Abstract
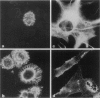
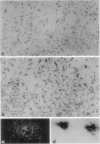
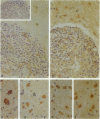
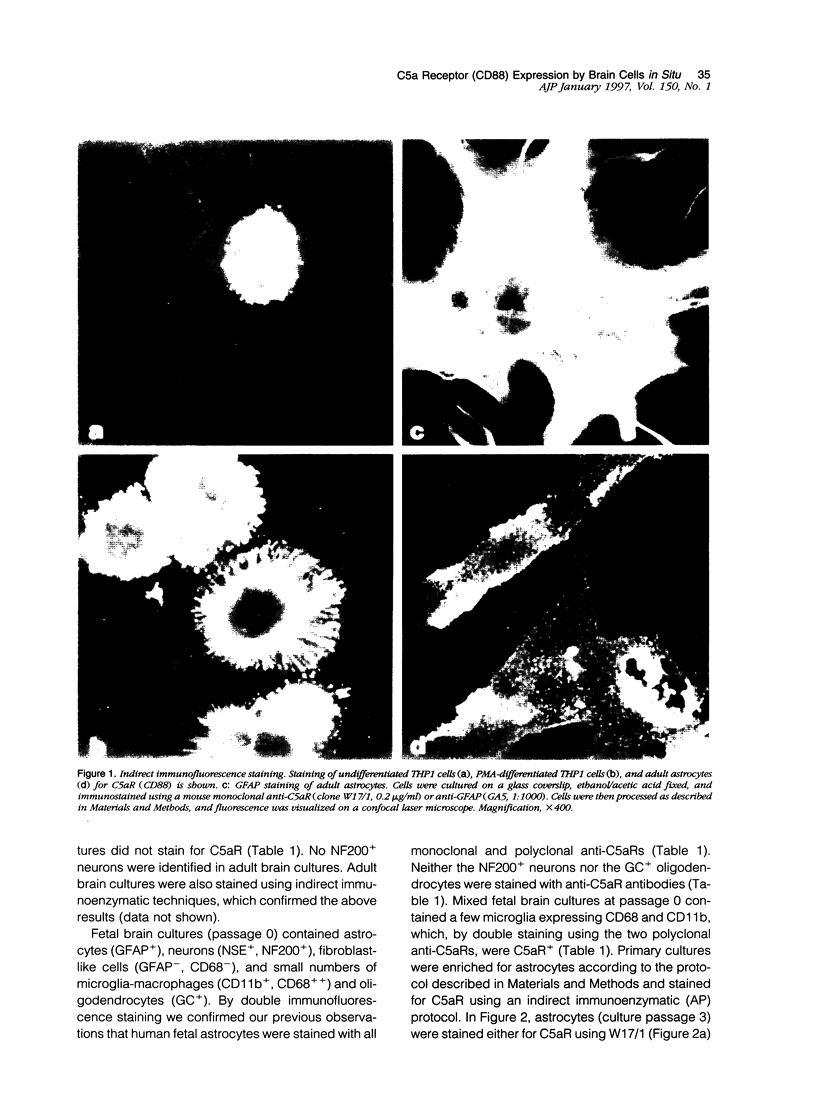
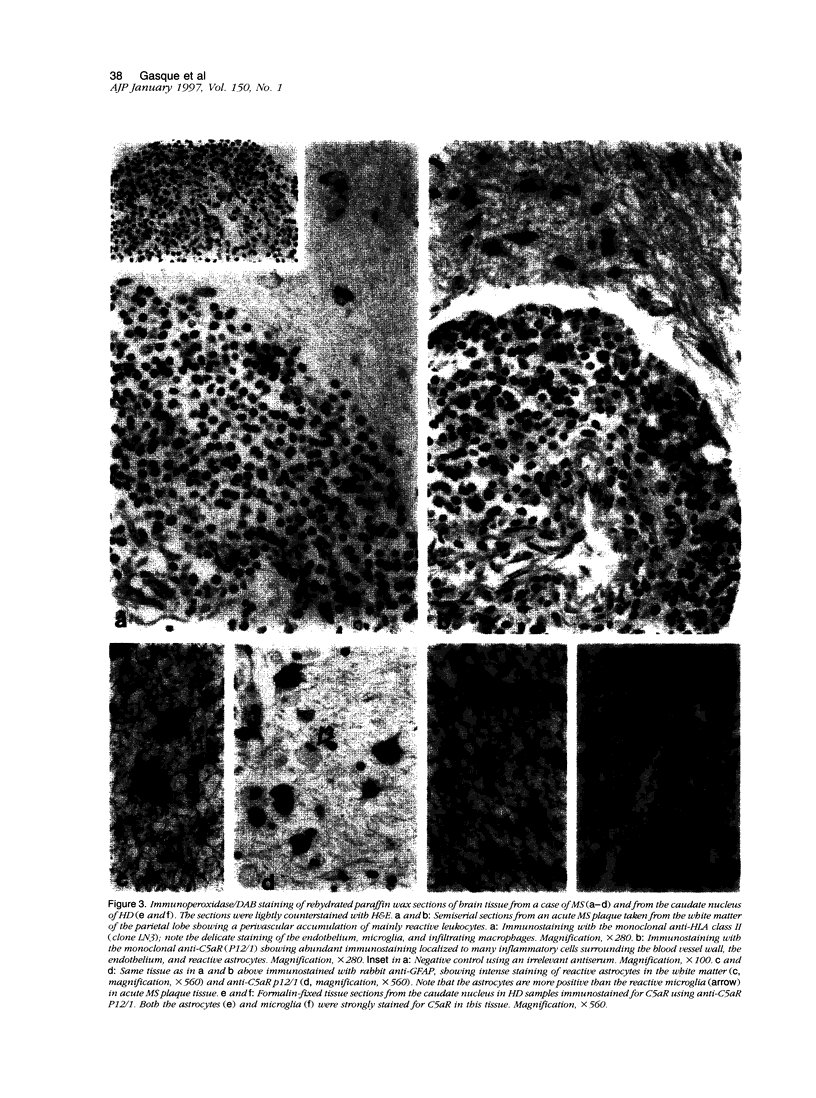
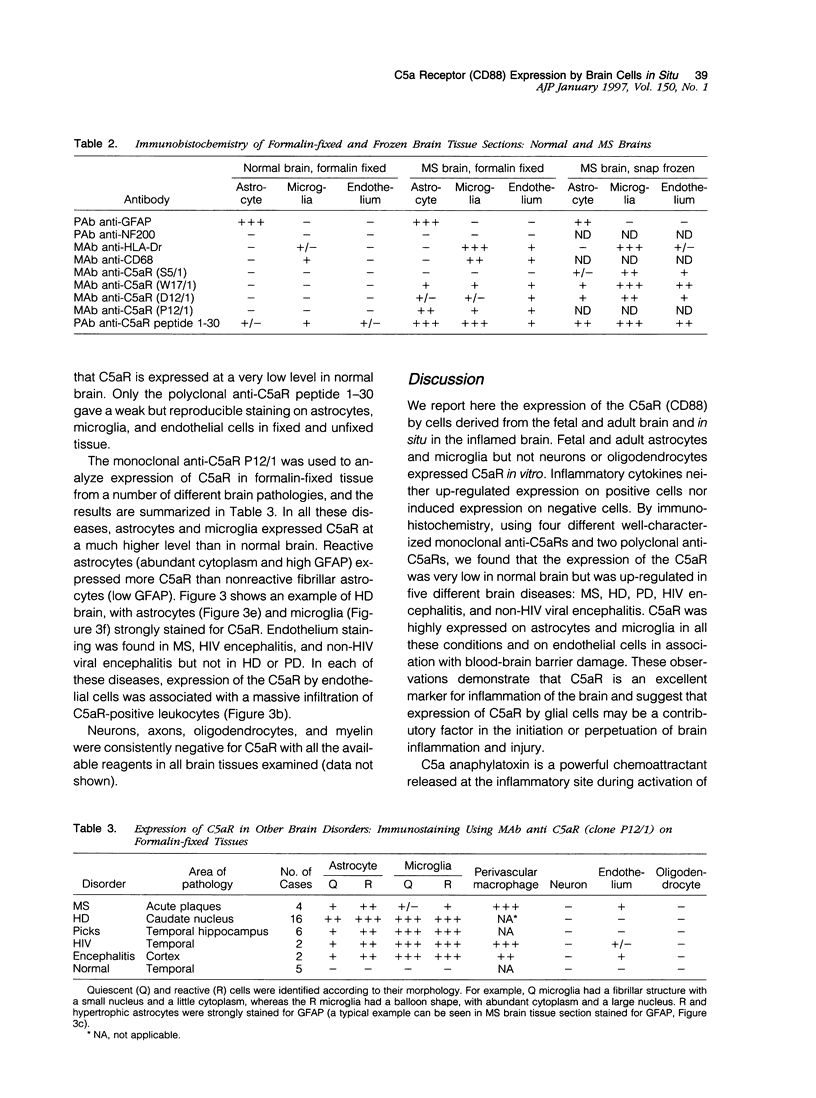
C5a receptor (C5aR, CD88) is a receptor originally described on neutrophils and monocyte-macrophages but recently found on hepatocytes, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and tissue mast cells. We recently reported that human fetal astrocytes expressed a functional C5aR in vitro. Here we examine C5aR expression in adult brain cultures by immunostaining with six different anti-C5aRs and show that C5aR is expressed constitutively by astrocytes, microglia, and fibroblast-like cells but not by oligodendrocytes. In fetal brain cultures we confirmed that astrocytes constitutively expressed C5aR and demonstrated that fetal microglia and fibroblast-like cells but not oligodendrocytes and neurones expressed C5aR. Incubation with inflammatory cytokines (interferon gamma, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor alpha) or phorbol ester failed to induce or up-regulate C5aR expression on fetal or adult brain cells. Immunohistochemistry was performed to determine the expression and distribution of C5aR in the normal and inflamed brain. In the normal brain C5aR was minimally expressed, whereas in inflamed brains from a variety of pathologies, C5aR expression was greatly up-regulated on reactive astrocytes and microglia and to a lesser extent on endothelial cells. We propose that expression of C5aR is a marker of central nervous system inflammation, and that C5aR expression on brain cells in inflammation plays an important role in cell activation and recruitment (gliosis).
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong R. C., Dorn H. H., Kufta C. V., Friedman E., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Pre-oligodendrocytes from adult human CNS. J Neurosci. 1992 Apr;12(4):1538–1547. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-04-01538.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. C., Harvath L., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Type 1 astrocytes and oligodendrocyte-type 2 astrocyte glial progenitors migrate toward distinct molecules. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Nov;27(3):400–407. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner R. R., Hugli T. E., Ember J. A., Morgan E. L. Expression of functional receptors for human C5a anaphylatoxin (CD88) on the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. Stimulation of acute-phase protein-specific mRNA and protein synthesis by human C5a anaphylatoxin. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 1;155(1):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ember J. A., Sanderson S. D., Hugli T. E., Morgan E. L. Induction of interleukin-8 synthesis from monocytes by human C5a anaphylatoxin. Am J Pathol. 1994 Feb;144(2):393–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman K. E., Vaporciyan A. A., Bonish B. K., Jones M. L., Johnson K. J., Glovsky M. M., Eddy S. M., Ward P. A. C5a-induced expression of P-selectin in endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1994 Sep;94(3):1147–1155. doi: 10.1172/JCI117430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füreder W., Agis H., Willheim M., Bankl H. C., Maier U., Kishi K., Müller M. R., Czerwenka K., Radaszkiewicz T., Butterfield J. H. Differential expression of complement receptors on human basophils and mast cells. Evidence for mast cell heterogeneity and CD88/C5aR expression on skin mast cells. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 15;155(6):3152–3160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasque P., Chan P., Fontaine M., Ischenko A., Lamacz M., Götze O., Morgan B. P. Identification and characterization of the complement C5a anaphylatoxin receptor on human astrocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Nov 15;155(10):4882–4889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Gerard N. P. C5A anaphylatoxin and its seven transmembrane-segment receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:775–808. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Hodges M. K., Drazen J. M., Weller P. F., Gerard C. Characterization of a receptor for C5a anaphylatoxin on human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1760–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haviland D. L., McCoy R. L., Whitehead W. T., Akama H., Molmenti E. P., Brown A., Haviland J. C., Parks W. C., Perlmutter D. H., Wetsel R. A. Cellular expression of the C5a anaphylatoxin receptor (C5aR): demonstration of C5aR on nonmyeloid cells of the liver and lung. