Abstract
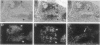
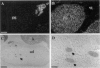
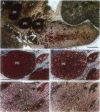
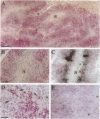
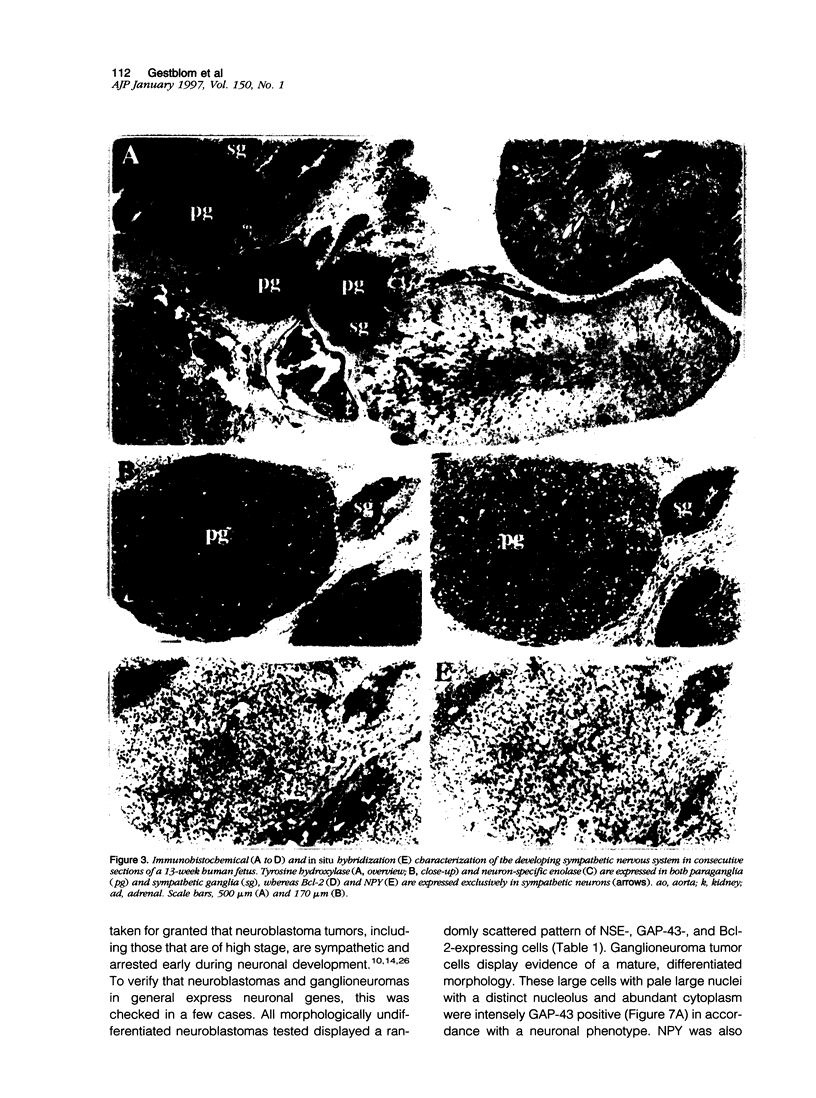
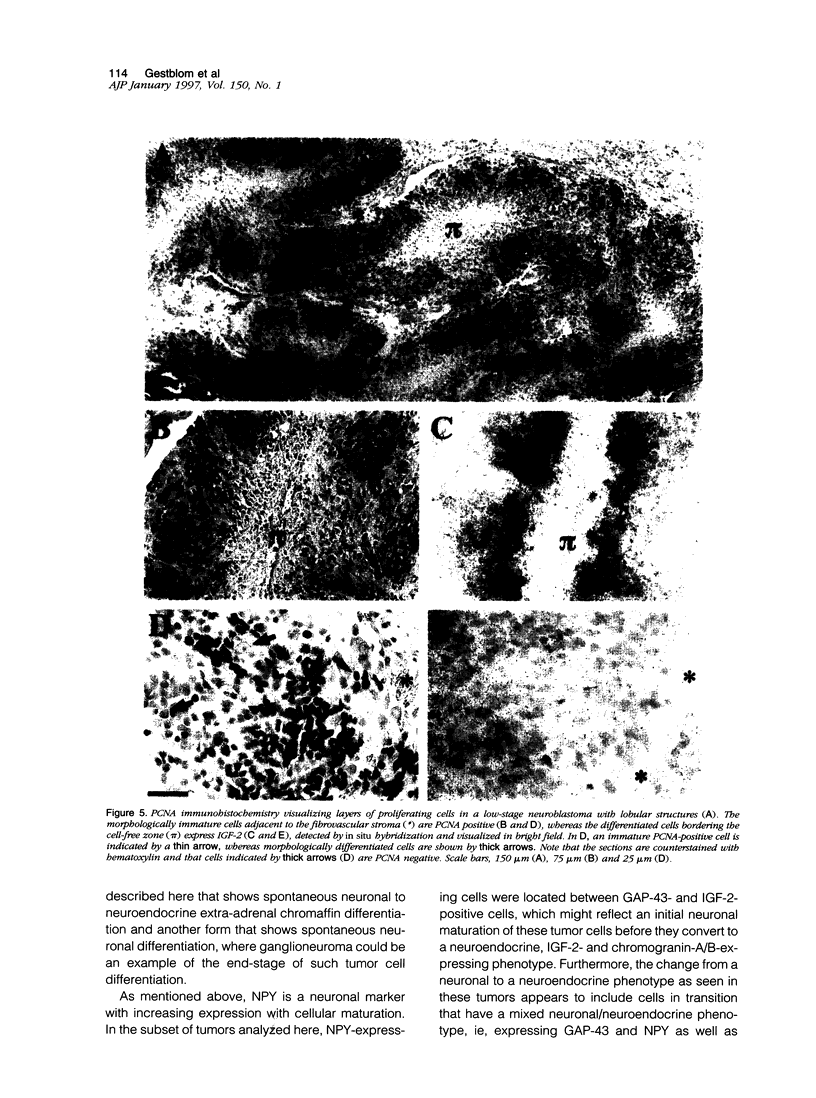
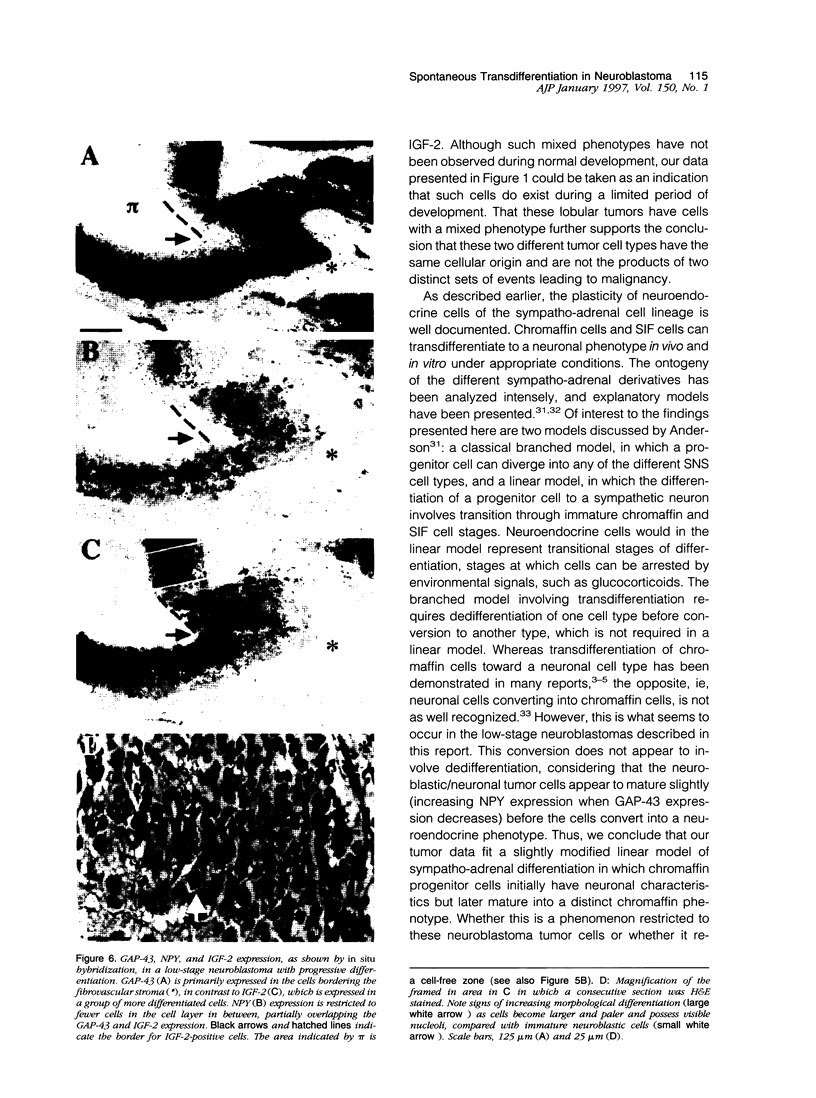
Neuroblastoma is an embryonal tumor derived from the sympathetic nervous system. Although all neuroblastomas have a neuronal character, a subset of tumors also show evidence of extra-adrenal neuroendocrine differentiation in discrete cell layers. A characterization of the cells of the developing human sympathetic nervous system was performed, identifying growth-associated protein-43, neuropeptide tyrosine, and Bcl-2 as marker genes for sympathetic neurons. Whereas all neuroblastomas express growth-associated protein-43, neuropeptide tyrosine, and Bcl-2, tumors with differentiating cells with neuroendocrine features expressed these genes only in the morphologically immature, proliferating cells. Thus, with neuroendocrine tumor cell differentiation, neuronal marker gene expression vanished and proliferation ceased and was succeeded by expression of chromogranin A/B and insulin-like growth factor-2, markers of neuroendocrine chromaffin differentiation. These tumors appear to provide examples of spontaneous lineage conversion from a neuronal to a neuroendocrine phenotype.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloe L., Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor-induced transformation of immature chromaffin cells in vivo into sympathetic neurons: effect of antiserum to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1246–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. A bipotential neuroendocrine precursor whose choice of cell fate is determined by NGF and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90823-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J. Cellular 'neoteny': a possible developmental basis for chromaffin cell plasticity. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Jacobson R. D., Virág I., Schilling J., Skene J. H. Primary structure and transcriptional regulation of GAP-43, a protein associated with nerve growth. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Pritchard J., Berthold F., Carlsen N. L., Castel V., Castelberry R. P., De Bernardi B., Evans A. E., Favrot M., Hedborg F. Revisions of the international criteria for neuroblastoma diagnosis, staging, and response to treatment. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Aug;11(8):1466–1477. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.8.1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Cooper M. J., Helman L. J., Thiele C. J., Seeger R. C., Israel M. A. Neuropeptide Y expression in the developing adrenal gland and in childhood neuroblastoma tumors. