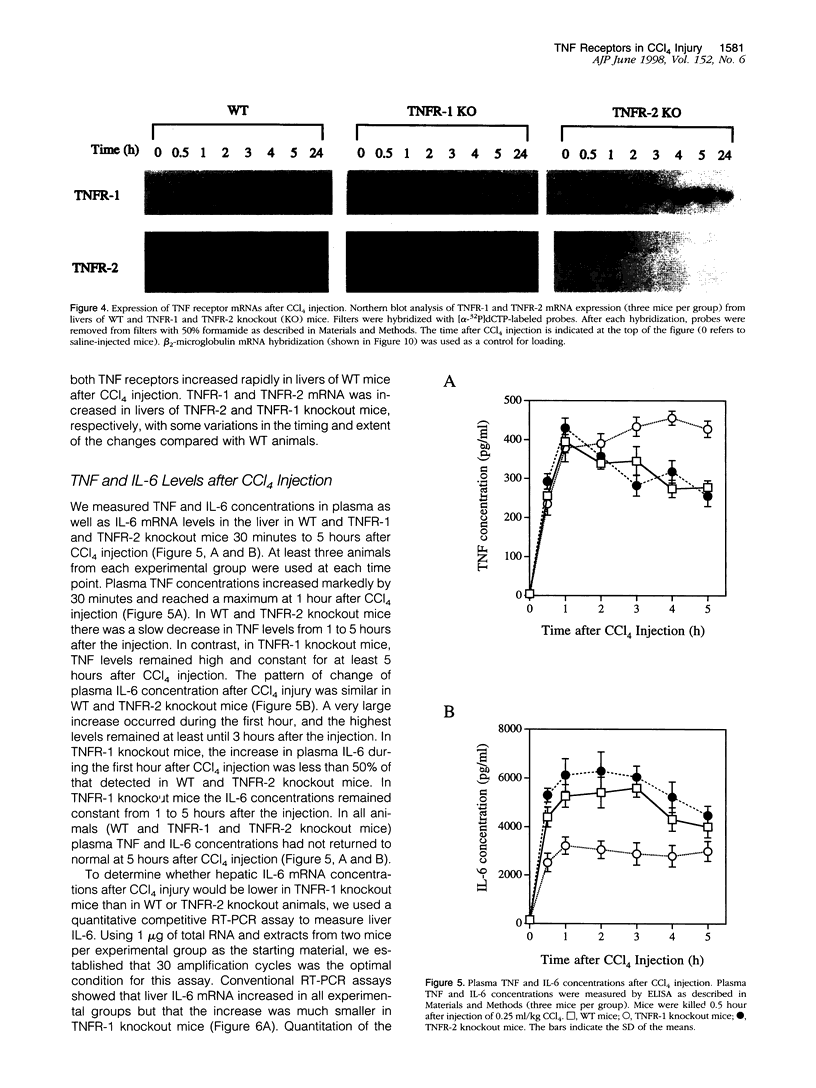
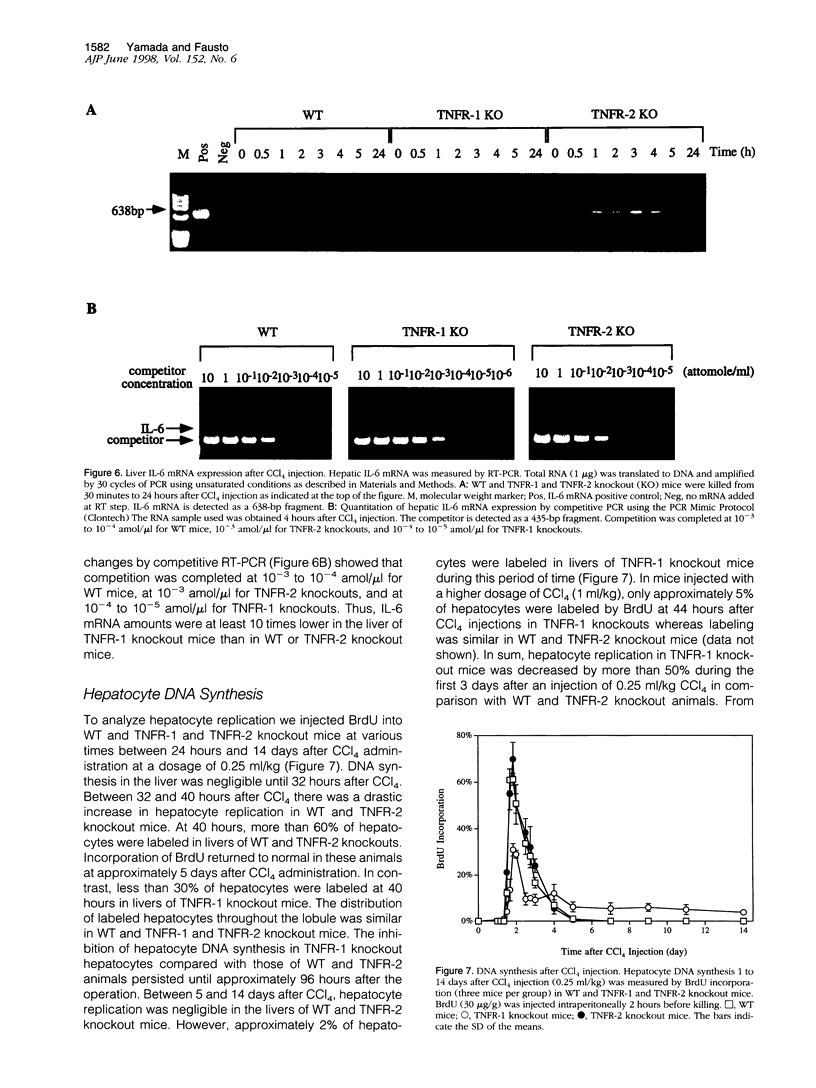
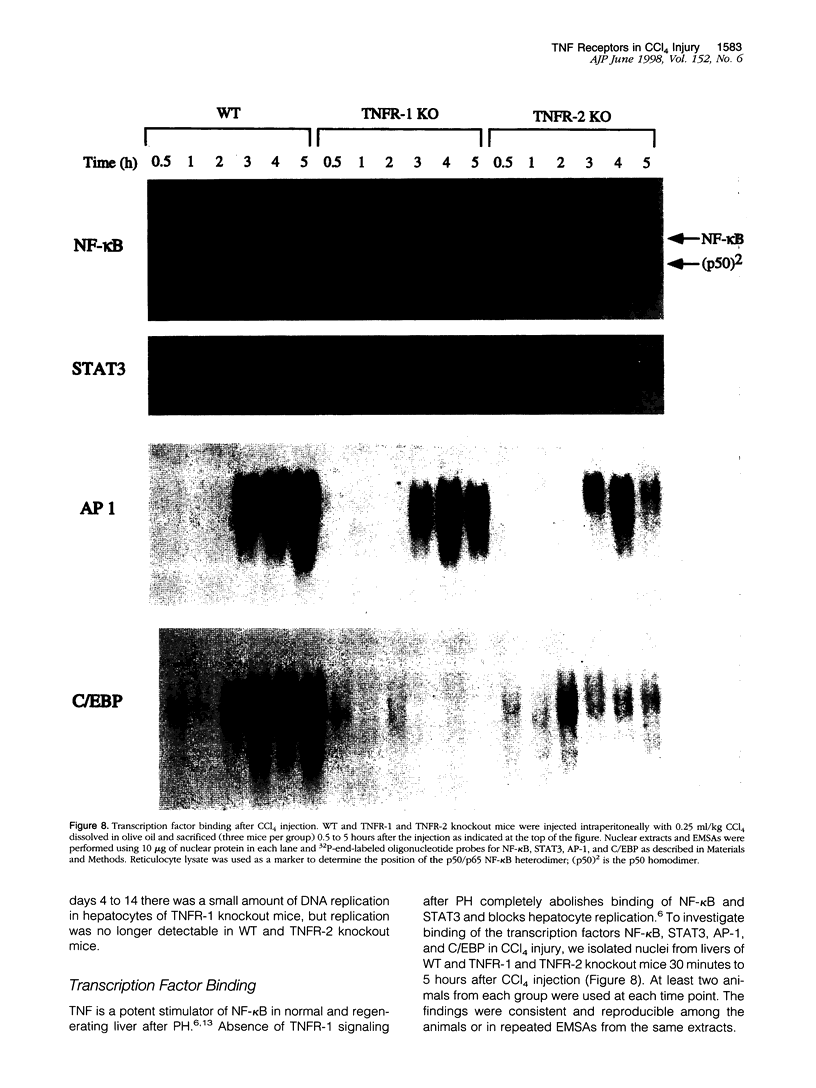
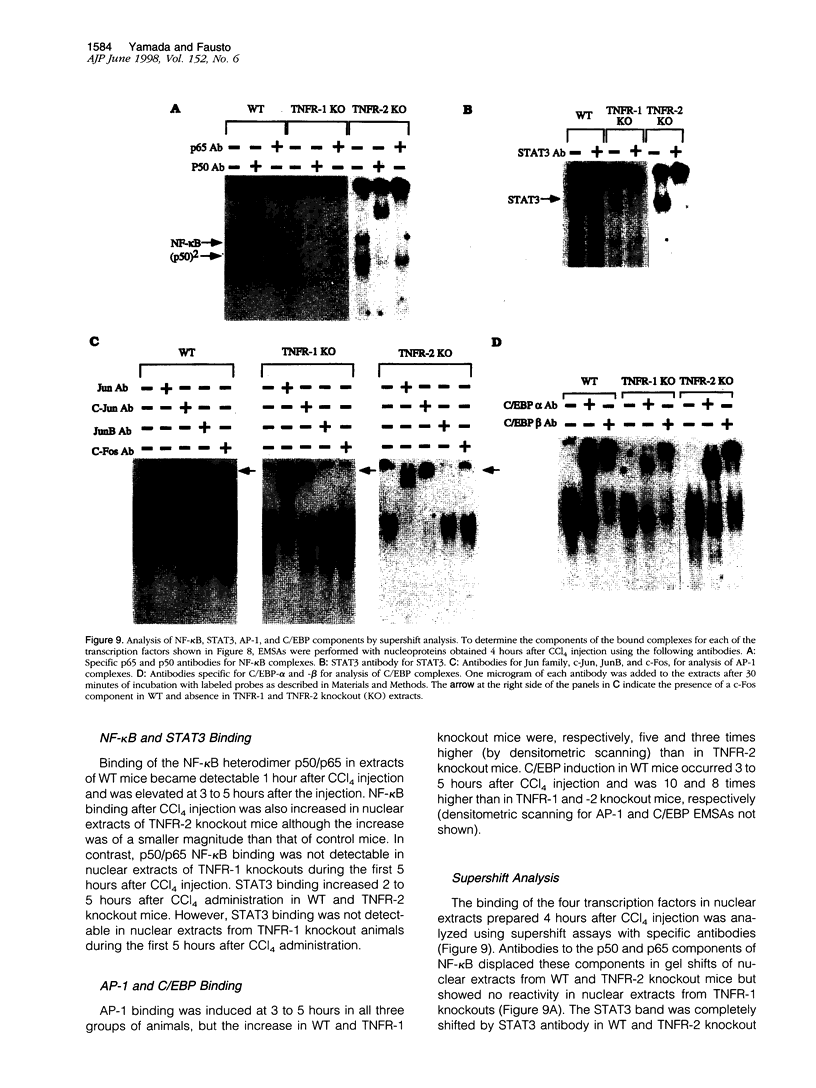
Signaling by tumor necrosis factor type 1 receptor (TNFR-1) is required for the initiation of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Using knockout mice that lack either TNFR-1 or TNFR-2, we determined whether signaling through TNF receptors is important for liver injury and hepatocyte proliferation induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Lack of TNFR-1 inhibited hepatocyte DNA synthesis after CCl4 injection. At 44 hours after the injection, replication of hepatocytes in TNFR-1 was 50% to 90% lower than in wild-type (WT) animals, depending on the dose injected. In WT animals, hepatocyte replication was essentially completed by 4 days after CCl4 injection, but replication at a low level persisted in TNFR-1 mice for at least 2 weeks. TNFR-1 knockout mice had little detectable NF-kappa B and STAT3 binding during the first 5 hours after CCl4, high plasma TNF, and reduced levels of plasma interleukin (IL)-6 and liver IL-6 mRNA. Injection of IL-6 30 minutes before CCl4 administration corrected the deficiency of hepatocyte replication at 44 hours and restored STAT3 binding to normal levels. In contrast, mice lacking TNFR-2 did not differ significantly from WT mice in NF-kappa B and STAT3 binding, IL-6 and TNF levels, or hepatocyte replication. Although AP-1 binding was induced in WT TNFR-1 and TNFR-2 knockout mice, binding in TNFR-2 knockouts was lower than in WT mice. C/EBP binding was much lower in TNFR-1 and TNFR-2 knockout mice than in WT mice. As assessed by morphological analysis and alanine aminotransferase levels, the acute injury caused by CCl4 appeared to be similar in the three groups of animals, but subsequent regeneration was impaired in mice lacking TNFR-1. We conclude that a TNFR-1 signaling pathway involving NF-kappa B, IL-6, and STAT3 is an important component of the hepatocyte mitogenic response induced by CCl4 injury in mouse liver.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerman P., Cote P., Yang S. Q., McClain C., Nelson S., Bagby G. J., Diehl A. M. Antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibit liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):G579–G585. