Abstract
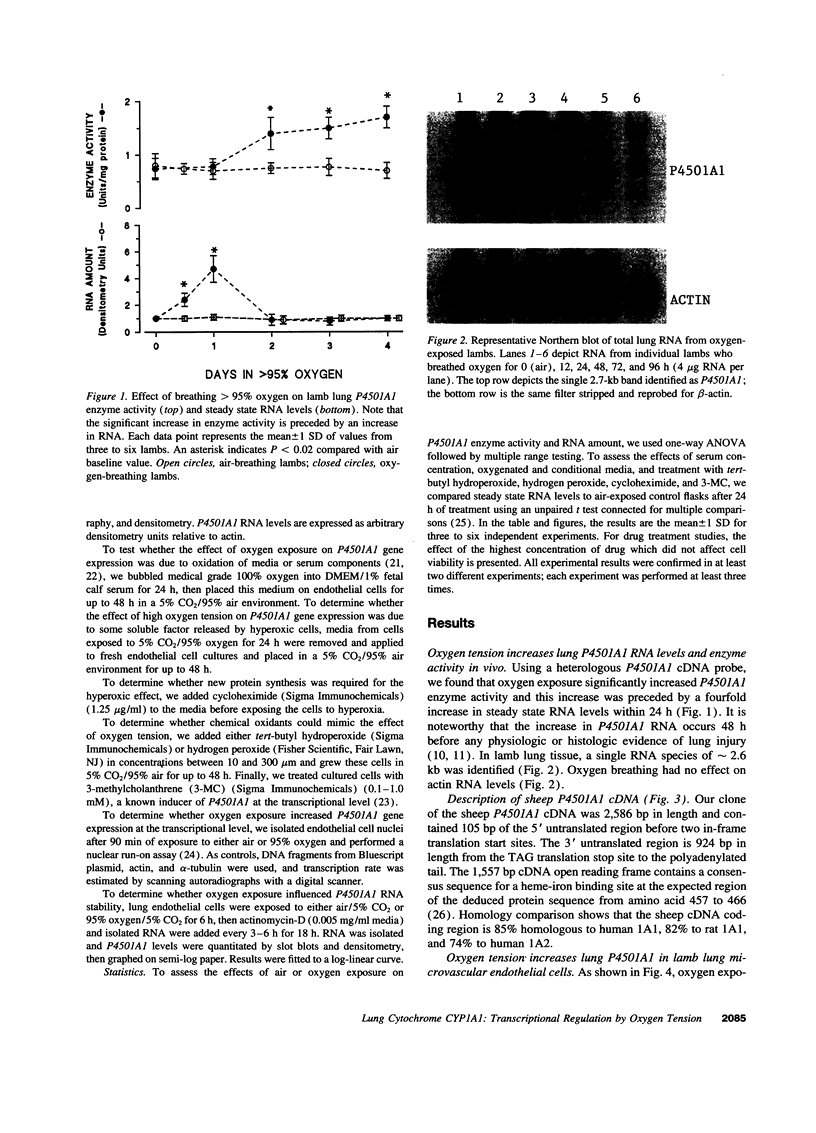
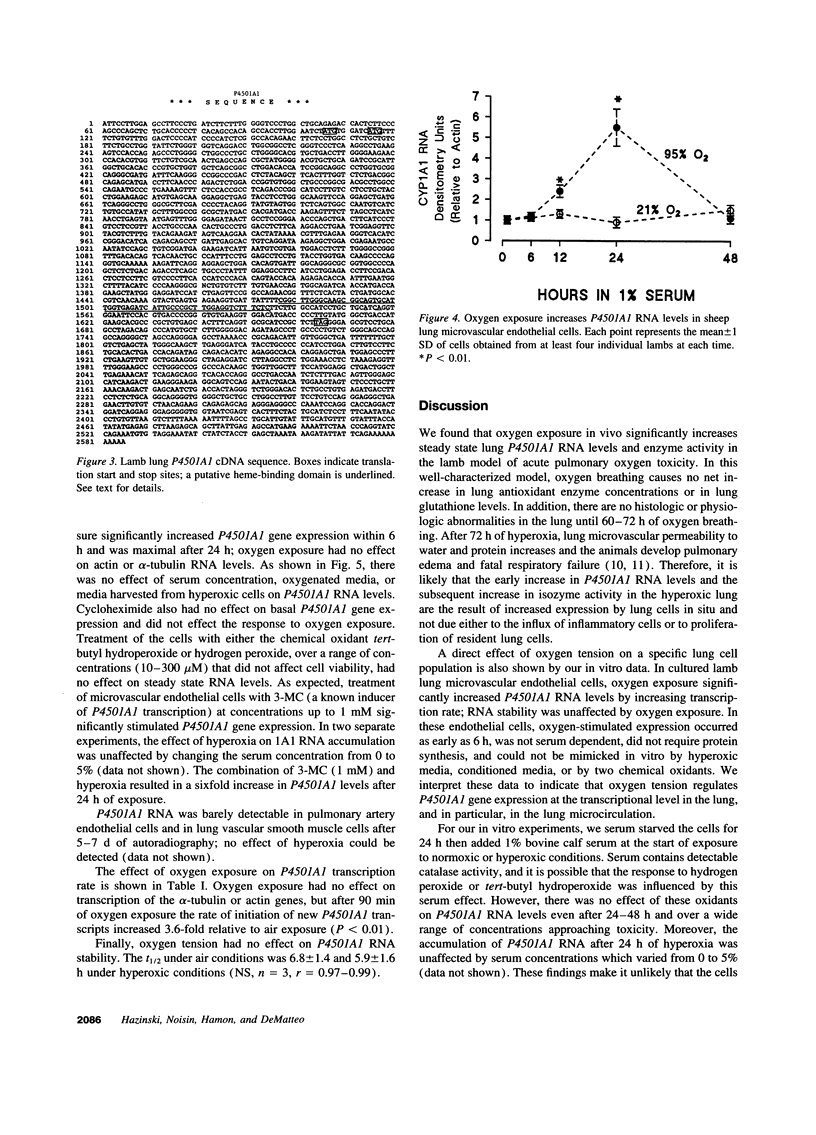
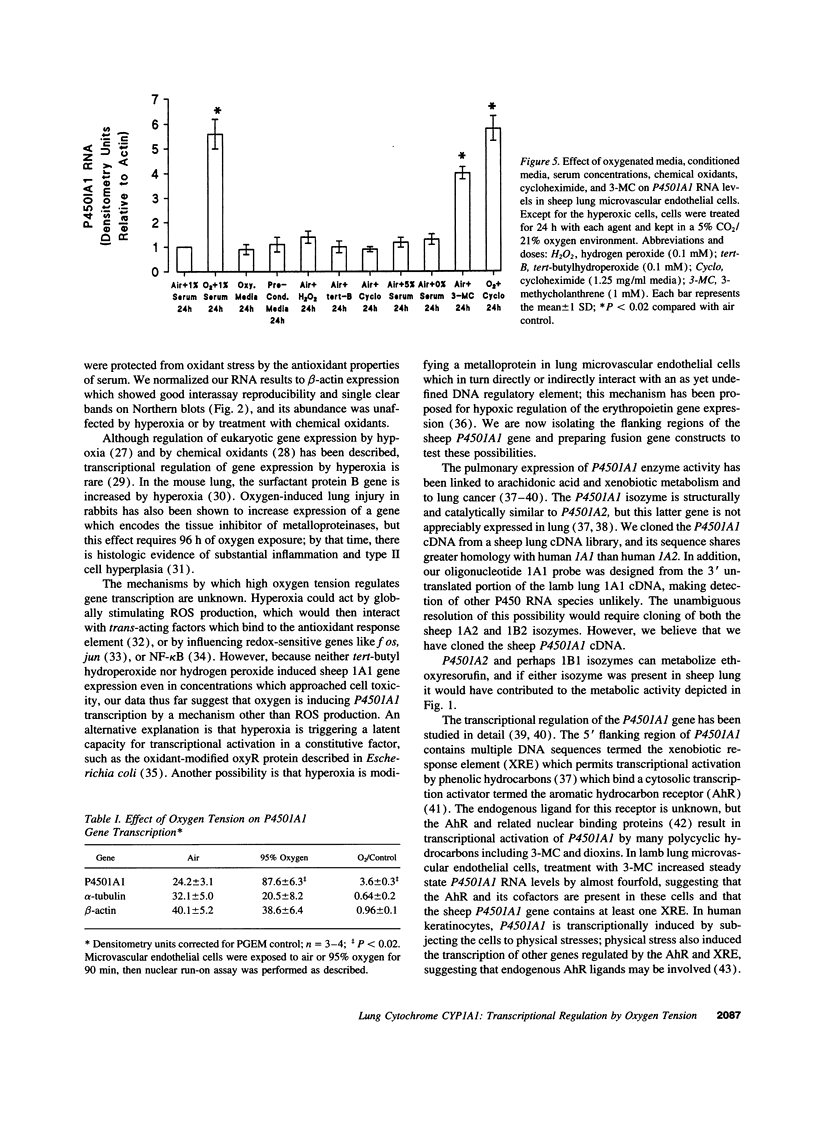
Lung cytochrome P450 activity has been linked to neoplasia and may produce reactive oxidant species and potent arachidonic acid metabolites. In lamb lung, oxygen breathing increases lung P450 activity, and inhibition of lung cytochrome P450 activity reduces oxygen-induced lung injury. The P4501A1 (CYP1A1) isozyme is present in many lung cells, including endothelial cells, and may therefore be involved in the pathogenesis of hyperoxic injury to microvascular endothelium. Therefore, to test the hypothesis that oxygen regulates P4501A1 gene expression in the lung, we cloned the sheep P4501A1 cDNA, and examined its regulation by oxygen breathing significantly increased lung P4501A1 RNA levels and that this increase preceded the increase in isozyme activity. Oxygen exposure also promptly increased P4501A1 RNA levels in cultured lamb lung microvascular endothelial cells but not in endothelial cells isolated from the main pulmonary artery or in lung smooth muscle cells. The oxygen-stimulated increase in P4501A1 RNA levels was not serum dependent, was unaffected by cycloheximide treatment, and could not be mimicked by treatment of the cells with oxygenated medium, conditioned medium, or by chemical oxidants. By nuclear run-on assay in cultured lung endothelial cells, oxygen increased the transcription rate of P4501A1 by almost fourfold after 90 min of oxygen exposure but had no significant effect on P4501A1 RNA stability. We conclude that oxygen tension, but not chemical oxidants, increases P4501A1 gene expression pretranslationally in lung microvascular endothelial cells. We speculate that oxygen induction of P450 activity in these cells may contribute to microvascular injury during oxygen breathing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchard K. L., Acquaviva A. M., Galson D. L., Bunn H. F. Hypoxic induction of the human erythropoietin gene: cooperation between the promoter and enhancer, each of which contains steroid receptor response elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5373–5385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbach K. M., Poland A., Bradfield C. A. Cloning of the Ah-receptor cDNA reveals a distinctive ligand-activated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8185–8189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Mayer R. T. Ethoxyresorufin: direct fluorimetric assay of a microsomal O-dealkylation which is preferentially inducible by 3-methylcholanthrene. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Nov-Dec;2(6):583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J. H., Karara A., Waxman D. J., Martin M. V., Falck J. R., Guenguerich F. P. Cytochrome P-450 enzyme-specific control of the regio- and enantiofacial selectivity of the microsomal arachidonic acid epoxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10865–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D. Morphologic changes in pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:721–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Halliwell B., Borish E. T., Pryor W. A., Ames B. N., Saul R. L., McCord J. M., Harman D. Oxygen radicals and human disease. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):526–545. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Amábile-Cuevas C. F. Redox redux: the control of oxidative stress responses. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):837–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke S. M., Fanburg B. L. Normobaric oxygen toxicity of the lung. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):76–86. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007103030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin D. The generation of radicals during the normal and abnormal functioning of cytochromes P-450. Basic Life Sci. 1988;49:491–500. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5568-7_76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström G., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Cytochrome P-450-dependent lipid peroxidation in reconstituted membrane vesicles. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 1;33(15):2521–2523. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90729-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. A., Dunning S. P., Bunn H. F. Regulation of the erythropoietin gene: evidence that the oxygen sensor is a heme protein. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1412–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.2849206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonder J. C., Proctor R. A., Will J. A. Genetic differences in oxygen toxicity are correlated with cytochrome P-450 inducibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6315–6319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O., Tagashira Y., Iizuka T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structural characteristics of cytochrome P-450. Possible location of the heme-binding cysteine in determined amino-acid sequences. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):807–817. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazinski T. A., Kennedy K. A., France M. L., Hansen T. N. Pulmonary O2 toxicity in lambs: physiological and biochemical effects of endotoxin infusion. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Oct;65(4):1579–1585. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.4.1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioannides C. Induction of cytochrome P 450 I and its influences in chemical carcinogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Feb;18(1):32–34. doi: 10.1042/bst0180032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal A. K., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Human P1-450 gene sequence and correlation of mRNA with genetic differences in benzo[a]pyrene metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4503–4520. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa Y., Yano S., Skoza L. Protective effect of interferon inducers against hyperoxic pulmonary damage. Lab Invest. 1984 Jan;50(1):62–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouri R. E., McKinney C. E., Slomiany D. J., Snodgrass D. R., Wray N. P., McLemore T. L. Positive correlation between high aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity and primary lung cancer as analyzed in cryopreserved lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5030–5037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Prough R. A., Burke M. D., Estabrook R. W. The preparation of microsomal fractions of rodent respiratory tract and their characterization. Cancer Res. 1974 Sep;34(9):2196–2203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Hoover R., Jones M. R., Berry L. C., Jr, Brigham K. L. In vitro effects of endotoxin on bovine and sheep lung microvascular and pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):165–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin R. F., Boyd M. R. Localization of metabolic activation and deactivation systems in the lung: significance to the pulmonary toxicity of xenobiotics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:217–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray G. I., Barnes T. S., Sewell H. F., Ewen S. W., Melvin W. T., Burke M. D. The immunocytochemical localisation and distribution of cytochrome P-450 in normal human hepatic and extrahepatic tissues with a monoclonal antibody to human cytochrome P-450. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;25(4):465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Jones J. E. Regulation of the mammalian cytochrome P1-450 (CYP1A1) gene. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(3):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J. Induction of benzo[a]pyrene Mono-oxygenase in liver cell culture by the photochemical generation of active oxygen species. Evidence for the involvement of singlet oxygen and the formation of a stable inducing intermediate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 15;158(1):109–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1580109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimental R. A., Liang B., Yee G. K., Wilhelmsson A., Poellinger L., Paulson K. E. Dioxin receptor and C/EBP regulate the function of the glutathione S-transferase Ya gene xenobiotic response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4365–4373. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineau T., Fernandez-Salguero P., Lee S. S., McPhail T., Ward J. M., Gonzalez F. J. Neonatal lethality associated with respiratory distress in mice lacking cytochrome P450 1A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5134–5138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannug A., Rannug U., Rosenkranz H. S., Winqvist L., Westerholm R., Agurell E., Grafström A. K. Certain photooxidized derivatives of tryptophan bind with very high affinity to the Ah receptor and are likely to be endogenous signal substances. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15422–15427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Reisz-Porszasz S., Hankinson O. Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Morton M. R., Pickett C. B. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11632–11639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Morton M. R., Pickett C. B. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11632–11639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savas U., Bhattacharyya K. K., Christou M., Alexander D. L., Jefcoate C. R. Mouse cytochrome P-450EF, representative of a new 1B subfamily of cytochrome P-450s. Cloning, sequence determination, and tissue expression. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):14905–14911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Albermann K., Baeuerle P. A. Nuclear factor kappa B: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun. 1992;17(4):221–237. doi: 10.3109/10715769209079515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. A., Bicknell R. The isolation and culture of microvascular endothelium. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):269–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serabjit-Singh C. J., Nishio S. J., Philpot R. M., Plopper C. G. The distribution of cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase in cells of the rabbit lung: an ultrastructural immunocytochemical characterization. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;33(3):279–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrens J. F., Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Hyperoxia increases H2O2 release by lung mitochondria and microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Sep;217(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90519-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz A. D., Roberts E. S., Coon M. J. Radical intermediates in the catalytic cycles of cytochrome P-450. Basic Life Sci. 1988;49:501–507. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5568-7_77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veness-Meehan K. A., Cheng E. R., Mercier C. E., Blixt S. L., Johnston C. J., Watkins R. H., Horowitz S. Cell-specific alterations in expression of hyperoxia-induced mRNAs of lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;5(6):516–521. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.6.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikenheiser K. A., Wert S. E., Wispé J. R., Stahlman M., D'Amore-Bruno M., Singh G., Katyal S. L., Whitsett J. A. Distinct effects of oxygen on surfactant protein B expression in bronchiolar and alveolar epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):L32–L39. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.1.L32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]