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 15;50(18):6055–6061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Hutchins G. M., Cohen P. S., Helman L. J., Mennie R. J., Israel M. A. Human neuroblastoma tumor cell lines correspond to the arrested differentiation of chromaffin adrenal medullary neuroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Apr;1(4):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaetano C., Matsumoto K., Thiele C. J. In vitro activation of distinct molecular and cellular phenotypes after induction of differentiation in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia I., Martinou I., Tsujimoto Y., Martinou J. C. Prevention of programmed cell death of sympathetic neurons by the bcl-2 proto-oncogene. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):302–304. doi: 10.1126/science.1411528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor prevents the death and stimulates the neuronal differentiation of clonal PC12 pheochromocytoma cells in serum-free medium. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):747–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedborg F., Ohlsson R., Sandstedt B., Grimelius L., Hoehner J. C., Pählman S. IGF2 expression is a marker for paraganglionic/SIF cell differentiation in neuroblastoma. Am J Pathol. 1995 Apr;146(4):833–847. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehner J. C., Hedborg F., Wiklund H. J., Olsen L., Påhlman S. Cellular death in neuroblastoma: in situ correlation of apoptosis and bcl-2 expression. Int J Cancer. 1995 Jul 4;62(1):19–24. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehner J. C., Olsen L., Sandstedt B., Kaplan D. R., Påhlman S. Association of neurotrophin receptor expression and differentiation in human neuroblastoma. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jul;147(1):102–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi V. V., Silverman J. F. Pathology of neuroblastic tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1994 May;11(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Smith J. Development of the peripheral nervous system from the neural crest. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:375–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrachi Y., Naranjo J. R., Levi B. Z., Pollard H. B., Lelkes P. I. PC12 cells differentiate into chromaffin cell-like phenotype in coculture with adrenal medullary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6161–6165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson R., Holmgren L., Glaser A., Szpecht A., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S. Insulin-like growth factor 2 and short-range stimulatory loops in control of human placental growth. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1993–1999. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortoft E., Bjelfman C., Hedborg F., Grimelius L., Påhlman S. The expression profile of alternatively spliced neuronal c-src RNA distinguishes between human tumours of the sympatho-adrenal lineage. Int J Cancer. 