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.4.G579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsura M., FitzGerald M. J., Fausto N., Sonenshein G. E. Nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel blocks transforming growth factor beta1-induced apoptosis of murine hepatocyte cell lines. Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Oct;8(10):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Reddy E. P. Transducers of life and death: TNF receptor superfamily and associated proteins. Oncogene. 1996 Jan 4;12(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellas R. E., FitzGerald M. J., Fausto N., Sonenshein G. E. Inhibition of NF-kappa B activity induces apoptosis in murine hepatocytes. Am J Pathol. 1997 Oct;151(4):891–896. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruccoleri A., Gallucci R., Germolec D. R., Blackshear P., Simeonova P., Thurman R. G., Luster M. I. Induction of early-immediate genes by tumor necrosis factor alpha contribute to liver repair following chemical-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology. 1997 Jan;25(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo C. A., Jr, Madden J. F., Gao W., Selvan R. S., Clavien P. A. Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation in the rodent. Hepatology. 1997 Dec;26(6):1513–1520. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cressman D. E., Diamond R. H., Taub R. Rapid activation of the Stat3 transcription complex in liver regeneration. Hepatology. 1995 May;21(5):1443–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cressman D. E., Greenbaum L. E., DeAngelis R. A., Ciliberto G., Furth E. E., Poli V., Taub R. Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science. 1996 Nov 22;274(5291):1379–1383. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Xu J., Alt E. Prevention of carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver injury by soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jun;108(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl A. M., Yin M., Fleckenstein J., Yang S. Q., Lin H. Z., Brenner D. A., Westwick J., Bagby G., Nelson S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces c-jun during the regenerative response to liver injury. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):G552–G561. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.4.G552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald M. J., Webber E. M., Donovan J. R., Fausto N. Rapid DNA binding by nuclear factor kappa B in hepatocytes at the start of liver regeneration. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Apr;6(4):417–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Regulated transcription of c-Ki-ras and c-myc during compensatory growth of rat liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1493–1498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell M., Douni E., Wajant H., Löhden M., Clauss M., Maxeiner B., Georgopoulos S., Lesslauer W., Kollias G., Pfizenmaier K. The transmembrane form of tumor necrosis factor is the prime activating ligand of the 80 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):793–802. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors in cellular signaling of soluble and membrane-expressed TNF. J Inflamm. 1995;47(1-2):8–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Milani S., Schuppan D., Stein H. Temporal and spatial patterns of proto-oncogene expression at early stages of toxic liver injury in the rat. Lab Invest. 1991 Sep;65(3):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A., Bluethmann H., Moore M. W., Lesslauer W. Tumor necrosis factor receptors (Tnfr) in mouse fibroblasts deficient in Tnfr1 or Tnfr2 are signaling competent and activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway with differential kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 8;271(45):28097–28104. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.45.28097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Degli Esposti S., Yao T., Diehl A. M., Zern M. A. Vitamin E therapy of acute CCl4-induced hepatic injury in mice is associated with inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B binding. Hepatology. 