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 15;154(4):1861–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy M., Jones J., Whittemore S. R., Haviland D. L., Wetsel R. A., Barnum S. R. Expression of the receptors for the C5a anaphylatoxin, interleukin-8 and FMLP by human astrocytes and microglia. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Aug;61(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(95)00075-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Gasque P. Expression of complement in the brain: role in health and disease. Immunol Today. 1996 Oct;17(10):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)20028-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. L., Ember J. A., Sanderson S. D., Scholz W., Buchner R., Ye R. D., Hugli T. E. Anti-C5a receptor antibodies. Characterization of neutralizing antibodies specific for a peptide, C5aR-(9-29), derived from the predicted amino-terminal sequence of the human C5a receptor. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):377–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. L., Sanderson S., Scholz W., Noonan D. J., Weigle W. O., Hugli T. E. Identification and characterization of the effector region within human C5a responsible for stimulation of IL-6 synthesis. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3937–3942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Dinarello C. A., Yancey K. B., Endres S., Lawley T. J., Frank M. M., Burke J. F., Gelfand J. A. C5a induction of human interleukin 1. Synergistic effect with endotoxin or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2635–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann M., Raedt U., Hebell T., Schmidt B., Zimmermann B., Götze O. Probing the human receptor for C5a anaphylatoxin with site-directed antibodies. Identification of a potential ligand binding site on the NH2-terminal domain. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3785–3794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peudenier S., Hery C., Montagnier L., Tardieu M. Human microglial cells: characterization in cerebral tissue and in primary culture, and study of their susceptibility to HIV-1 infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):152–161. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranscht B., Clapshaw P. A., Price J., Noble M., Seifert W. Development of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells studied with a monoclonal antibody against galactocerebroside. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2709–2713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Gelfand J. A., Dinarello C. A. Recombinant C5a stimulates transcription rather than translation of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor: translational signal provided by lipopolysaccharide or IL-1 itself. Blood. 1990 Oct 15;76(8):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz W., McClurg M. R., Cardenas G. J., Smith M., Noonan D. J., Hugli T. E., Morgan E. L. C5a-mediated release of interleukin 6 by human monocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Nov;57(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90043-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupf N., Williams C. A., Berkman A., Cattell W. S., Kerper L. Binding specificity and presynaptic action of anaphylatoxin C5a in rat brain. Brain Behav Immun. 1989 Mar;3(1):28–38. doi: 10.1016/0889-1591(89)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhrao S. K., Neal J. W., Gasque P., Morgan B. P., Newman G. R. Role of complement in the aetiology of Pick's disease? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996 May;55(5):578–593. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199605000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A. Structure, function and cellular expression of complement anaphylatoxin receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Schupf N., Hugli T. E. Anaphylatoxin C5a modulation of an alpha-adrenergic receptor system in the rat hypothalamus. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Jul;9(1-2):29–40. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(85)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]