1995 Jan 3;60(1):38–44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910600105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. Control of cell fate in a vertebrate neurogenic lineage. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1035–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90379-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer H., Acheson A. L., Thibault J., Thoenen H. Developmental potential of quail dorsal root ganglion cells analyzed in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 1986 Sep;6(9):2616–2624. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-09-02616.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidl K., Unsicker K. The determination of the adrenal medullary cell fate during embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Chatten J., Newton W. A., Jr, Sachs N., Hamoudi A. B., Chiba T., Marsden H. B., Misugi K. Histopathologic prognostic factors in neuroblastic tumors: definition of subtypes of ganglioneuroblastoma and an age-linked classification of neuroblastomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Aug;73(2):405–416. doi: 10.1093/jnci/73.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler-Federsppiel B. S., Cras P., Gheuens J., Andries D., Lowenthal A. Human gamma gamma-enolase: two-site immunoradiometric assay with a single monoclonal antibody. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):22–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Krisch B., Otten U., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-induced fiber outgrowth from isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells: impairment by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3498–3502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanselow J., Grabczyk E., Ping J., Baetscher M., Teng S., Fishman M. C. GAP-43 transgenic mice: dispersed genomic sequences confer a GAP-43-like expression pattern during development and regeneration. J Neurosci. 1994 Feb;14(2):499–510. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-02-00499.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Terenghi G., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY) immunoreactivity in norepinephrine-containing cells and nerves of the mammalian adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1460–1462. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waseem N. H., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Structural conservation and the detection of a nucleolar form. J Cell Sci. 1990 May;96(Pt 1):121–129. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtman R. J., Axelrod J. Control of enzymatic synthesis of adrenaline in the adrenal medulla by adrenal cortical steroids. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2301–2305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]