1995 Nov;22(5):1474–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Mariathasan S., Nahm M. H., Baranyay F., Peschon J. J., Chaplin D. D. Role of lymphotoxin and the type I TNF receptor in the formation of germinal centers. Science. 1996 Mar 1;271(5253):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5253.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler K. M., Torrance D. S., Smith C. A., Goodwin R. G., Stremler K. E., Fung V. P., Madani H., Widmer M. B. Soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors are effective therapeutic agents in lethal endotoxemia and function simultaneously as both TNF carriers and TNF antagonists. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1548–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Yamazaki M. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates DNA synthesis of mouse hepatocytes in primary culture and is suppressed by transforming growth factor beta and interleukin 6. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jan;150(1):134–139. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeberg P., Biempica L., Czaja M. J. Timing of protooncogene expression varies in toxin-induced liver regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Feb;154(2):294–300. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Goeddel D. V., Reynolds C., Figari I. S., Weber R. F., Fendly B. M., Palladino M. A., Jr Stimulation of human T-cell proliferation by specific activation of the 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4637–4641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor, other cytokines and disease. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:317–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Kirillova I., Peschon J. J., Fausto N. Initiation of liver growth by tumor necrosis factor: deficient liver regeneration in mice lacking type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Feb 18;94(4):1441–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L., Fisher G., Miller R. E., Peschon J., Lynch D. H., Lenardo M. J. Induction of apoptosis in mature T cells by tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1995 Sep 28;377(6547):348–351. doi: 10.1038/377348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]